Geology Cross Section Worksheet
The Geology Cross Section Worksheet is a valuable tool for students and professionals in the field of geology. This underutilized resource allows individuals to delve into the complexities of geological formations and gain a deeper understanding of the earth's composition. By providing a clear layout of different rock layers and their respective characteristics, this worksheet enables learners to analyze and interpret geological phenomena with ease and accuracy.
Table of Images 👆
- Rock Layers From Oldest to Youngest Worksheet
- Printable Volcano Worksheets
- Law of Superposition Fossils Worksheet
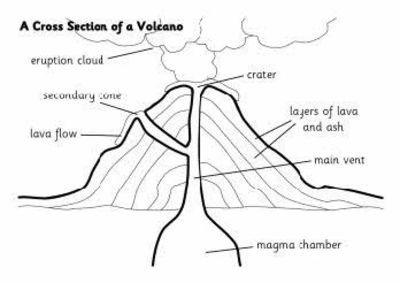
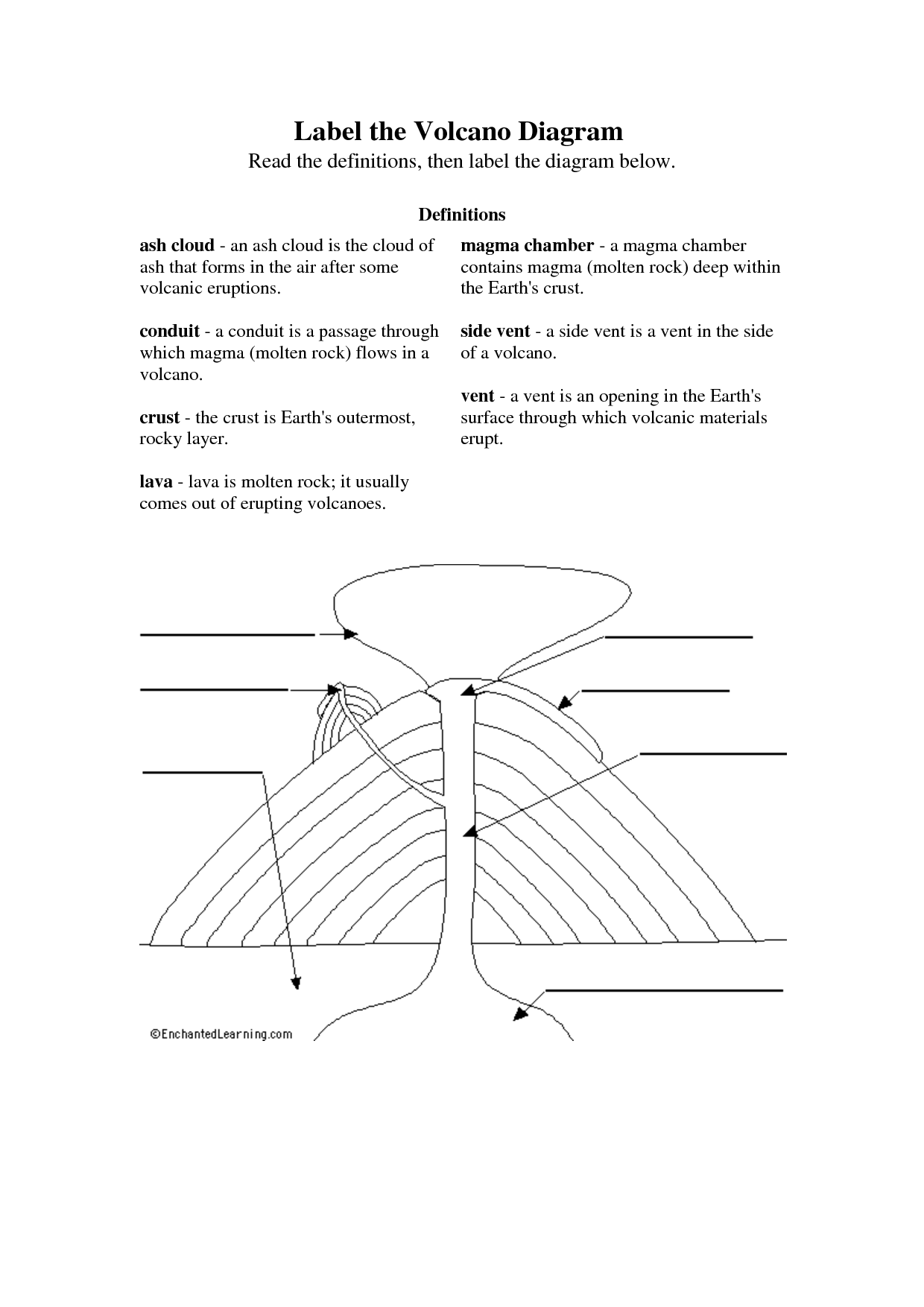
- Volcano Diagram Label
- Murder Mystery Classroom Activity
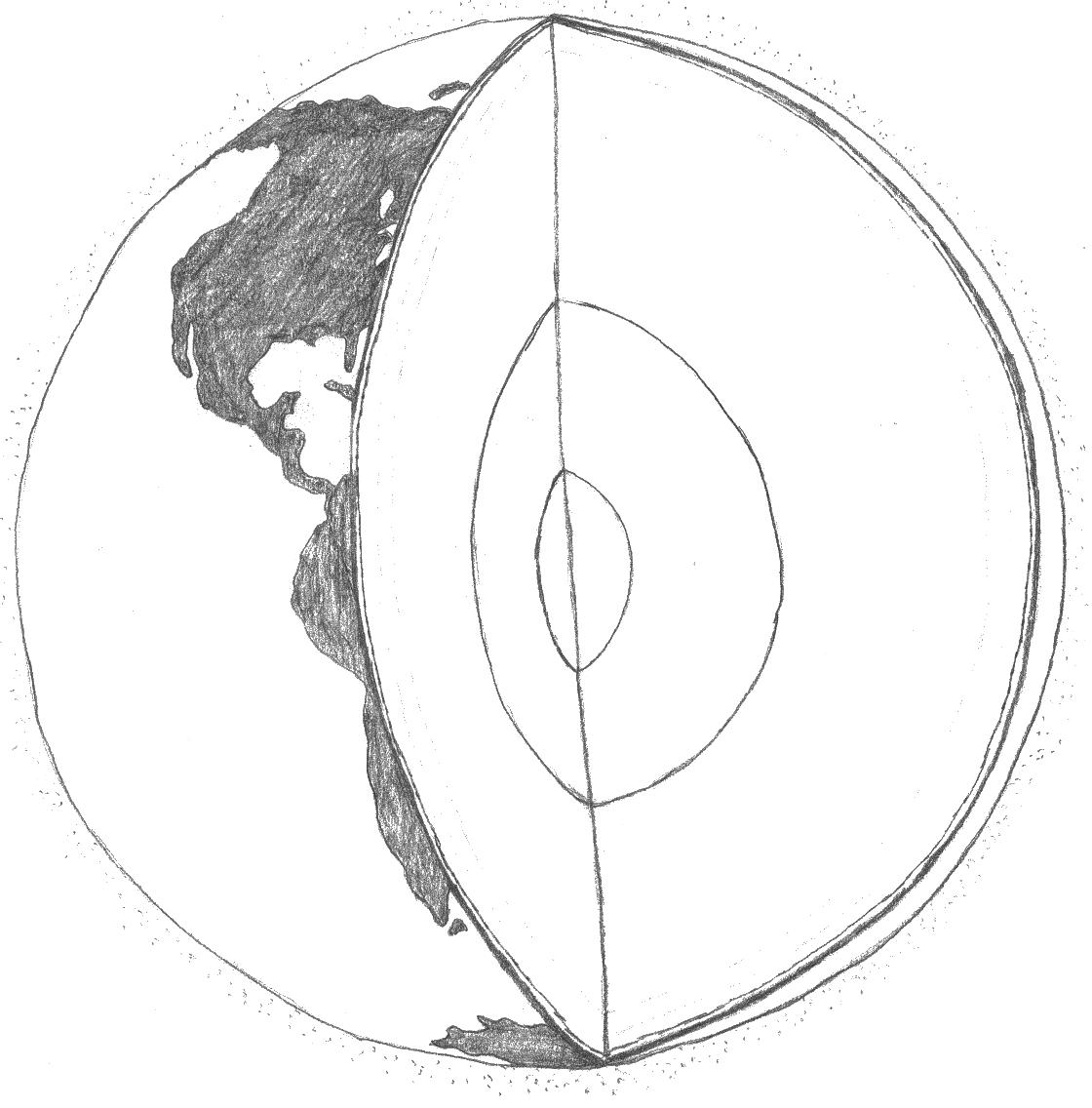
- Earth Layers Coloring Sheet
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
- Volcanoes Worksheets 5th Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a cross section in geology?
A cross section in geology is a two-dimensional representation of a vertical slice through the Earth's crust, typically showing the various rock layers, structures, and features present beneath the surface. It provides geologists with a detailed view of the subsurface geology and is used to interpret the geological history, structure, and resources of a particular area. Cross sections are commonly used in geologic mapping, exploration, and resource development projects to better understand the underground characteristics of a region.
How are cross sections created in geology?
Cross sections in geology are typically created by interpreting data from various sources such as geological maps, borehole logs, seismic surveys, and field observations. Geologists use these data to construct a vertical representation of the subsurface geology at a specific location, showing the arrangement and relationships of different rock layers, faults, folds, and other structures. By visually representing the subsurface in a cross section, geologists can better understand the geological history and potential resource distribution in the area.
What information can be determined from a cross section?
A cross section provides information about the internal structure and composition of an object, such as geological formations, biological specimens, or engineering materials. By examining a cross section, scientists and researchers can determine features such as layering, mineral composition, fault lines, growth patterns, and structural integrity, helping to understand the history, development, and properties of the object being studied.
What are the key components of a geology cross section?
A geology cross section typically includes key components such as stratigraphic layers showing the various rock formations and their ages, faults and folds indicating tectonic activity, geological contacts where different rock units meet, symbols for features like mineral deposits or geological structures, a scale bar to show the vertical and horizontal extents accurately, and annotations to provide additional information about the geological features depicted in the section.
How are rock layers represented in a cross section?
Rock layers in a cross section are typically represented as horizontal lines of various lengths and thicknesses, each line corresponding to a different rock layer. The layers are arranged in the sequence they occur in the Earth's crust, with the oldest layers found at the bottom and the youngest at the top. This representation helps geologists interpret the relative ages and relationships between different rock units in a given area.
What do different types of lines and symbols mean in a geology cross section?
Different types of lines and symbols in a geology cross section represent various geological features and information such as rock layers, faults, folds, geological contacts, strike and dip measurements, and other structural elements. These lines and symbols help geologists accurately interpret the subsurface geology, relationships between different rock units, and the history of the area being studied, providing valuable insights for resource exploration, engineering projects, and understanding geological processes.
How are faults represented in a cross section?
Faults are represented in a cross section by showing a discontinuity or break in the rock layers. A fault is typically shown as a dashed or solid line with an arrow pointing in the direction of the movement that has occurred along the fault. This helps geologists understand the relative movement of the rock layers on either side of the fault and the deformation that has taken place in the Earth's crust.
What is the purpose of labeling and annotating features in a geology cross section?
Labeling and annotating features in a geology cross section serves the purpose of providing clarity and understanding of the various geological elements present in the section. By identifying and describing different rock layers, faults, folds, and other structures, geologists can interpret the history and formation of the area. This information helps in creating a detailed geological map, understanding tectonic processes, and making informed decisions related to resource exploration, land use planning, and environmental management.
How can a geology cross section help in understanding geological history?
A geology cross section is a visual representation of the subsurface geology that displays the variation and arrangement of rock layers, faults, and other geological features. By studying a cross section, geologists can interpret the sequence of geological events that have shaped the area over time. This includes understanding the deposition of different rock layers, the occurrence of tectonic movements such as folding and faulting, and the intrusion of igneous rocks. By analyzing a cross section, geologists can reconstruct the geological history of an area, including the timing and nature of past geological processes, providing valuable insights into the evolution of the Earth's crust.
Do geologists always agree on the interpretation of a cross section?
No, geologists do not always agree on the interpretation of a cross section. Different geologists may have varying expertise, perspectives, and interpretations based on the data available, leading to disagreements on how to interpret the geological features shown in a cross section. Ongoing research, discussions, and collaboration within the geological community help address these differences and lead to a more comprehensive understanding of Earth's subsurface.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments