Formal and Informal Writing Worksheets
Are you looking for worksheets to improve your formal and informal writing skills? Look no further, as we have a wide range of worksheets available to help you enhance your understanding of entity and subject in both types of writing. From clear explanations to engaging activities, our worksheets are designed to suit learners of various levels and provide opportunities for practice and reinforcement.
Table of Images 👆
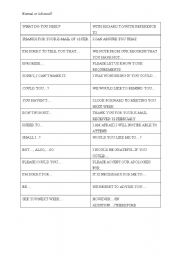
- Writing Formal and Informal Letters
- Writing an Informal Business Letter
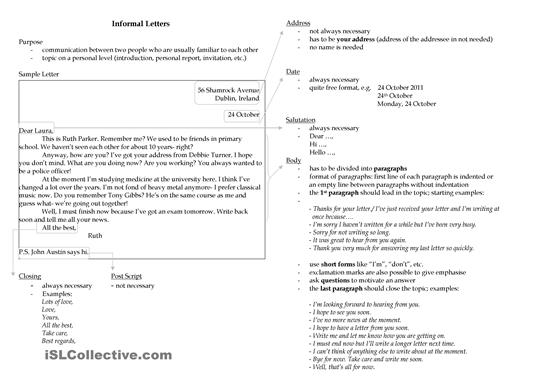
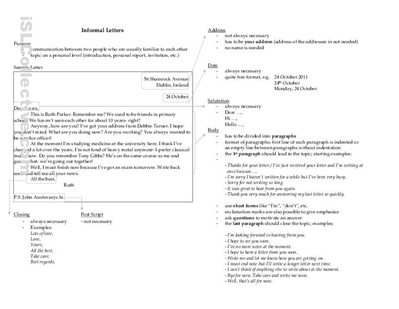
- Informal Letter Writing Samples
- Formal and Informal Spanish Words
- Formal Writing Letters Worksheets
- Friendly Letter Format Worksheet
- High School English Worksheets
- Formal and Informal Business Letters
- 6th Grade Writing Worksheets
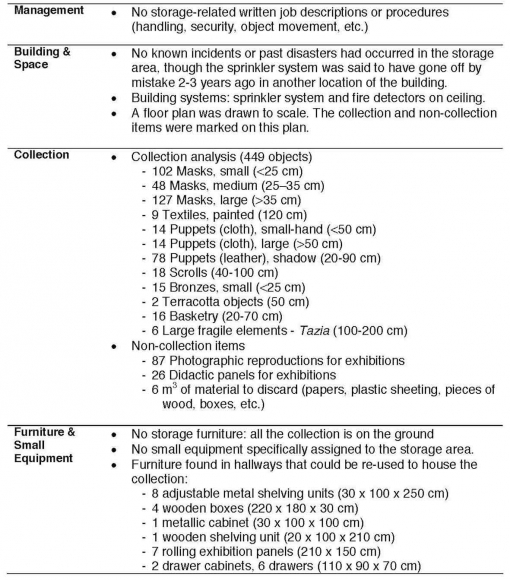
- Museum Condition Report Template
- The Cay Activities and Lessons
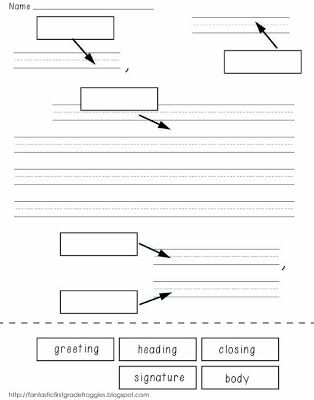
- Label Parts of Friendly Letter
- Alphabet Coloring Pages
- Missing Letters Worksheet
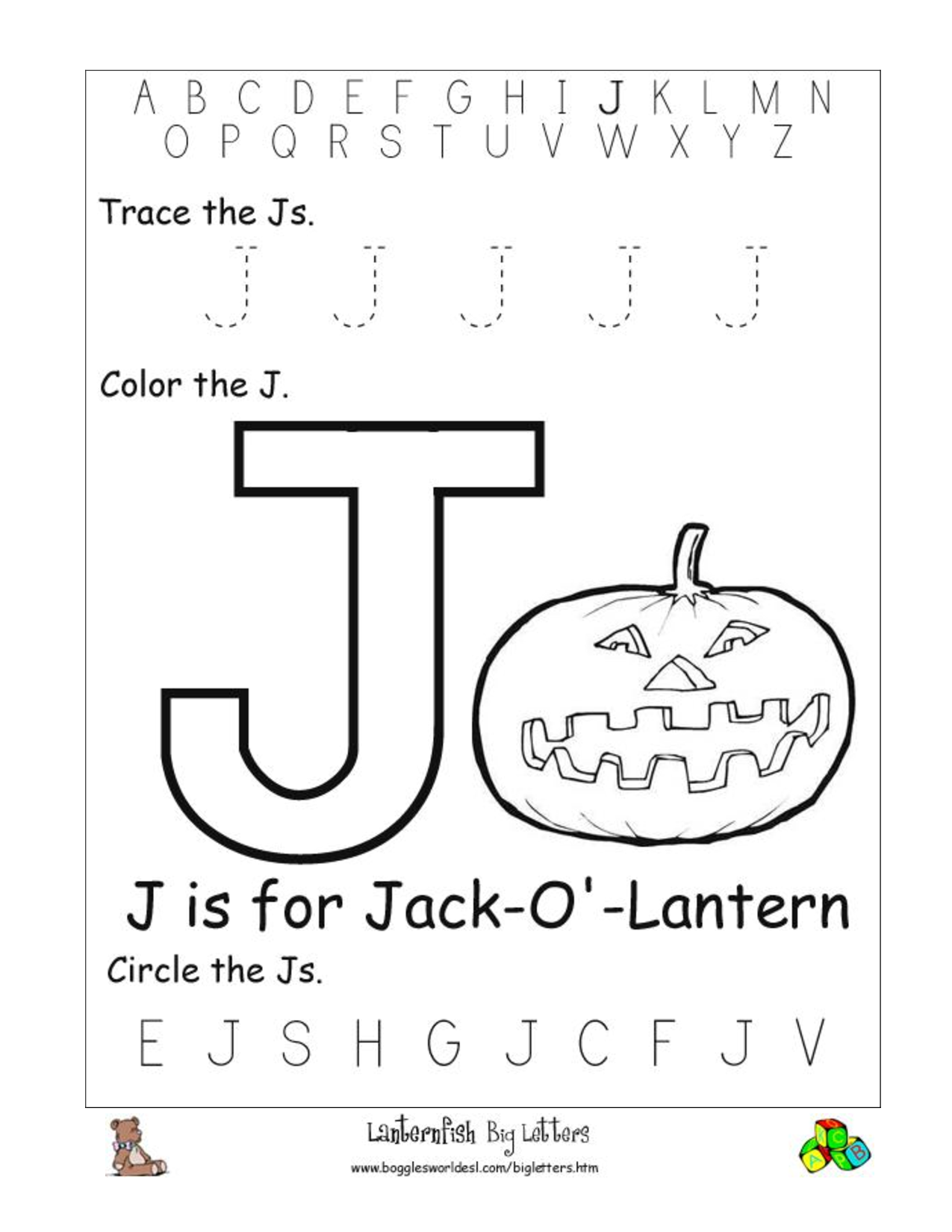
- Letter J Printable Worksheets
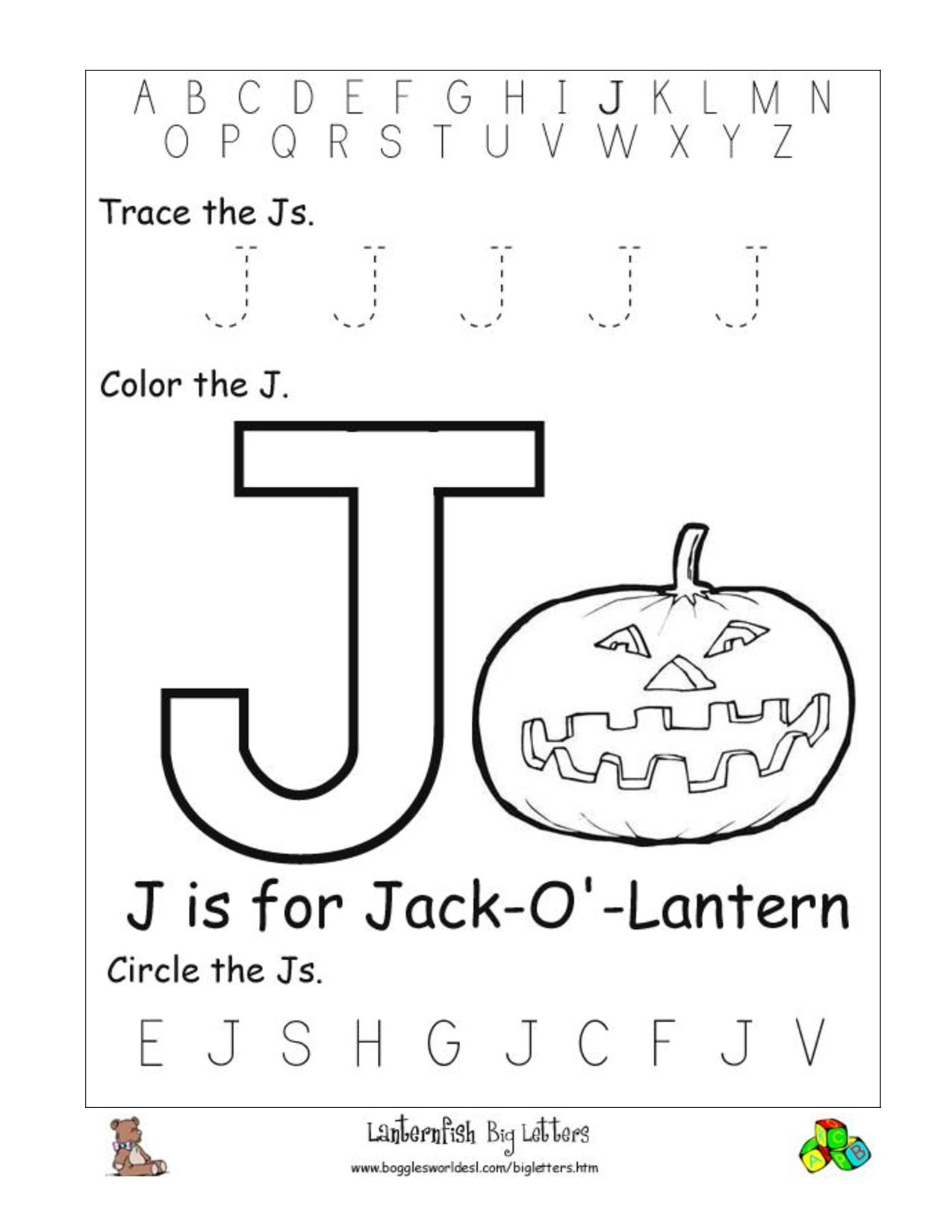
- Letter J Printable Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is formal writing?
Formal writing is a type of communication that follows a prescribed format, style, and tone. It is characterized by its adherence to grammatical rules, structured organization, use of professional language, and avoidance of personal pronouns and colloquial expressions. Formal writing is typically used in academic, professional, and official settings where clarity, precision, and professionalism are valued.
What is informal writing?
Informal writing refers to a style of writing that is casual, conversational, and relaxed in tone. It often includes personal anecdotes, colloquial language, and a more relaxed grammar and punctuation style than formal writing. Informal writing is typically used in settings where the writer wants to establish a more personal connection with the reader, such as in emails, text messages, personal blogs, or social media posts.
What are the key characteristics of formal writing?
Formal writing is characterized by the use of professional language and tone, adherence to grammar and punctuation rules, avoidance of contractions and slang, as well as the inclusion of citations and references when necessary. It also typically follows a specific structure such as an introduction, body paragraphs with clear topic sentences and supporting details, and a conclusion that summarizes key points. Additionally, formal writing often maintains a serious and objective stance, with an emphasis on clarity and precision in communication.
What are the key characteristics of informal writing?
Informal writing typically features a conversational tone, with the use of everyday language and contractions. It may include personal opinions, anecdotes, and colloquial expressions. It often lacks strict adherence to grammar rules and formal structure, allowing for more creative and engaging communication. Additionally, informal writing tends to prioritize clarity and connection with the audience over formal conventions.
What types of documents typically require formal writing?
Documents that typically require formal writing include academic papers, business reports, professional emails, legal contracts, official letters, grant proposals, research papers, and resumes. These types of documents often require a clear and organized structure, a professional tone, proper grammar and punctuation, and adherence to specific formatting guidelines.
What types of documents typically require informal writing?
Documents that typically require informal writing include personal emails, text messages, social media posts, blog posts, personal letters, and notes to colleagues or friends. These types of communication usually have a conversational tone and allow for a more relaxed and friendly style of writing.
How does the tone differ between formal and informal writing?
The tone in formal writing is more professional, structured, and impersonal, using complex language and avoiding contractions, slang, or colloquial expressions. Informal writing, on the other hand, is more conversational, casual, and often includes personal pronouns, contractions, and familiar language, creating a more relaxed and engaging tone.
What are some common examples of formal language used in formal writing?
Some common examples of formal language used in formal writing include avoiding contractions (e.g. do not instead of don't), using complete sentences with proper punctuation and grammar, employing a professional tone and vocabulary, refraining from slang or colloquialisms, and adhering to specific formatting requirements such as using appropriate headings and subheadings.
What are some common examples of casual language used in informal writing?
Common examples of casual language used in informal writing include contractions (e.g. "can't," "won't"), slang terms (e.g. "cool," "awesome"), colloquial expressions (e.g. "I'm gonna," "wanna"), and abbreviations (e.g. "lol," "btw"). These informal language elements help to create a conversational tone and connect with readers on a more personal level.
What are the main differences in structure and organization between formal and informal writing?
Formal writing typically follows a structured format with clear organization, using specific language, complete sentences, and proper grammar. It often includes a formal tone, avoids contractions, slang, and first or second person pronouns. In contrast, informal writing may have a more relaxed structure with a conversational tone, allowing for contractions, slang, and the use of personal pronouns. It may also include elements of creativity and personal expression that are not commonly found in formal writing.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments