First Grade Rocks and Minerals Worksheets
Are you a first-grade teacher or parent looking to introduce your little ones to the fascinating world of rocks and minerals? Well, you're in luck! We have curated a collection of engaging and educational worksheets that will help you teach your kids all about these natural wonders.
Table of Images 👆
- Types of Rocks Worksheets Free
- Science Rocks and Minerals Worksheet
- Science Rocks and Minerals Worksheet
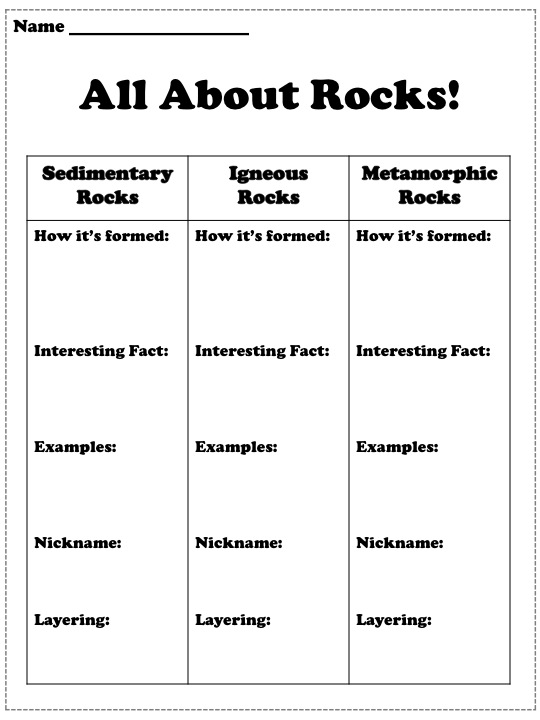
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheets 3rd Grade
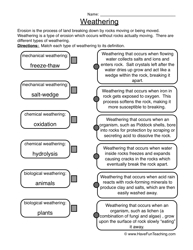
- Weathering and Erosion Worksheets 4th Grade
- 3 Types of Rocks Worksheets for Kids
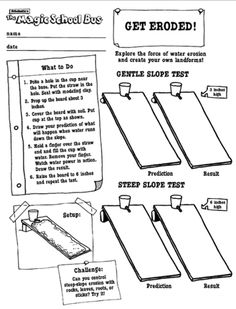
- Magic School Bus Weathering and Erosion
- Element Word Search Answer Key
- Soil Worksheets Grade 2
- Natural Disaster Worksheets
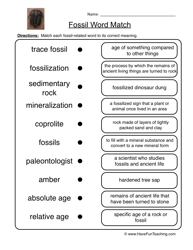
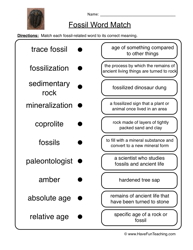
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
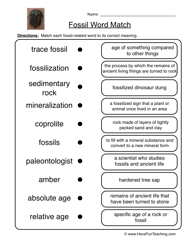
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
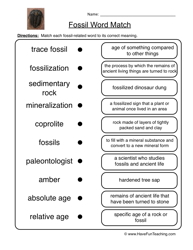
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
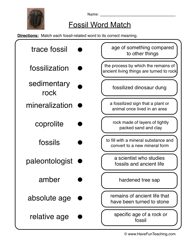
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
More 1st Grade Worksheets
First Grade Reading Comprehension WorksheetsFirst Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Telling Time Worksheets for First Grade
Writing Worksheets for 1st Graders
Easy 1st Grade Math Worksheets
Math Worksheets Subtraction 1st Grade
For First Grade Addition Worksheets
For First Grade Phonics Worksheets
Plural Nouns Worksheets 1st Grade
Irregular Plurals Worksheets 1st Grade
What is a mineral?
A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic solid substance with a predictable chemical composition and a crystalline structure formed through natural geological processes.
How are rocks formed?
Rocks are formed through a process called the rock cycle, which involves various geological processes such as weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction, melting, and cooling. It begins with the solidification of molten rock (magma or lava) to form igneous rocks, which can then be weathered and eroded into sediment. This sediment can then be compacted and cemented together to form sedimentary rocks. In some cases, these rocks may undergo heat and pressure deep within the Earth, causing them to change into metamorphic rocks. The cycle continues as rocks are recycled and transformed over time due to geological forces.
What are the characteristics of igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks are formed through the solidification and cooling of molten magma. They typically have a coarse-grained structure due to slow cooling below the Earth's surface or a fine-grained structure from rapid cooling on the surface. Igneous rocks often exhibit interlocking crystals and can contain minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica. They are typically hard and dense, with a wide range of colors, and may contain gas bubbles or vesicles. Igneous rocks can be further classified based on their mineral composition and texture into different types such as granite, basalt, and obsidian.
What is the difference between sedimentary and metamorphic rocks?
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments over time, while metamorphic rocks are formed from the transformation of existing rocks due to high heat and pressure within the Earth's crust. Sedimentary rocks are typically layered and contain fossils and other sedimentary structures, while metamorphic rocks have distinct foliated or non-foliated textures resulting from the recrystallization of minerals.
How are minerals and rocks used in everyday life?
Minerals and rocks are used in everyday life in a variety of ways. They are essential components of construction materials, such as concrete, asphalt, and bricks. They are also used in manufacturing products like electronics, jewelry, cosmetics, and household items. Additionally, minerals and rocks are used in agriculture for fertilizers and soil amendments. Minerals are also important in health as they are used in supplements and pharmaceuticals. Overall, minerals and rocks play a crucial role in our daily lives by providing the raw materials for many of the products and infrastructure we rely on.
What are the three main types of rocks?
The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and cementation of sediments, and metamorphic rocks are formed from the alteration of existing rocks due to high heat and pressure.
How are fossils formed in sedimentary rocks?
Fossils are formed in sedimentary rocks through a process called fossilization. When an organism dies, its remains are typically buried by sediments such as mud, sand, or clay. Over time, these sediments accumulate on top of the remains, creating layers. The weight and pressure from these layers cause the remains to undergo mineralization, where the organic material is replaced by minerals, turning it into a fossil. The slow process of sedimentation and mineralization preserves the structure and shape of the organism, allowing us to study and learn about ancient life forms.
What are the physical properties of minerals?
Physical properties of minerals include color, luster (appearance of a mineral's surface in reflected light), hardness (resistance to scratching), cleavage (tendency to break along flat surfaces), fracture (ability to break irregularly), specific gravity (ratio of a mineral's weight to the weight of an equal volume of water), and crystal form (shape of a mineral's internal arrangement of atoms). Other physical properties may include streak (color of a mineral in powdered form), transparency, and magnetism.
How are rocks and minerals important in Earth's processes?
Rocks and minerals are important in Earth's processes because they make up the building blocks of the planet's crust, which is constantly being reshaped through processes like weathering, erosion, and plate tectonics. Rocks and minerals also play a critical role in the cycling of nutrients and elements in the Earth's ecosystems, providing essential resources for plants, animals, and humans. Additionally, minerals have economic value as sources of precious metals, gemstones, and other resources essential for industries such as construction, technology, and manufacturing.
How can we identify different types of rocks and minerals?
To identify different types of rocks and minerals, one can use various methods such as observing physical characteristics like color, texture, and luster, conducting hardness tests, performing streak tests to determine the color of the mineral's powder, assessing crystal shape and structure, using a magnifying glass or a microscope to examine details, and employing chemical tests like acid reactions or specific reagents for mineral identification. Additionally, utilizing tools like a geologist's hammer, a scratch plate, a magnet, or a UV light can aid in the identification process.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments