Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology worksheets are an essential tool for students in grade school who are looking to solidify their understanding of the subject. Designed to cover a wide range of topics, these worksheets aim to help students grasp complex biological concepts and develop crucial skills for scientific inquiry. Whether you are a parent seeking additional resources for your child or a teacher looking to supplement your lessons, biology worksheets can provide a structured and interactive way to engage with the subject material.
Table of Images 👆
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is the purpose of studying biology?
Studying biology helps us understand the intricate mechanisms of living organisms, from the smallest cells to entire ecosystems, enabling us to better comprehend and address vital issues such as human health, conservation of biodiversity, and tackling global challenges like disease outbreaks and environmental degradation. It also fuels advancements in medical research, biotechnology, and agricultural practices, ultimately contributing to the improvement of human lives and the sustainability of our planet.
What are the characteristics of living organisms?
Living organisms have several characteristics, including organization and structure, metabolism, growth and development, response to stimuli, reproduction, adaptation to their environment, and the ability to evolve. These characteristics collectively help define living organisms and distinguish them from non-living things.
Explain the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. This process takes place in chloroplasts, where chlorophyll captures sunlight and uses it to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The overall chemical reaction is 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2. The glucose produced is used by the plant for energy and growth, while the oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct.
Describe the structure and function of DNA.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms. The backbone of DNA is made up of sugar and phosphate molecules, while the rungs of the DNA ladder consist of four different nitrogenous bases – adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These bases pair up in a specific way (A-T and G-C) to form the double helix structure of DNA. The sequence of these bases carries the genetic code that determines an organism's traits and characteristics. DNA replicates itself during cell division, ensuring that the genetic information is passed on to daughter cells accurately. Additionally, DNA serves as a template for the synthesis of RNA, which in turn directs the production of proteins that carry out various functions in the body.
How do cells reproduce?
Cells reproduce through a process called cell division. In this process, a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each containing a complete set of genetic information. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells, and meiosis, which produces four genetically diverse daughter cells. Each type of cell division plays a crucial role in growth, development, repair, and reproduction in organisms.
What is the role of enzymes in biological reactions?
Enzymes serve as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy needed for reactions to occur. They facilitate these reactions by binding to specific substrates and converting them into products, ultimately enabling essential processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction to occur efficiently within cells.
Explain the concept of natural selection.
Natural selection is the process by which organisms that are better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more successfully than those that are less well adapted. Over time, this leads to the accumulation of advantageous traits in a population, as individuals with these traits are more likely to pass them on to the next generation. This mechanism of evolution was famously described by Charles Darwin and is driven by environmental pressures that shape the genetic composition of a species, ultimately resulting in its adaptation to its surroundings.
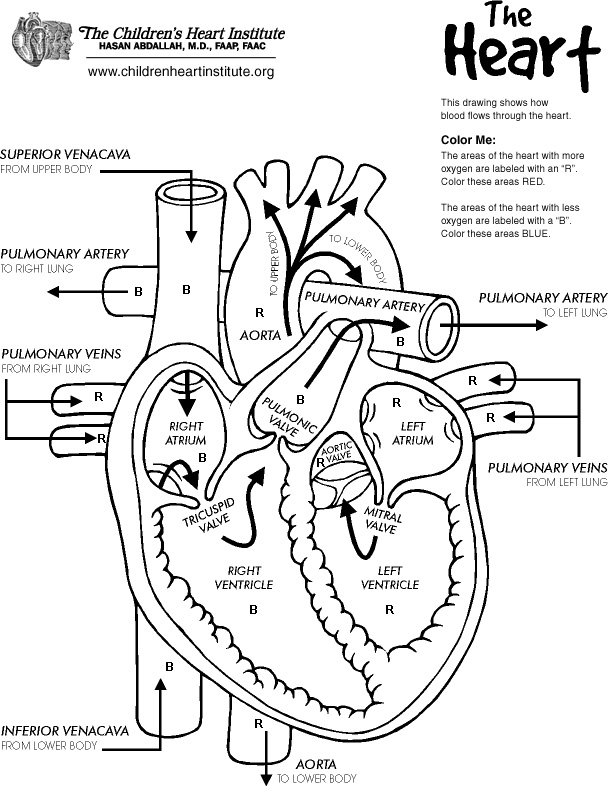
Describe the human respiratory system.
The human respiratory system is composed of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Air is inhaled through the nose or mouth, passing through the pharynx, larynx, and trachea before reaching the bronchi and alveoli in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is expelled during the process of respiration. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles play a vital role in expanding and contracting the lungs to facilitate breathing.
What are the different types of ecological relationships?
There are several types of ecological relationships in nature, including mutualism (both organisms benefit), commensalism (one benefits, the other is unaffected), parasitism (one benefits, the other is harmed), competition (both are negatively affected), and predation (one organism kills and consumes the other). These relationships play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems and maintaining biodiversity.
Explain the process of cell division.
Cell division is a complex process by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two daughter cells. The process involves several phases, including interphase, where the cell prepares for division by replicating its DNA and organelles, followed by mitosis, where the nucleus divides into two identical sets of chromosomes, and cytokinesis, where the cell physically splits into two separate cells. Each phase is tightly regulated by a series of checkpoints to ensure accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material. Overall, cell division is crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of multicellular organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments