Foil Method with Variables Worksheets
Are you a math student struggling with understanding the Foil Method? Look no further! We have designed a series of worksheets specifically targeted towards individuals learning how to expand and simplify expressions using variables and the Foil Method.
Table of Images 👆
- Foil Math Worksheets
- Distributive Property Worksheets 7th Grade
- Foil Quadratic Equations Worksheets With
- Foil Method Worksheets with Answers
- Foil Method Worksheet
- Algebra Foil Method Worksheets
- Distance and Displacement Worksheet
- FOIL Method Algebra 1 Worksheets
- FOIL Method Math
- Foil Method Worksheet
- Factoring Polynomials Worksheet
- Math Foil Method Worksheet
- Factoring by Grouping Worksheet
- Factoring Puzzle Worksheet
- Factoring by Grouping Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of using the FOIL method when working with variables in worksheets?
The purpose of using the FOIL method when working with variables in worksheets is to simplify the process of multiplying two binomials together. By following the FOIL acronym (which stands for First, Outer, Inner, Last), you can systematically multiply the terms in the brackets and combine like terms to quickly arrive at a simplified expression. This method is particularly useful for expanding expressions and solving algebraic equations efficiently.
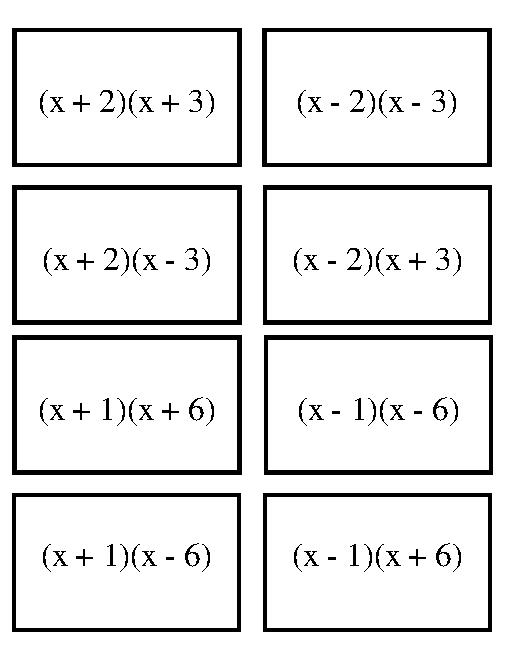
How do you identify the first terms in the FOIL method?
In the FOIL method, the first terms are the terms that come first from each of the two binomials being multiplied together. For example, in the expression (a + b)(c + d), the first terms are "a" from the first binomial (a + b) and "c" from the second binomial (c + d).
What is the significance of the operation used in the FOIL method?
The operation used in the FOIL method, which stands for First, Outer, Inner, Last, is significant because it provides a systematic way to multiply two binomials efficiently and accurately. By following the order of operations outlined in FOIL, we are able to distribute each term of the first binomial to every term of the second binomial, ensuring that all pairs of terms are correctly multiplied together. This method helps simplify the process of multiplying binomials and makes it easier to expand and simplify algebraic expressions.
How do you determine the outer terms in the FOIL method?
To determine the outer terms in the FOIL method, you multiply the first term of the first binomial by the second term of the second binomial and vice versa. The outer terms refer to the terms that are on the outside edges of the two binomials being multiplied. By multiplying these terms, you can find the product that contributes to the overall result of the FOIL method calculation.
What is the role of the inner terms in the FOIL method?
The inner terms in the FOIL method are responsible for multiplying the inside terms of two binomials. This step involves multiplying the second terms of each binomial in a set of two binomials. The inner terms are crucial for accurately calculating the product of these terms and combining them with the results from the other multiplication steps in the FOIL method to ultimately expand and simplify the expression.
How do you correctly distribute the terms in the FOIL method?
To correctly distribute the terms in the FOIL method, you should multiply the First terms of each set of parentheses, then the Outer terms, followed by the Inner terms, and finally the Last terms. This systematic approach ensures that all terms are properly multiplied together, resulting in the correct product of the given expressions.
What is the importance of combining like terms in the FOIL method?
Combining like terms in the FOIL method is important because it allows for a more simplified and organized expression. By combining like terms, you can gather similar terms together and make it easier to identify patterns, simplify calculations, and ultimately reach a final solution more efficiently. This process helps in reducing errors and confusion, making the FOIL method more manageable and effective.
What should be done if there are any remaining exponents after using the FOIL method?
If there are any remaining exponents after using the FOIL method, you should further simplify the expression by combining like terms and following the rules of exponents. This may involve multiplying coefficients, adding or subtracting exponents, and simplifying terms until the expression is in its simplest form.
Can the FOIL method be applied to equations with more than two variables?
The FOIL method is typically used for multiplying binomials, which have two terms each. When dealing with equations with more than two variables, such as trinomials or polynomials, you can apply the FOIL method by breaking down the multiplication into smaller steps. For example, when multiplying two trinomials, you can multiply each term in the first trinomial by each term in the second trinomial, and then combine like terms. The process is more complex but you can still use the principles of FOIL to simplify the multiplication.
How can the FOIL method help simplify expressions and solve equations involving variables?
The FOIL method, which stands for First, Outer, Inner, Last, is a technique used to multiply two binomials. By following the sequence of multiplying each term in the first binomial by each term in the second binomial, you can simplify expressions and solve equations involving variables. This method helps organize the multiplication process and ensures that all terms are accounted for, ultimately leading to a simplified expression or solution in algebraic equations.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






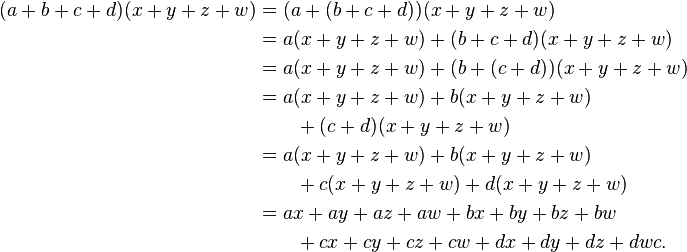
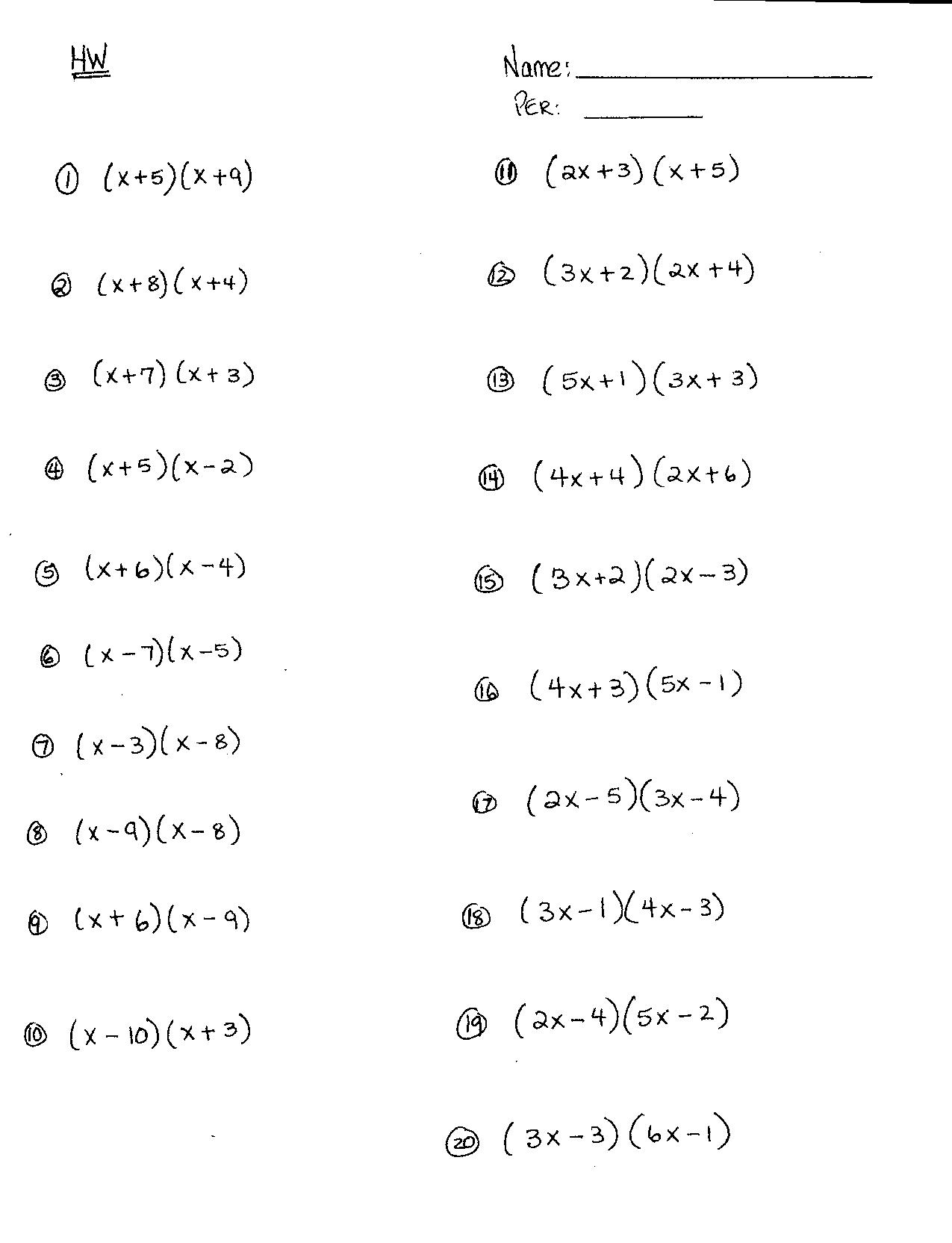





















Comments