Food Web Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a teacher or a homeschooling parent in search of a comprehensive resource that can help your students grasp the complex concept of food webs? Look no further! In this blog post, we will be sharing an essential tool for teaching and assessing understanding - the Food Web Worksheet Answer Key. With this resource, you can effectively guide your students through the intricacies of how energy flows in an ecosystem and the interdependence of organisms within a community.
Table of Images 👆
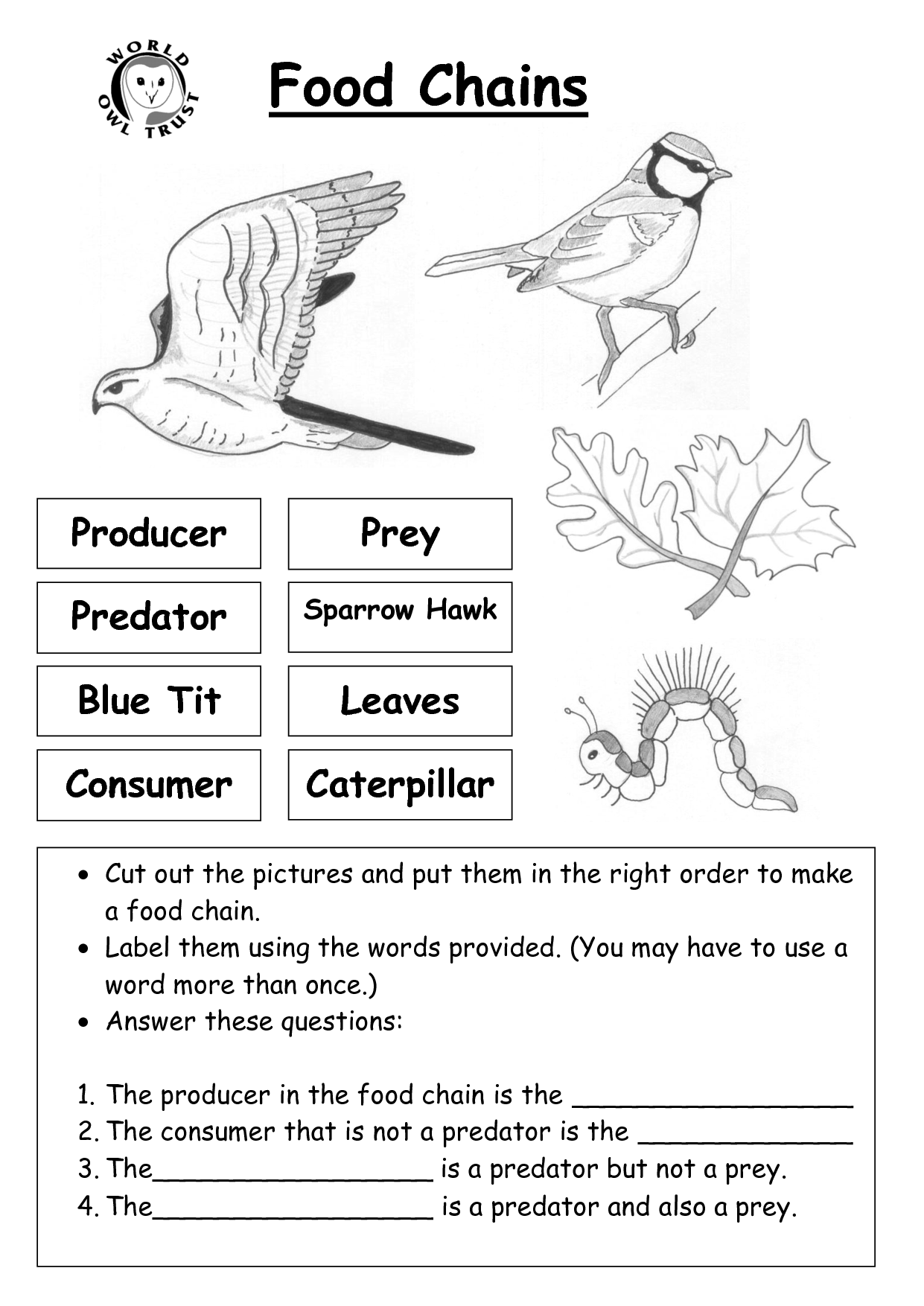
- Food Web Worksheet
- Ecosystem Worksheet Answer Key
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Bogglesworldesl Answers Crosswords Food Chain
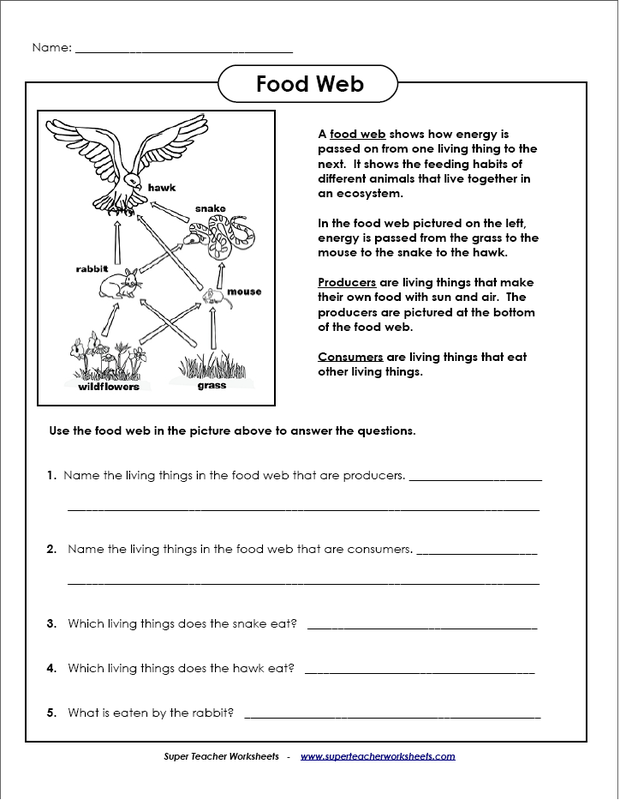
- Owl Food Web Worksheet
- Food Web Worksheet Answers
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Energy Pyramid Worksheet Answer Key
- Producers Consumers and Decomposers Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
What is a food web?
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains that illustrate the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. It shows how different organisms are linked through feeding relationships, with each organism occupying a specific trophic level depending on their role in the consumption and transfer of energy within the ecosystem.
How are food webs different from food chains?
Food webs are more complex than food chains because they show interconnected relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem, depicting how multiple food chains are linked together. In contrast, food chains represent a single linear pathway of energy transfer from one organism to another in a specific ecosystem. Food webs provide a more comprehensive view of the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem by illustrating the multiple feeding relationships that exist between different organisms.
What are primary producers?
Primary producers are organisms, typically plants and some types of bacteria, that produce their own energy through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They form the base of the food chain by converting sunlight or inorganic compounds into organic matter, which is then consumed by higher trophic levels in an ecosystem.
Give an example of a primary producer.
An example of a primary producer is a plant, such as grass, that uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into energy through the process of photosynthesis.
What is a primary consumer?
A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on producers, such as plants or algae, as their primary food source. They are also known as herbivores and form the second trophic level in a food chain, following the producers. Examples of primary consumers include rabbits, deer, and grasshoppers.
Provide an example of a primary consumer.
One example of a primary consumer is a rabbit that feeds on plants such as grass, leaves, and vegetables.
What are secondary consumers?
Secondary consumers are organisms in the food chain that feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores. They are typically carnivores or omnivores and play a crucial role in controlling the population of primary consumers. By feeding on herbivores, secondary consumers help regulate the ecosystem by maintaining a balanced food chain.
Give an example of a secondary consumer.
An example of a secondary consumer is a snake that eats mice.
What role do decomposers play in a food web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food web as they break down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, into simpler nutrients. This decomposition process releases essential nutrients back into the ecosystem, which are then recycled and made available for primary producers to use in photosynthesis. Without decomposers, the nutrients trapped in dead organisms would be locked away, hindering the functioning of the ecosystem and the flow of energy through the food web.
How does an imbalance in a food web affect the entire ecosystem?
An imbalance in a food web can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, if a predator population decreases due to human activities or disease, the prey population may increase rapidly. This can lead to overgrazing of vegetation, which in turn affects other species reliant on that vegetation for food or habitat. Ultimately, the entire ecosystem can become destabilized as populations fluctuate and intricate relationships between species are disrupted, leading to potential extinctions and loss of biodiversity.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments