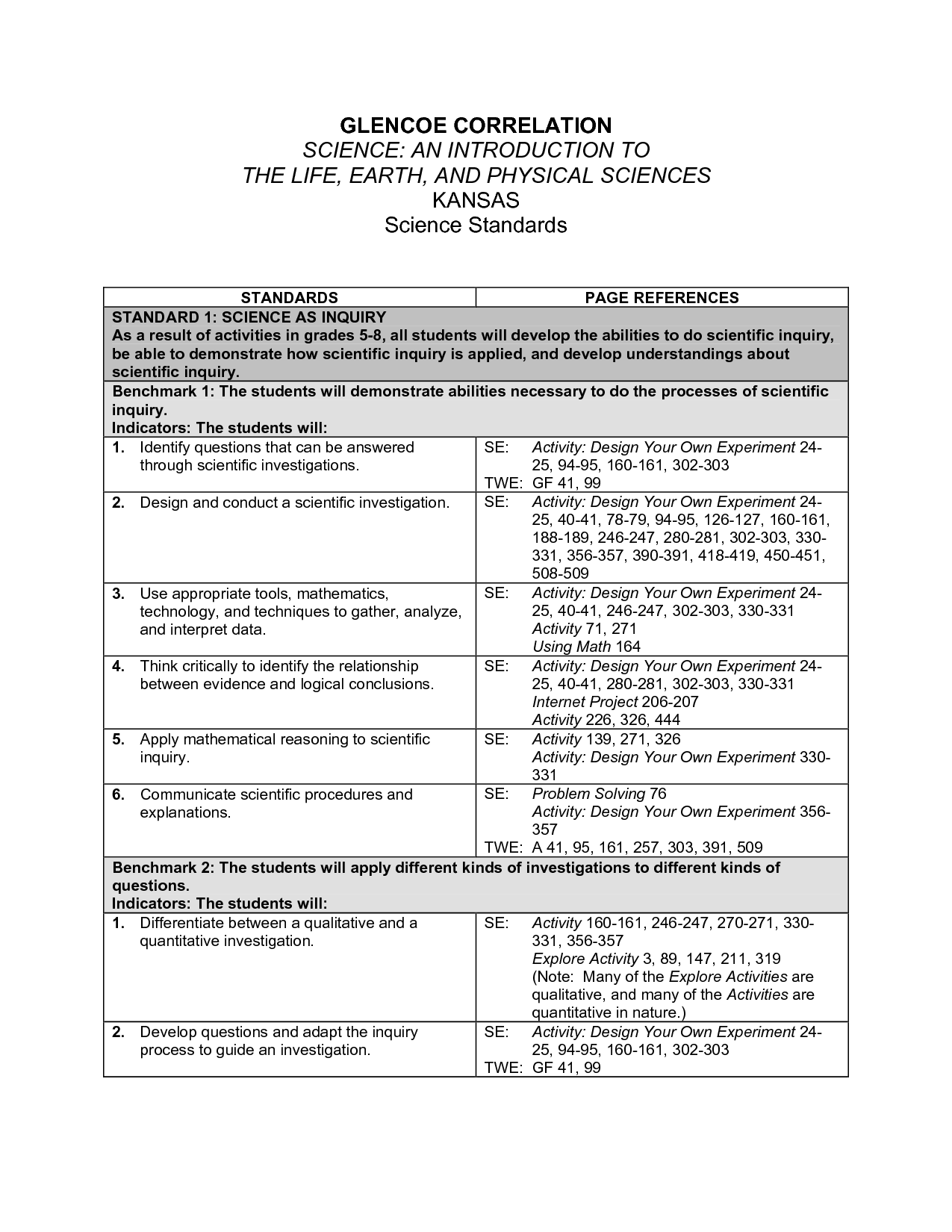
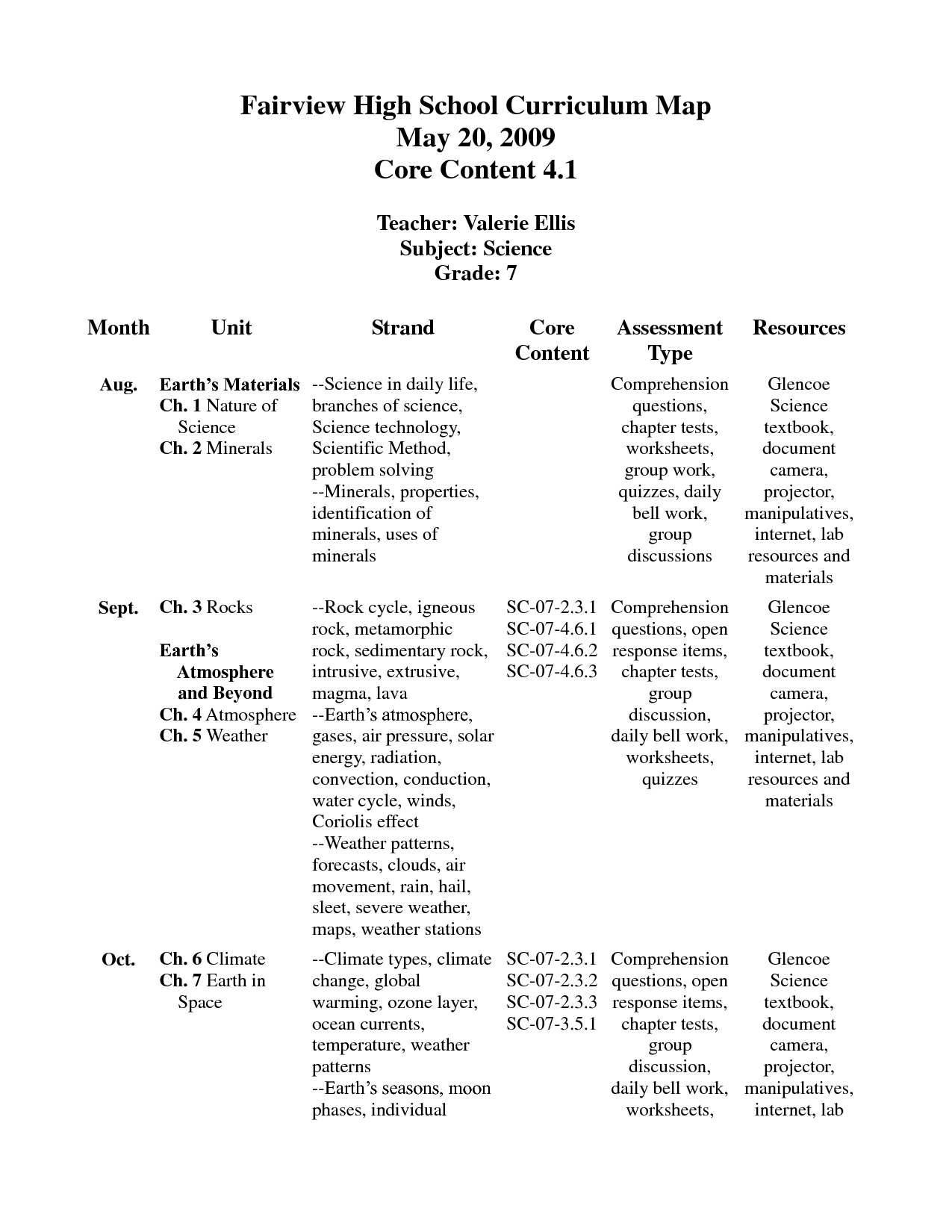
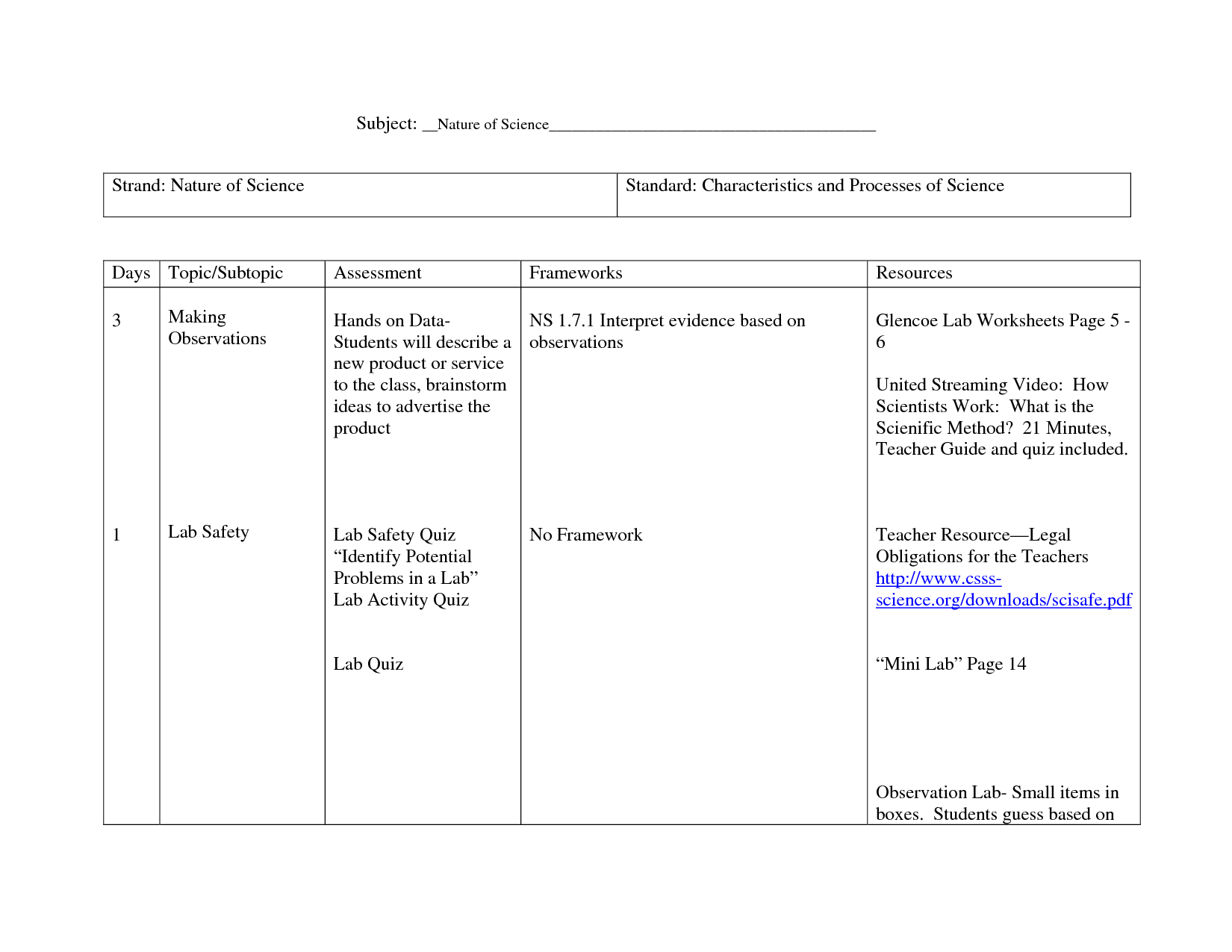
Glencoe Earth Science Worksheets
If you're an Earth Science teacher or a student looking for additional practice and reinforcement, Glencoe Earth Science Worksheets are a valuable resource to consider. Designed to accompany the Glencoe Earth Science textbook, these worksheets provide an additional entity of support and subject matter for educators and students alike in the field of Earth Science.
Table of Images 👆
- Earth Science Worksheets Answers
- Earth Science Worksheets High School
- Glencoe Physical Science
- WebQuest Answer Key
- Glencoe Earth Science Worksheet Answers
- Physical Science Newtons Laws Worksheet Answer Key
- High School Science Worksheets
- 6th Grade Science Worksheets
- Prentice Hall Earth Science Worksheet Answers
- Plate Tectonics Worksheet Answers
- 8th Grade Earth Science
- Glencoe Earth Science Chapter 1 Study Guide Answers Key
- Conceptual Physics Answers Chapter 9
- Physical Science Glencoe Note Taking Worksheet Answer Key
- Earth Science Printable Worksheets
- Glencoe Health Answer Key Chapter 2
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What are the three main types of rocks?
The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, and metamorphic rocks are formed from the alteration of existing rocks due to high temperature and pressure.
How does the rock cycle work?
The rock cycle works by moving rocks through a series of processes including weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, cementation, melting, cooling, and recrystallization. It begins with molten rock, or magma, cooling and solidifying to form igneous rocks. These rocks can then be broken down through weathering and erosion into sediment, which is later compacted and cemented together to form sedimentary rocks. Under high heat and pressure, these rocks can be transformed into metamorphic rocks. The cycle continues as any type of rock can melt and recrystallize to form new igneous rocks, completing the cycle.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering is the process of breaking down and wearing away rocks and other materials on Earth's surface, typically caused by exposure to weather conditions like rain, wind, and temperature changes. Erosion, on the other hand, involves the movement of weathered material by agents such as water, wind, and ice. In simpler terms, weathering breaks down rocks, while erosion moves the broken-down material from one place to another.
How do geologists determine the age of rocks?
Geologists determine the age of rocks using various dating techniques such as radiometric dating, which relies on the natural decay of radioactive isotopes within rocks to calculate their age. Other methods include relative dating, which compares the positions of rock layers to determine their relative age, and stratigraphy, which examines the layers of rock in a specific area to estimate the age of the rocks based on the principle of superposition. By combining these techniques, geologists can accurately determine the age of rocks and piece together the Earth's geological history.
What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources?
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished over time, such as sunlight, wind, and water. Nonrenewable resources, on the other hand, are finite and will eventually run out, such as fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. The main difference lies in the sustainability of their availability for future generations, with renewable resources being able to be used indefinitely without depletion.
What are the main factors that contribute to climate change?
The main factors that contribute to climate change include increased greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide and methane, from human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation. Other contributing factors are land use changes, industrial processes, agricultural practices, and waste disposal methods. These activities trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming and changes in climate patterns that have significant environmental impacts.
How do plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanic activity?
Plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanic activity through the movement and interaction of Earth's lithospheric plates. When two plates interact, stress builds up along their boundaries as they try to slide past or collide with each other. This stress is eventually released in the form of an earthquake when the built-up pressure exceeds the strength of the rocks. Volcanic activity occurs when one tectonic plate subducts beneath another, melting rocks in the process and leading to the formation of magma chambers. The magma can then make its way to the surface through volcanic eruptions, creating new landforms and releasing pent-up pressure from within the Earth's crust.
Describe the process of fossil formation.
Fossil formation begins when an organism dies and is quickly buried by sediment. Over time, the organic materials of the organism decompose, leaving behind hard parts such as bones, shells, or teeth. These hard parts can become mineralized as minerals from the surrounding sediment seep into the pores and cavities, preserving the remains. Through compaction and cementation, the sediment hardens into rock, encasing and protecting the fossil. Over millions of years, geological processes such as uplift, erosion, and exposure can bring the fossil back to the surface where it can be discovered and studied by scientists.
What are the main causes of soil erosion?
The main causes of soil erosion include factors such as deforestation, agriculture practices like overgrazing and monoculture farming, construction activities that disrupt natural vegetation, and extreme weather events like heavy rainfall. These actions can reduce the ability of the soil to retain moisture and nutrients, leading to the erosion of the topsoil layer and degradation of land productivity.
Why are wetlands important for the environment?
Wetlands are critical for the environment because they serve as natural filters, purifying water by trapping pollutants and sediments. They also help prevent flooding by absorbing excess water, support a diverse array of plant and animal species, and act as carbon sinks by storing large amounts of carbon dioxide. Additionally, wetlands play a crucial role in regulating climate by influencing regional weather patterns and providing habitats for countless species, making them essential for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem resilience.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments