Gene Mutation Worksheet Answers
Are you a student or a teacher looking for reliable answers to gene mutation worksheets? Look no further, as this blog post will provide you with accurate and comprehensive answers to help you better understand and tackle this topic. Whether you are learning about gene mutations in biology class or teaching your students about this important concept, having access to reliable answers can greatly enhance the learning experience. So, let's delve into the world of gene mutations and discover the answers you've been seeking.
Table of Images 👆
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- 13 3 Mutations Worksheet Answers
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Gene Expression Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a gene mutation?
A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of a gene, which can result in a variety of outcomes such as altering the protein it encodes, affecting its function, or causing it to be turned on or off incorrectly. Gene mutations can be inherited or occur spontaneously, and they can lead to genetic disorders or an increased risk of developing certain diseases.
A gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence that can result in changes to the structure or function of a gene.
Yes, a gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence that can lead to changes in the structure or function of a gene, potentially affecting how the gene is expressed and the resulting protein that is produced.
What causes gene mutations?
Gene mutations can be caused by various factors, including errors in DNA replication, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, and even spontaneous genetic changes. In some cases, mutations can be inherited from parents who carry a mutated gene. Other factors like environmental influences and lifestyle choices can also contribute to the occurrence of gene mutations.
Gene mutations can be caused by various factors, including errors in DNA replication, environmental factors (such as radiation or chemicals), and genetic predispositions.
Yes, gene mutations can indeed be caused by various factors such as errors in DNA replication, exposure to environmental factors like radiation or chemicals, and genetic predispositions that may increase the likelihood of mutations occurring. These mutations can lead to changes in the DNA sequence, potentially impacting the functioning of genes and resulting in genetic disorders or diseases.
What are the different types of gene mutations?
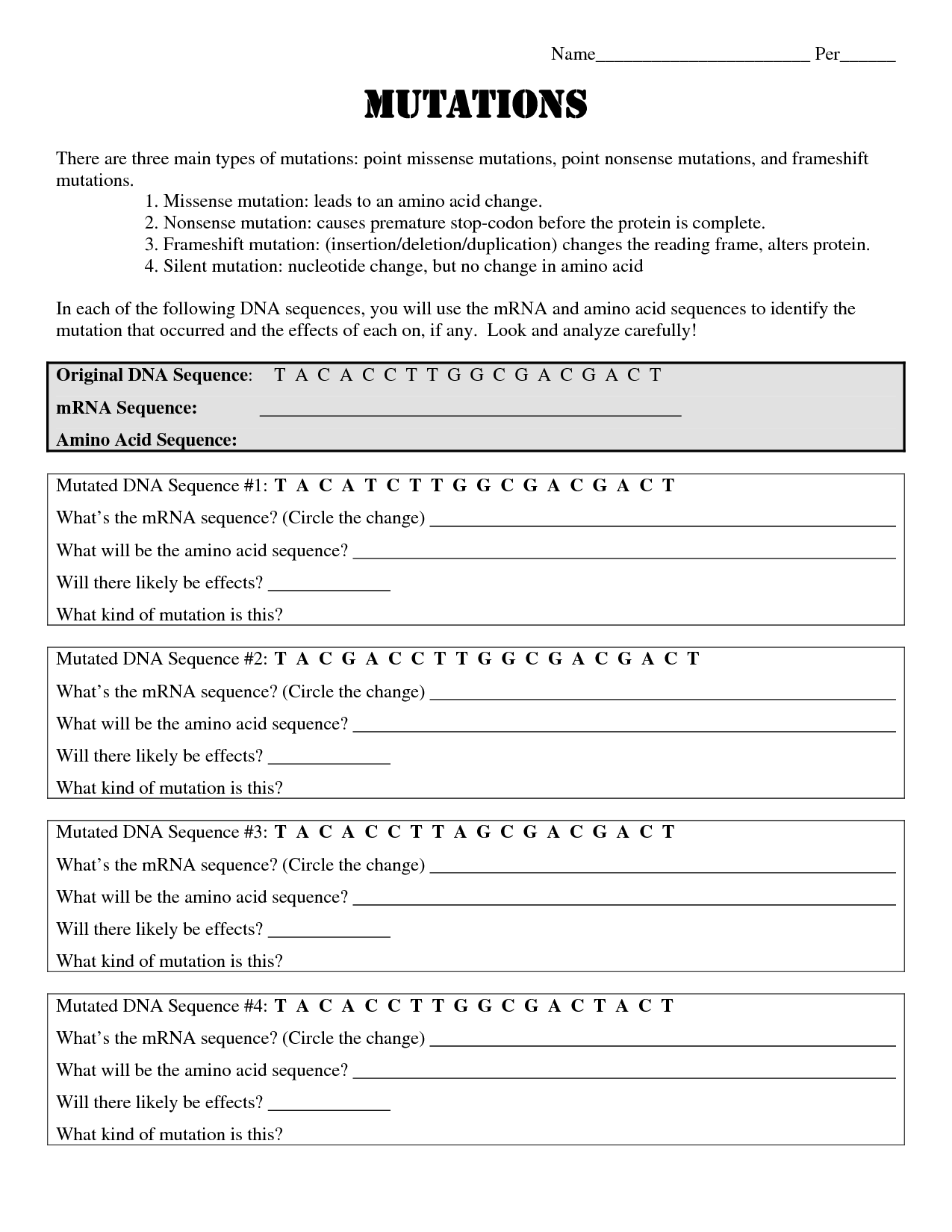
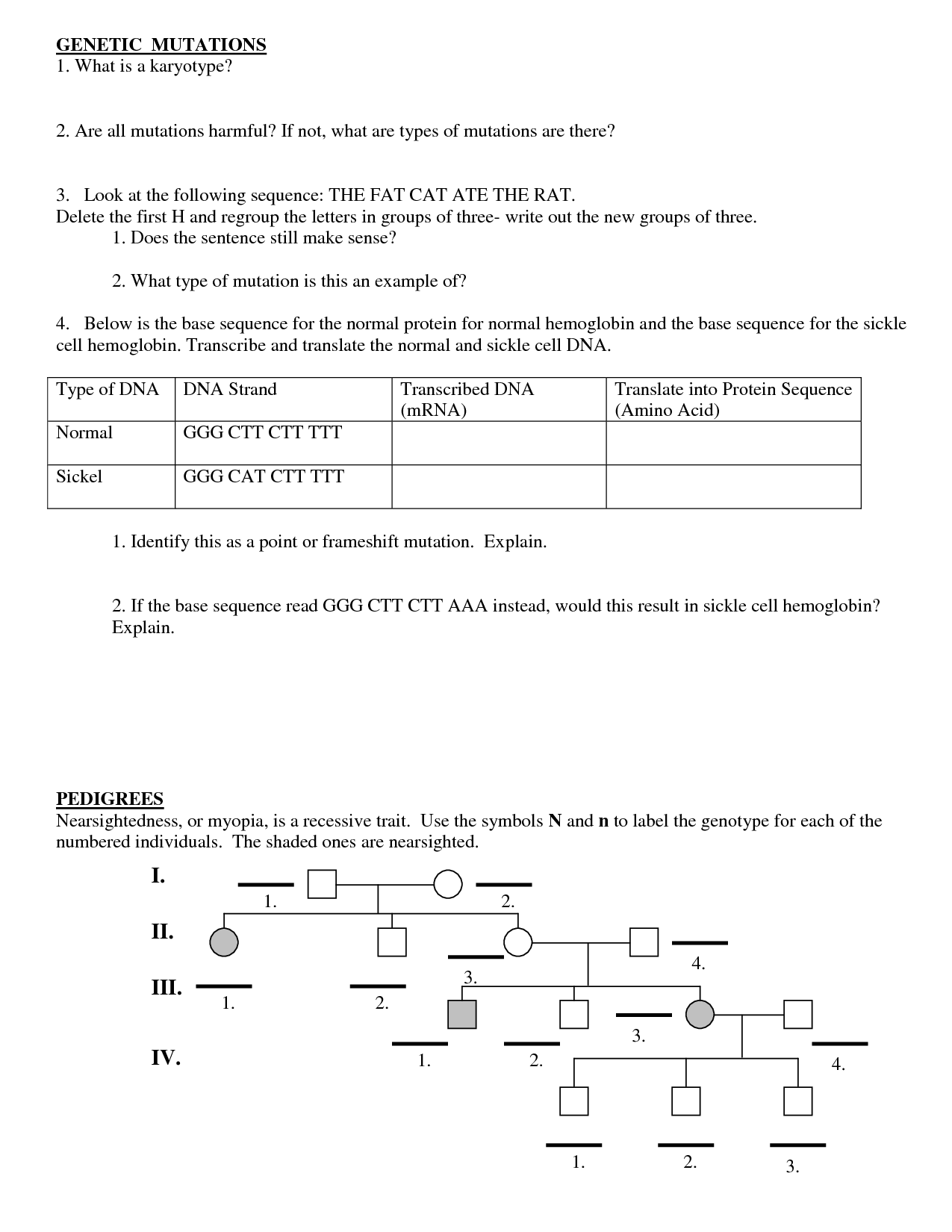
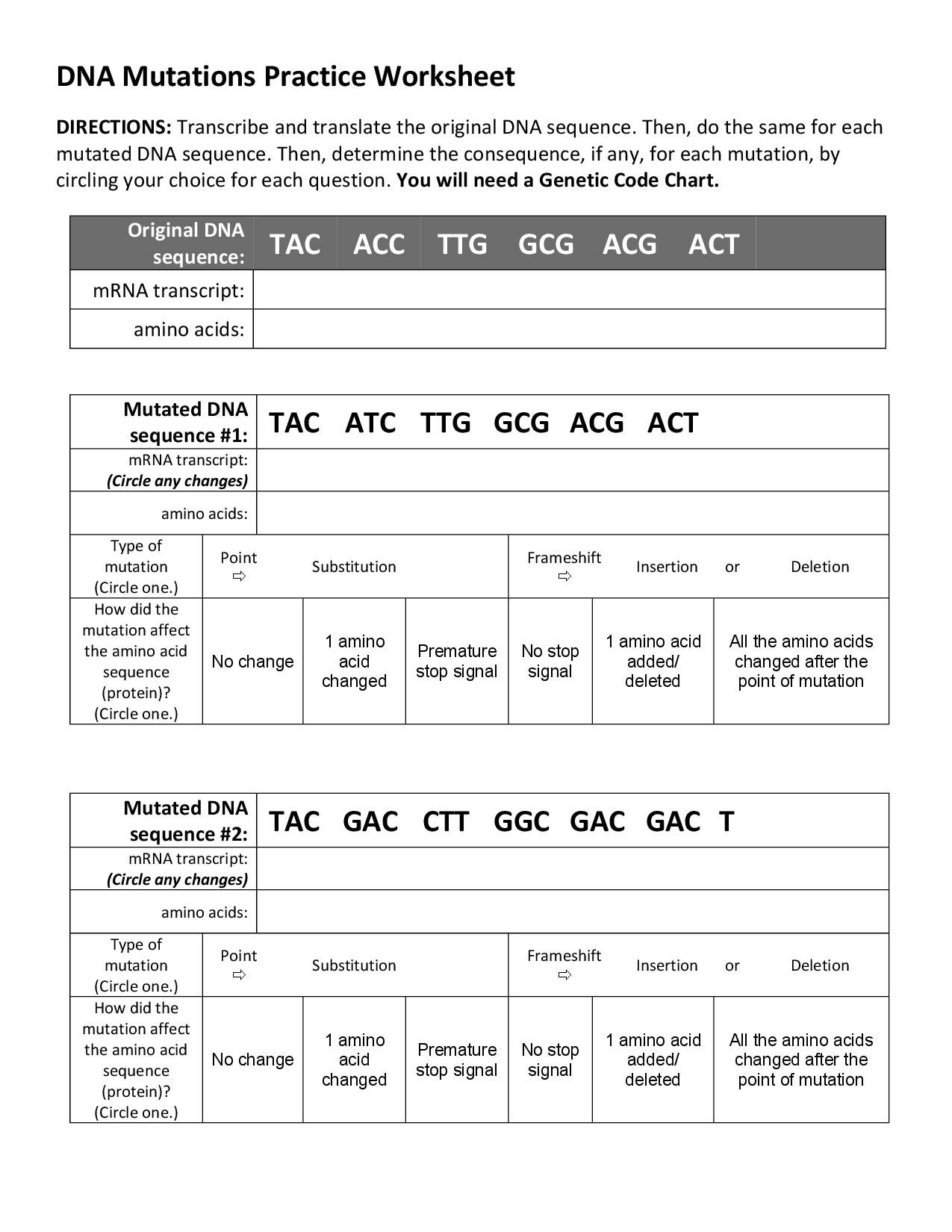
There are several types of gene mutations, including substitutions (where one base pair is replaced with another), insertions (where an extra base pair is inserted into the DNA sequence), deletions (where a base pair is removed from the DNA sequence), and frameshift mutations (caused by insertions or deletions that shift the reading frame of the genetic code). These mutations can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence of a protein, potentially affecting its structure and function.
The main types of gene mutations include point mutations (substitutions, insertions, or deletions), frameshift mutations, and chromosomal mutations (such as insertions, deletions, inversions, or translocations).
Point mutations involve changes at a single nucleotide level, either substituting one base for another, inserting an extra base, or deleting a base. Frameshift mutations occur when the insertion or deletion of nucleotides shifts the reading frame of the genetic code. Chromosomal mutations involve changes in the structure or number of whole chromosomes, leading to large-scale genetic alterations within an organism.
How can gene mutations impact protein production?
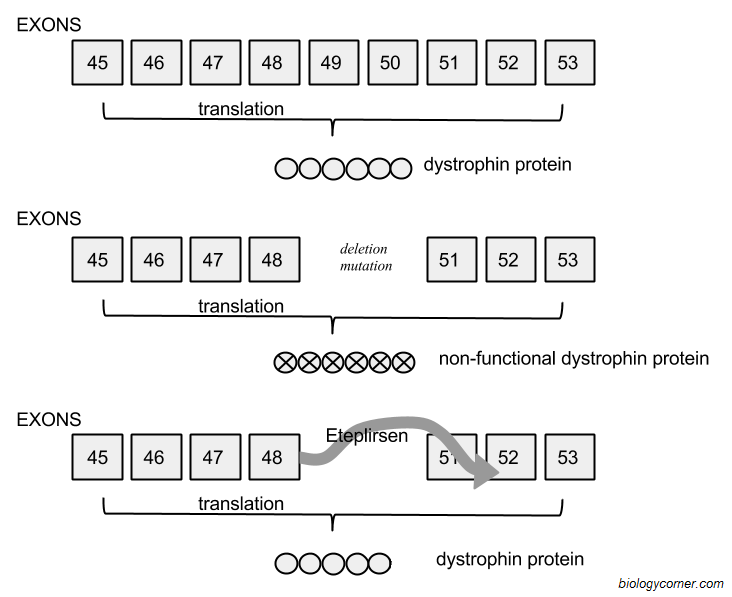
Gene mutations can impact protein production by altering the sequence of nucleotides within a gene, leading to changes in the amino acid sequence of the corresponding protein. This can result in the production of a non-functional protein, a protein with altered function, or even the complete absence of a protein. Mutations can impact various stages of protein synthesis, including transcription, translation, and post-translational modifications, ultimately affecting the overall structure and function of the protein in the cell or organism.
Gene mutations can lead to changes in protein production by altering the coding sequence of the gene, resulting in the synthesis of an abnormal protein or the absence of a functional protein.
Yes, that is correct. Gene mutations can indeed cause changes in protein production by affecting the gene's coding sequence, leading to the synthesis of abnormal proteins or the absence of functional proteins. These alterations can impact various cellular processes and potentially result in genetic disorders or diseases.
Do all gene mutations have negative effects?
No, not all gene mutations have negative effects. Some gene mutations can be neutral or even beneficial, depending on the specific change in the DNA sequence and how it affects the function of the resulting protein. Neutral mutations may have no impact at all, while beneficial mutations can provide advantages that help an organism survive and adapt to its environment.
No, not all gene mutations have negative effects. Some mutations can have neutral effects, while others can even confer certain advantages, such as increased resistance to diseases.
Yes, that's correct! While some gene mutations can be harmful and cause diseases or disorders, others can be neutral or even beneficial, providing an advantage in certain environments. These advantageous mutations can lead to increased resistance to diseases, improved physical traits, or other benefits that can be passed down to future generations.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments