Function of Organelles Worksheet
Organelles are small, specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions to help it carry out its tasks. For students studying biology or cellular biology, understanding the functions of organelles is vital. A well-structured worksheet can provide a comprehensive overview of these functions, allowing students to grasp the concept easily and effectively.
Table of Images 👆
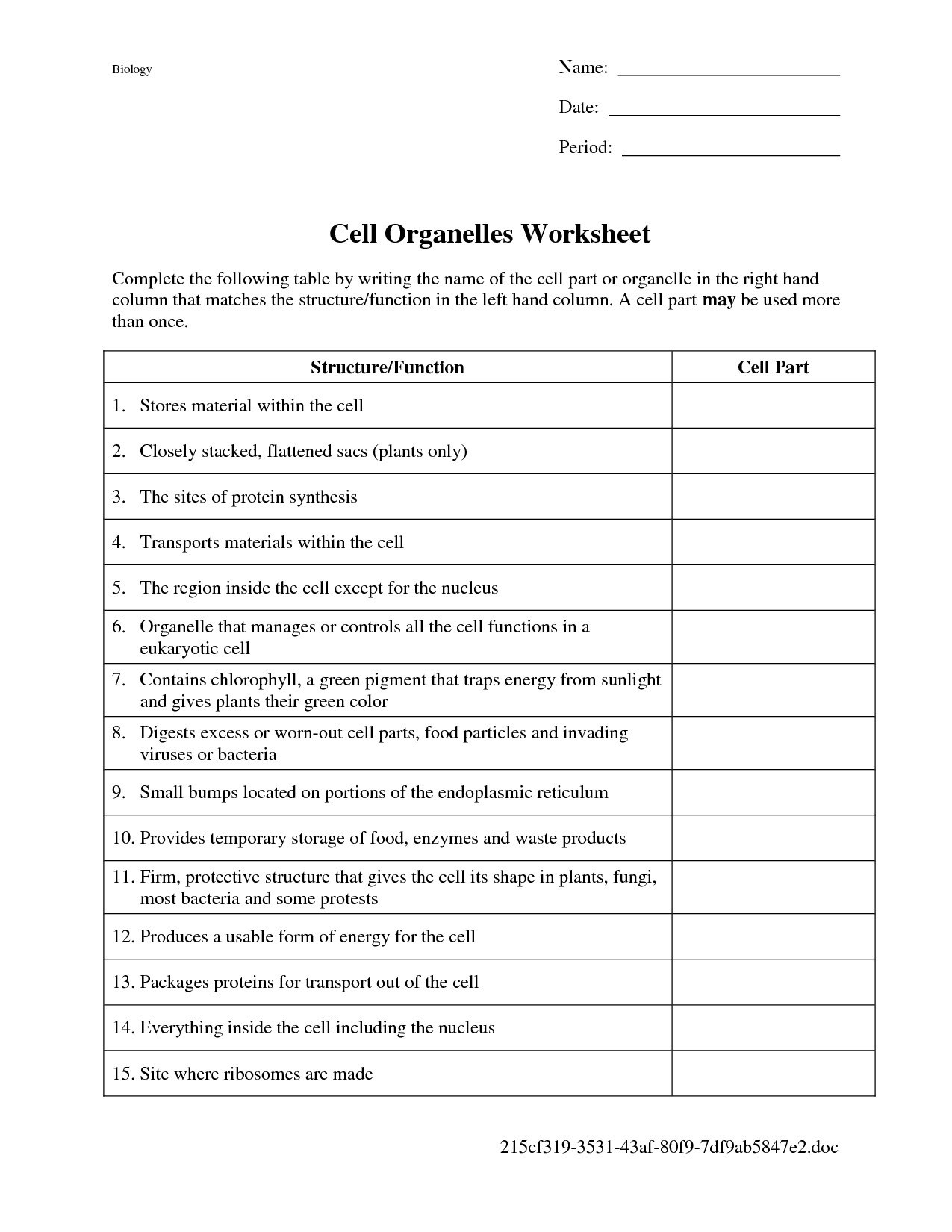
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
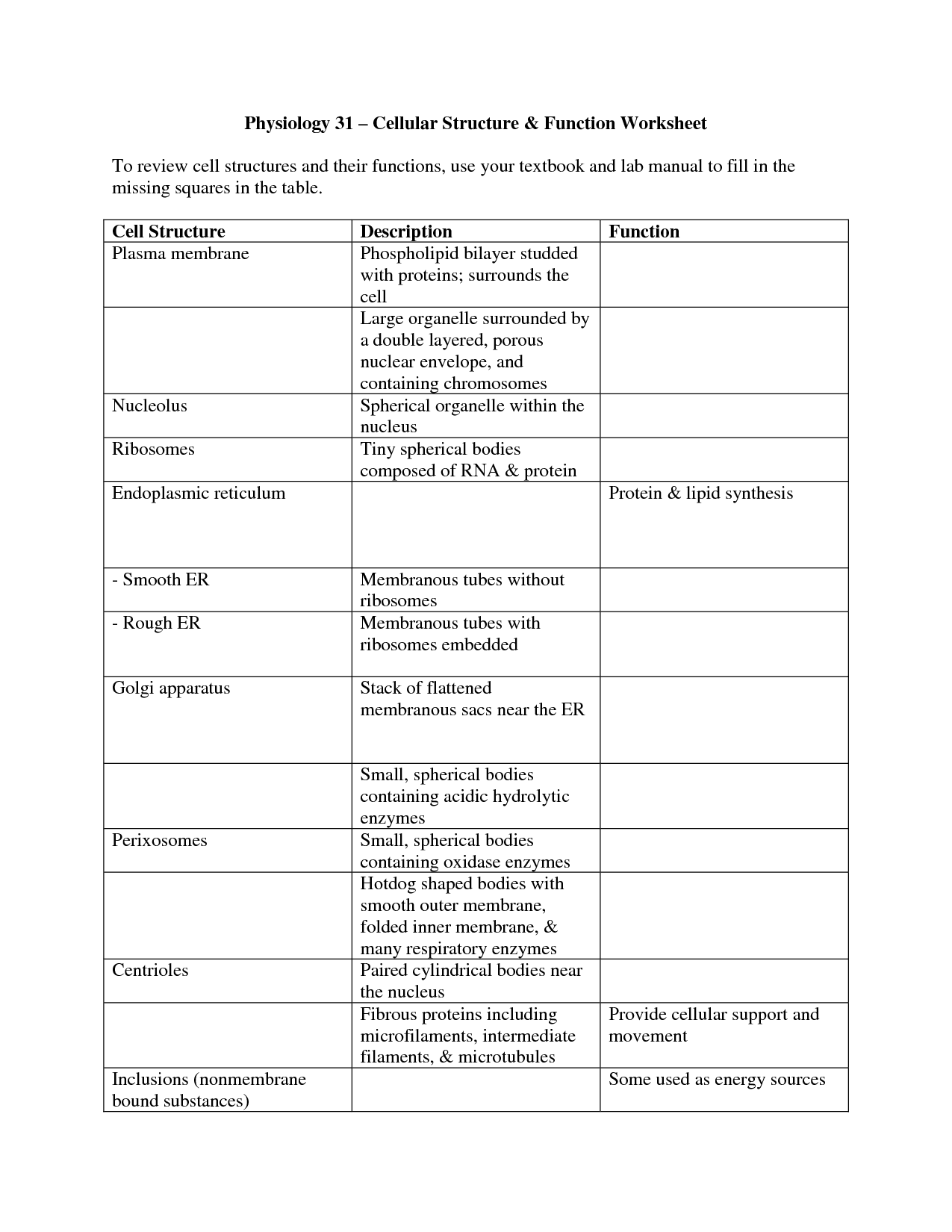
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
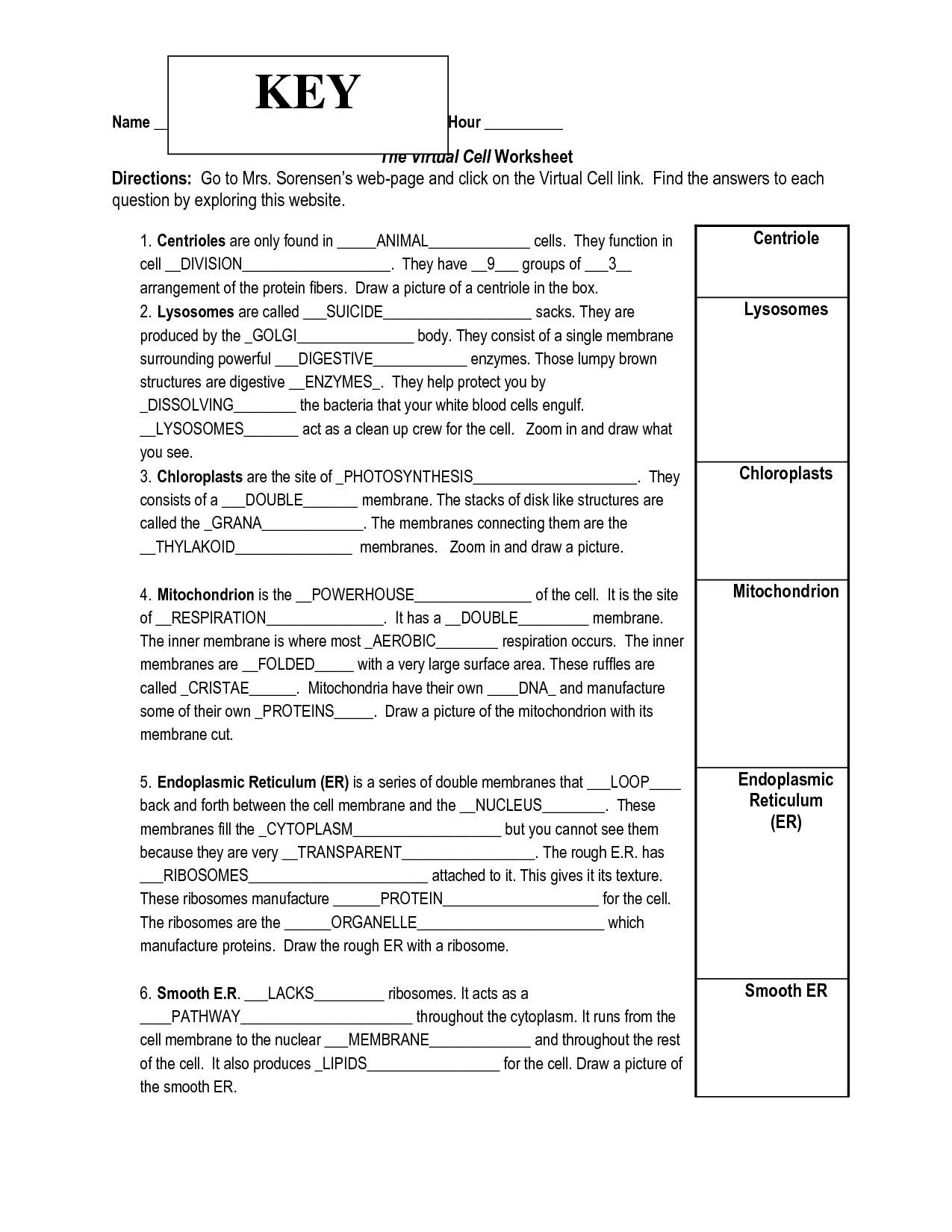
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
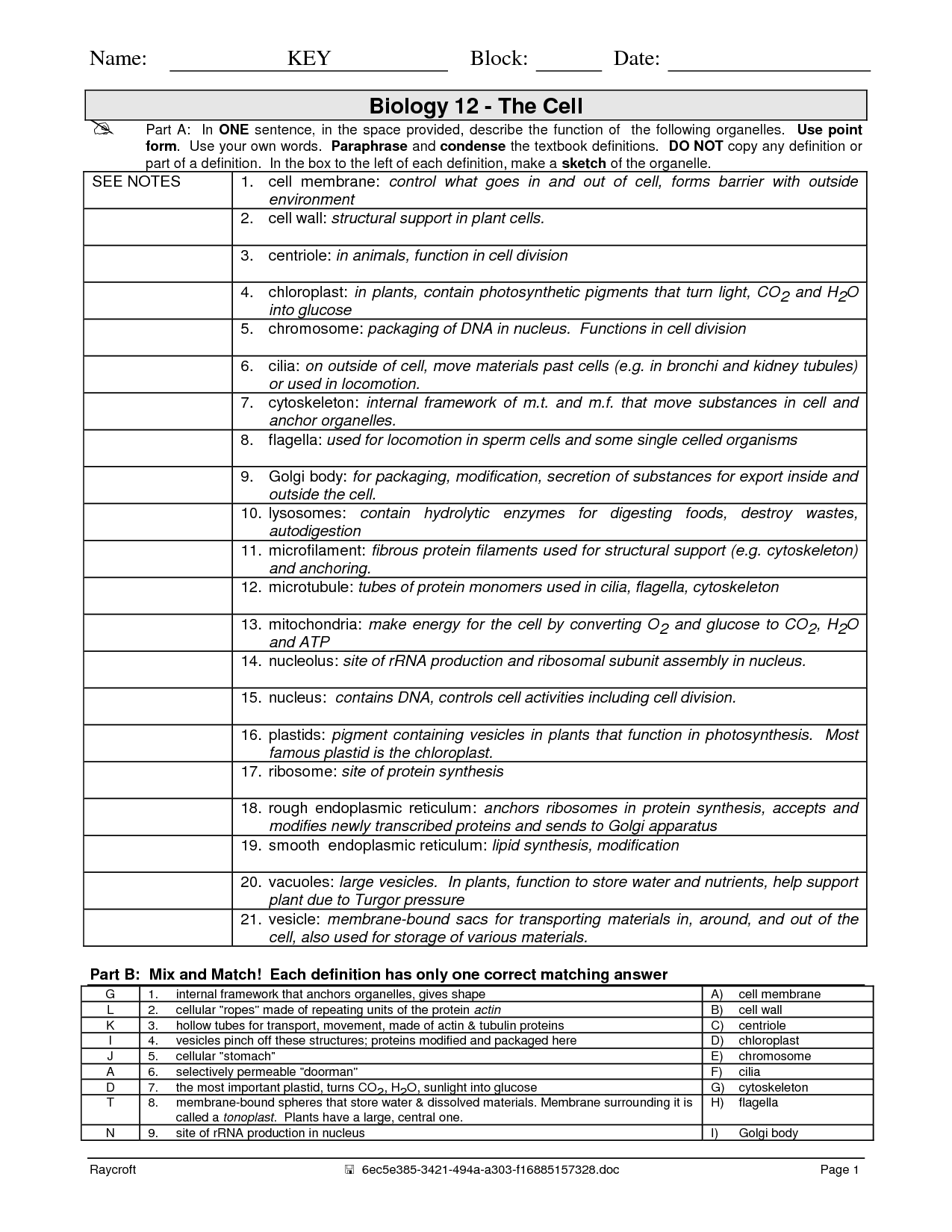
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheets Answer Key
- Cell Crossword Answers Holt Science and Technology
- Cell Organelles and Functions
- Plant and Animal Cell Organelles Quiz
- Cell Organelles and Functions
- Biology Cell Reproduction Worksheets Answers
- Science Fair Project Rubric
- Skeletal System Crossword Puzzle Answers
- Skeletal System Crossword Puzzle Answers
- Skeletal System Crossword Puzzle Answers
- Skeletal System Crossword Puzzle Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
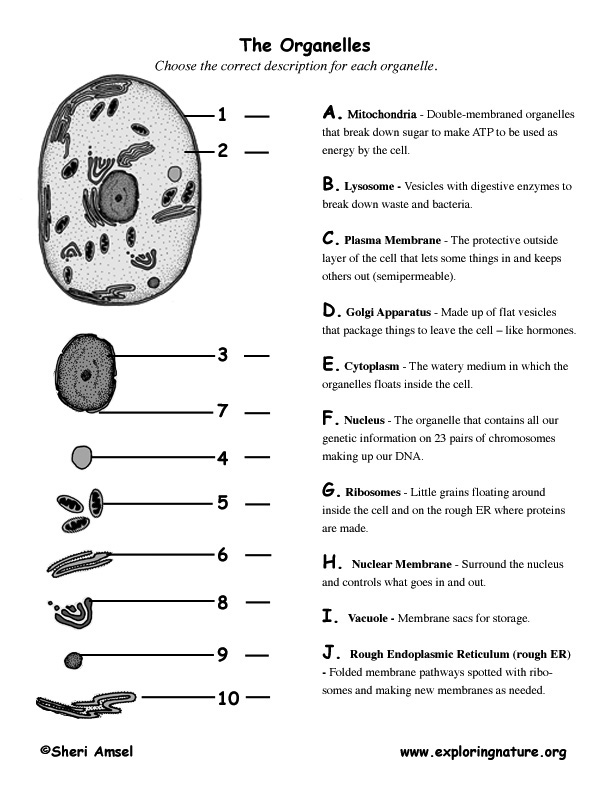
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus is the control center of a cell, responsible for storing and protecting the cell's genetic material (DNA) and coordinating gene expression. It regulates the cell's activities by controlling protein synthesis and cell division, as well as managing the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus through the nuclear membrane. Overall, the nucleus plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell's functions and ensuring proper growth and development.
How does the mitochondria contribute to cellular energy production?
Mitochondria contribute to cellular energy production through a process called cellular respiration, where they produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules, the primary energy carrier in cells. The mitochondria generate ATP through the breakdown of glucose and other nutrients in a series of metabolic reactions that take place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. This process involves the electron transport chain, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, all of which work together to produce ATP for the cell to use as energy.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in protein synthesis?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by providing a large surface area for ribosomes to attach and synthesize proteins. The rough ER, studded with ribosomes, is involved in the synthesis of proteins that are either secreted by the cell or inserted into the cell membrane. The smooth ER is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification. Overall, the endoplasmic reticulum is essential for the proper folding, modification, and transport of proteins within the cell.
What function does the Golgi apparatus serve in a cell?
The Golgi apparatus serves as a packaging and distribution center in a cell, where it modifies, sorts, and packages molecules like proteins and lipids that are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It plays a crucial role in processing these molecules and directing them to their correct destinations within the cell or for secretion outside of the cell.
How do lysosomes contribute to cellular waste disposal?
Lysosomes contribute to cellular waste disposal by containing enzymes that break down unwanted materials such as old organelles, debris, and foreign substances. These enzymes inside the lysosomes break down the waste materials into smaller molecules that can be recycled or excreted by the cell. This process of breaking down and recycling cellular waste is essential for maintaining a healthy and functioning cell.
What is the function of the vacuole in plant cells?
The vacuole in plant cells primarily functions as a storage organelle, storing nutrients, ions, waste products, and pigments. It also helps maintain turgor pressure, playing a crucial role in maintaining the cell's shape and providing structural support to the plant. Additionally, the vacuole can also help regulate the cell's pH balance and detoxify harmful substances.
What role does the chloroplast play in photosynthesis?
The chloroplast is responsible for carrying out the process of photosynthesis in plant cells. Within the chloroplast, pigments such as chlorophyll capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy through a series of biochemical reactions. This process ultimately produces glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, providing energy for the plant to grow and thrive.
How does the ribosome contribute to protein production?
The ribosome is the cellular machinery responsible for translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins through a process called translation. It reads the sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA and synthesizes a corresponding sequence of amino acids to form a protein. The ribosome catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, ultimately leading to the production of functional proteins that are essential for various cellular processes and functions in living organisms.
What is the function of the cytoplasm in a cell?
The cytoplasm in a cell serves as a medium for the organelles to reside and function. It facilitates cellular processes by providing a platform for various metabolic reactions to occur. Additionally, the cytoplasm contains nutrients, ions, and other molecules essential for cellular activities, and it also plays a role in supporting the structure and shape of the cell.
How does the cell membrane regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell?
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell through a process called selective permeability. This means that the membrane allows certain molecules to pass through while blocking others. It achieves this by using specialized proteins and channels that control the entry and exit of substances based on their size, charge, and solubility. Additionally, the membrane can actively transport molecules against their concentration gradient using energy in the form of ATP. Together, these mechanisms help maintain the internal environment of the cell and ensure proper functioning.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments