For Tissues and Membranes Worksheets
Worksheets are an invaluable resource for students studying tissues and membranes, as they provide a structured and hands-on approach to learning about this complex topic. These worksheets dive into the fascinating world of cells, examining their organization, functions, and interactions within various tissues and membranes. By engaging with these worksheets, students can deepen their understanding of the subject and reinforce key concepts through practical exercises and thought-provoking questions.
Table of Images 👆
- Plant Tissue Worksheet Answers
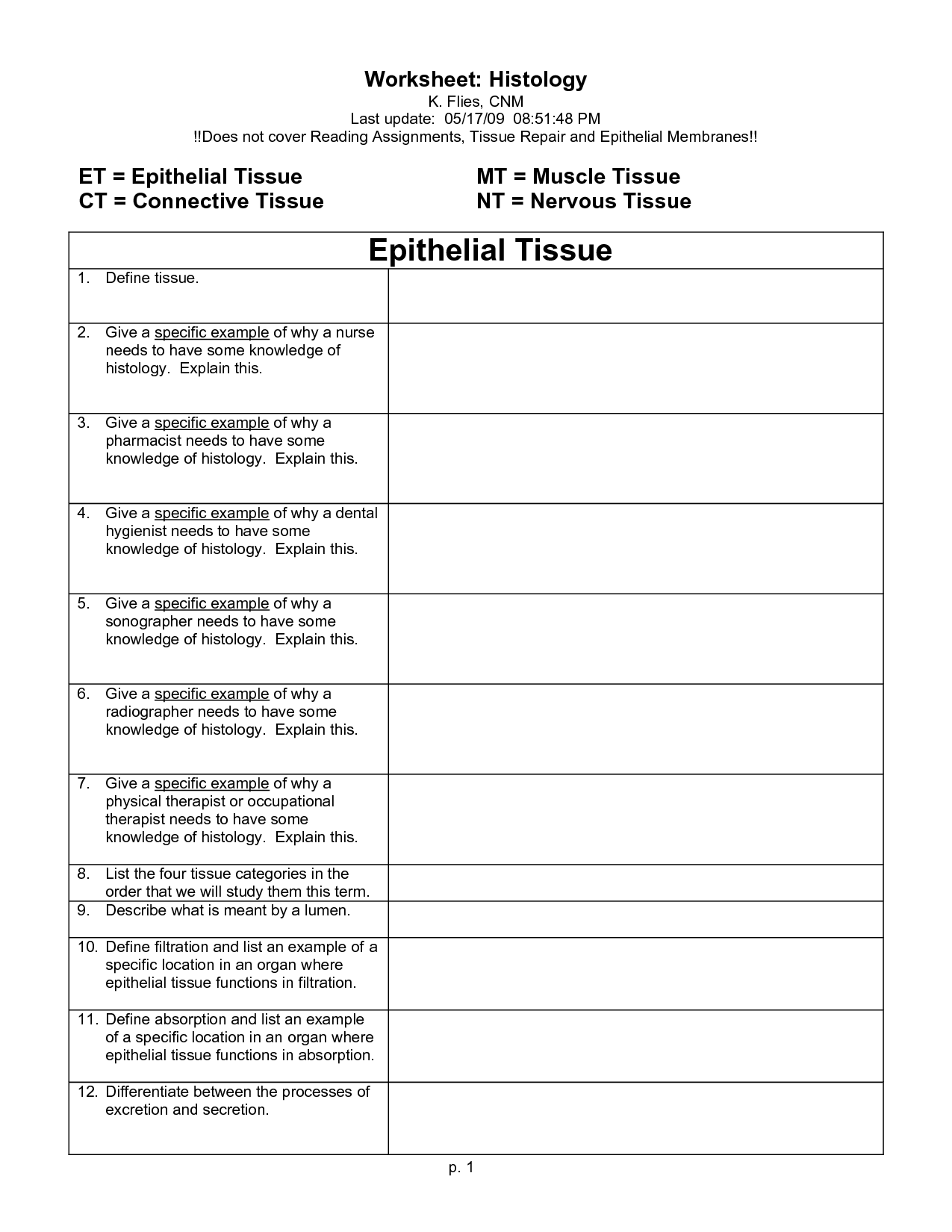
- Anatomy Epithelial Tissues Worksheet Answers
- All About My Mom Printable Worksheet
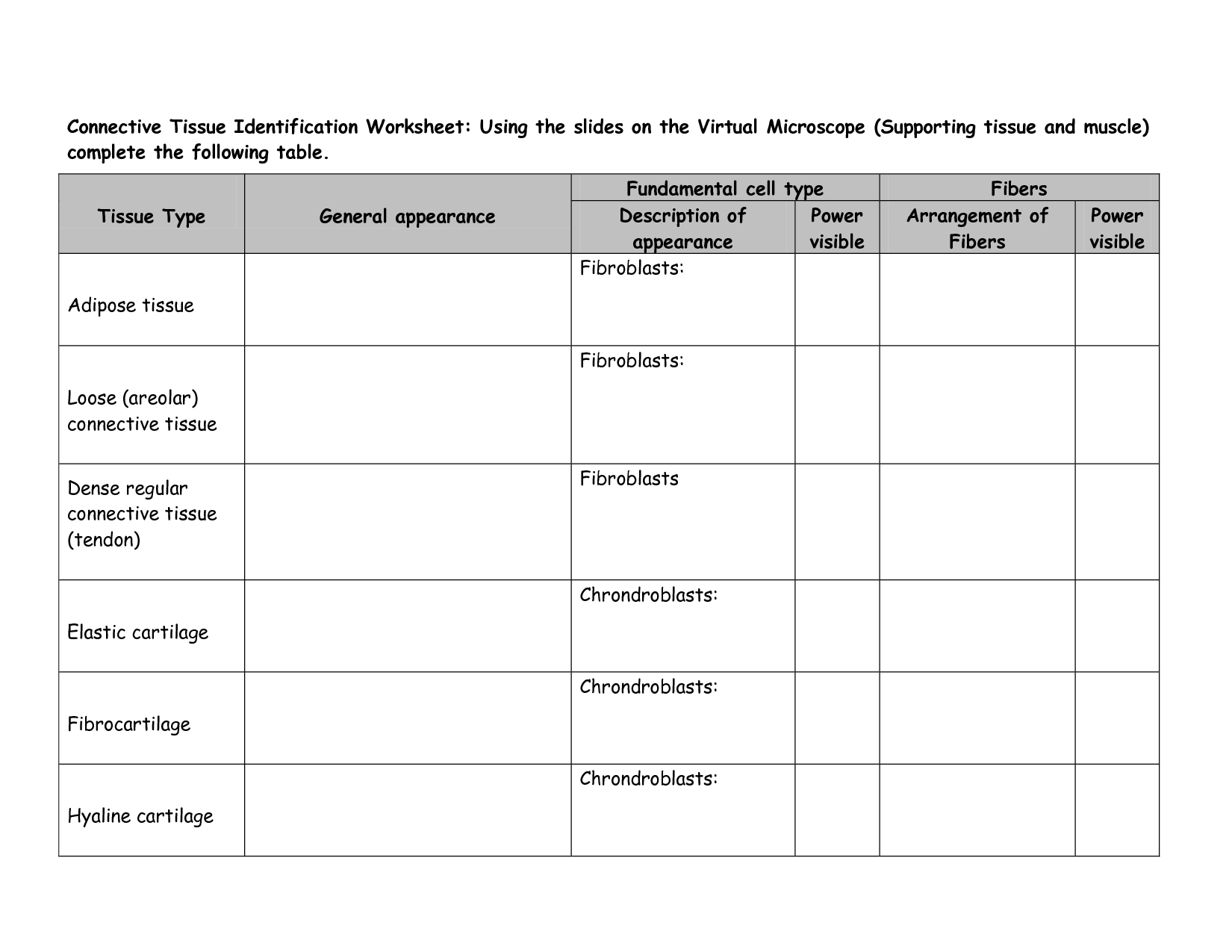
- Connective Tissue Worksheet Answers
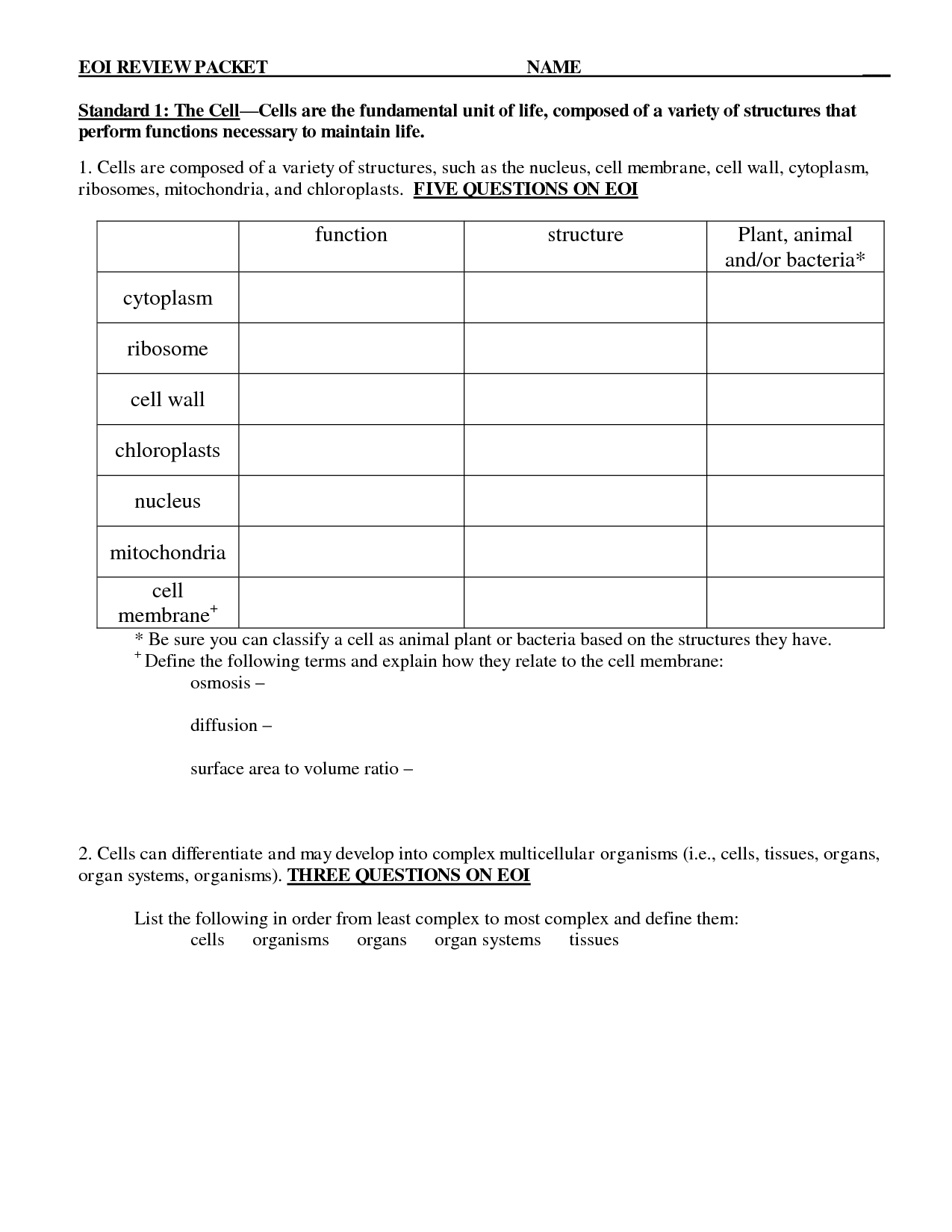
- Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Worksheet Answers
- Histology of Nervous Tissue Worksheet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Tissue Identification Worksheet
- Cells Tissues Organs Worksheet Answers
- Muscle Tissue Worksheet Answers
- Worksheets 5th Grade Science Tissues and Organs
- Animal Development Stages Worksheet
- Organ System Crossword Puzzle
- Cancer and Cell Cycle Worksheet
- Natural Selection Worksheet High School
- The Muscular System Worksheets Answer Key Chapter 6
- Cranial Bones Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue functions as a protective barrier against physical and chemical damage, as well as against pathogens. It also controls the exchange of materials between the organism and its environment, such as absorption, secretion, and sensation. Additionally, epithelial tissue plays a role in producing specialized structures to carry out specific functions, such as hair, nails, and glands.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, which is responsible for voluntary movements; cardiac muscle, found in the heart and responsible for involuntary contractions to pump blood; and smooth muscle, which is found in organs and blood vessels, and is also involuntary.
How does connective tissue differ from other types of tissue?
Connective tissue differs from other types of tissue in the body by its primarily supportive and connecting function. It helps to bind, support, and protect organs and other structures, as well as providing the framework for the body. Connective tissue is characterized by having a matrix with varying amounts of fibers such as collagen and elastin, which give it strength and elasticity. It also contains specialized cells like fibroblasts, adipocytes, and macrophages that contribute to its diverse functions, making connective tissue a distinct type of tissue in the body.
Describe the structure and function of the respiratory membrane.
The respiratory membrane is a structure that consists of a layer of epithelial cells lining the alveoli in the lungs, along with the capillary endothelial cells that surround them. This membrane is very thin, allowing for the efficient exchange of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries. Oxygen diffuses across the respiratory membrane from the alveoli into the blood, while carbon dioxide moves in the opposite direction. This process is essential for supplying oxygen to the body's tissues and removing carbon dioxide, supporting cellular respiration and overall physiological function.
What is the role of the synovial membrane in the joints?
The synovial membrane in the joints secretes synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint, reducing friction between the bones and allowing for smooth movement. Additionally, the synovial membrane helps to nourish and provide oxygen to the cartilage within the joint, promoting joint health and function.
How does the composition and structure of the skin change in different regions of the body?
The composition and structure of the skin vary in different regions of the body due to factors such as thickness, presence of hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. For example, the skin on the palms and soles is thicker with a thicker layer of dead skin cells, while the skin on the face is thinner and has a higher density of hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Additionally, skin on areas with more sun exposure, like the face and arms, may have more melanin to provide protection from UV damage. Overall, the skin adapts to the specific needs and functions of each region of the body.
Explain the difference between simple and stratified epithelial tissue.
Simple epithelial tissue is composed of a single layer of cells, while stratified epithelial tissue is made up of multiple layers of cells. Simple epithelial tissue is mainly involved in absorption, secretion, and filtration, and is found in areas where there is less wear and tear. In contrast, stratified epithelial tissue provides a protective barrier against mechanical, chemical, and biological stress, and is found in areas exposed to more wear and tear, such as the skin and lining of the mouth and esophagus.
What are the three layers of the meninges and their respective functions?
The three layers of the meninges are the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The dura mater, the outermost layer, provides protection and support for the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid mater, the middle layer, helps cushion these structures and contains cerebrospinal fluid. The pia mater, the innermost layer, is a thin membrane that directly covers the brain and spinal cord, providing support and nourishment to these vital structures.
Describe the structure and function of the capillary membrane.
The capillary membrane is a single layer of endothelial cells surrounded by a basement membrane. It is very thin, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the blood and tissues. The structure of the capillary membrane facilitates this exchange by its thinness and permeability to small molecules, while larger molecules and cells are typically unable to pass through. This selective permeability is crucial for maintaining fluid balance and delivering essential nutrients to cells while removing waste products, ensuring proper functioning of tissues and organs in the body.
How does the structure of the alveolar membrane facilitate gas exchange in the lungs?
The alveolar membrane's structure facilitates gas exchange in the lungs through its thinness and high surface area. The membrane is made up of a single layer of thin epithelial cells, allowing for a short diffusion distance for gases to cross. Additionally, the membrane is surrounded by a dense network of capillaries, providing a large surface area for efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the bloodstream. This perfect combination of thinness and large surface area ensures rapid and effective gas exchange in the alveoli.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments