Force and Motion Worksheet PDF
If you're a science teacher in need of engaging and educational resources for your students, look no further than the Force and Motion Worksheet PDF. Designed specifically for middle school students, this worksheet offers a comprehensive review of key concepts related to the principles of force and motion.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Motion Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Rotational Motion Worksheet Answers
- The Rock Cycle Worksheet and Answer Key
- Physics Forces Worksheet
- Heat and Thermal Energy Worksheet
- Motion and Reference Point Worksheet
- Science Worksheets Push and Pull
- Moon and Tides Worksheet
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheet
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
- Printable Turtle Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is force?
Force is a physical quantity that describes the interaction between objects resulting in a push or pull that can cause an object to accelerate, decelerate, or deform. It is typically measured in units such as newtons and is central to understanding the motion and behavior of objects in the field of physics.
How is force measured?
Force is typically measured using a unit called newtons (N). The measurement of force is determined by multiplying an object's mass (measured in kilograms) by its acceleration (meters per second squared), according to Newton's Second Law of Motion. This calculation helps to quantify the amount of force being exerted on an object in a specific direction.
What are the different types of forces?
There are four fundamental forces in nature: gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force. Gravitational force is responsible for the attraction between objects with mass, electromagnetic force deals with the interactions between charged particles, strong nuclear force holds atomic nuclei together, and weak nuclear force is involved in radioactive decay processes.
What is friction?
Friction is a force that resists the motion of objects that are in contact with each other. It occurs when two surfaces slide against each other or when an object moves through a fluid, such as air or water. Friction is caused by microscopic irregularities on the surfaces that interact with each other, creating resistance to the motion of the objects.
How does friction affect motion?
Friction is a force that resists the motion of objects in contact with each other. When two surfaces rub against each other, friction creates a resistance that slows down the movement of the objects. This resistance can cause objects to come to a stop or make it harder for them to move. Friction also plays a crucial role in allowing objects to grip surfaces and preventing slipping. Overall, friction directly affects motion by influencing the speed and direction of objects in contact.
What is inertia?
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. This means that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by an external force.
How does mass affect inertia?
Mass directly affects inertia. Inertia is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion, and the greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia. This means that an object with more mass requires more force to change its velocity or direction compared to an object with less mass. In essence, mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and this quantity determines the object's inertia.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
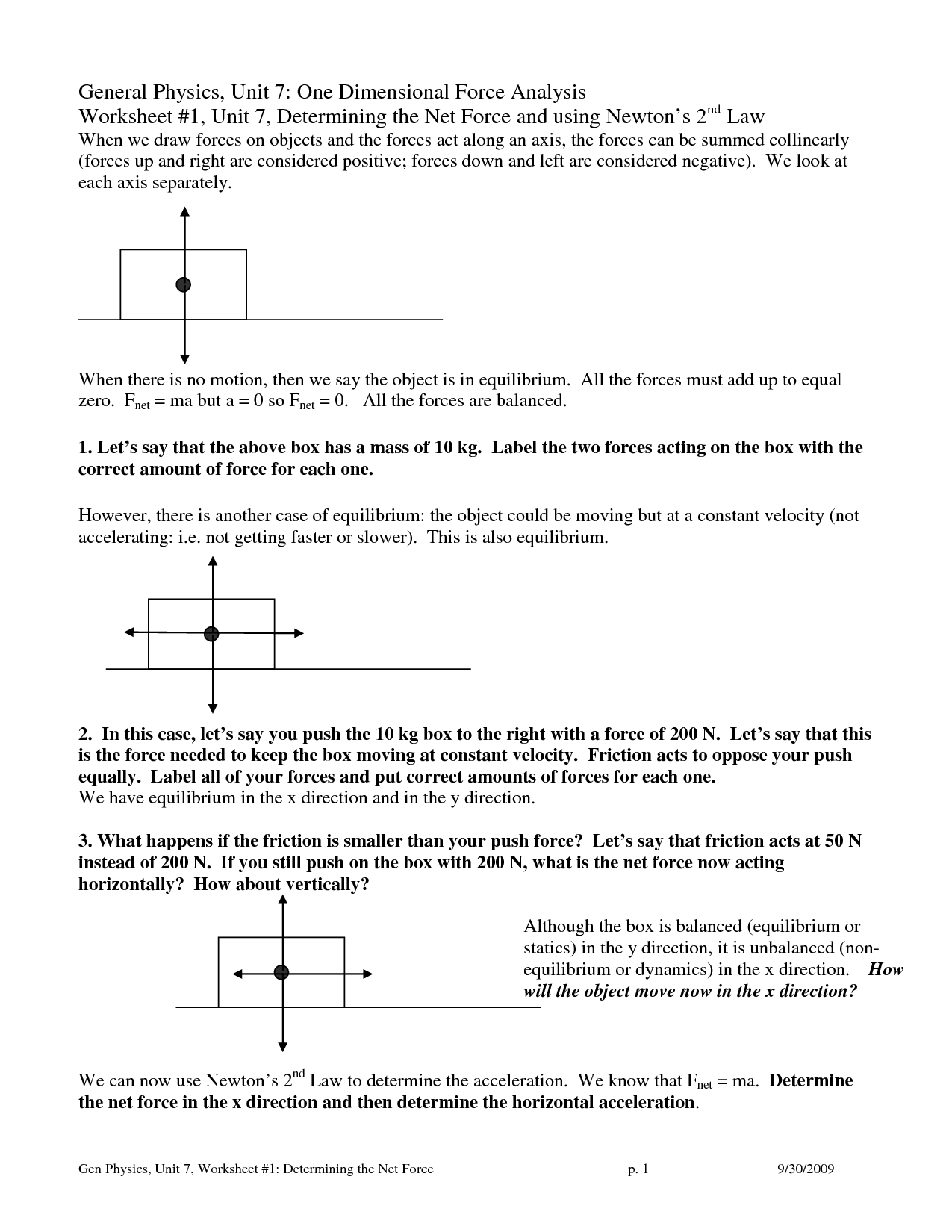
What is Newton's second law of motion?
Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This can be represented by the equation F = ma, where F is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration produced. In simpler terms, the greater the force applied to an object, the greater the acceleration it will experience, while a heavier object will have a smaller acceleration for the same force compared to a lighter object.
What is Newton's third law of motion?
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force back on the first object.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments