Fiber Food Worksheet
Are you searching for a helpful tool to teach your children about the importance of fiber in their diet? Look no further than the Fiber Food Worksheet. This engaging resource is designed to educate and entertain kids between the ages of 7 and 10 about the various sources of fiber and its benefits for their health. By using this worksheet, parents and teachers can introduce this essential nutrient in a fun and interactive way, encouraging children to make healthy food choices that will support their overall well-being.
Table of Images 👆
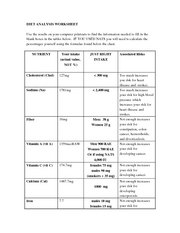
- Diet Analysis Worksheet
- Measuring Cups and Spoons Worksheets
- Diverticulitis Food List PDF
- Rainbow Food Chart for Kids
- Energy Crossword Puzzle
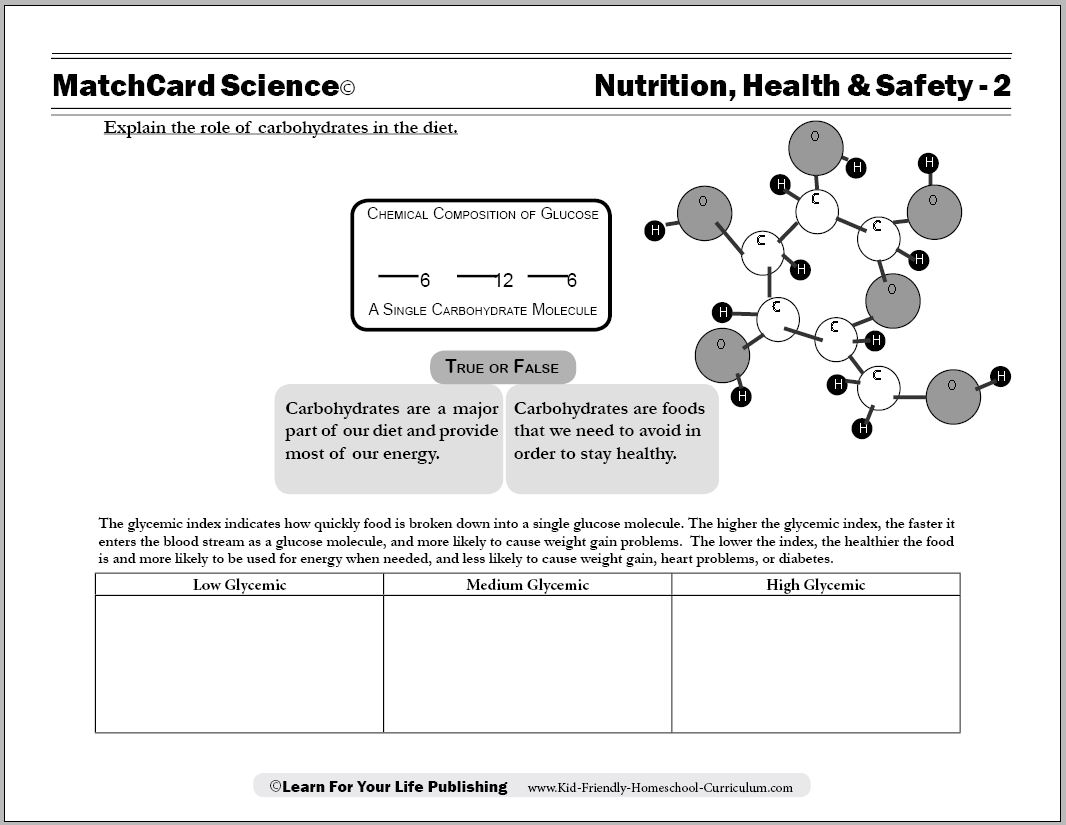
- Carbohydrate Worksheet and Answers
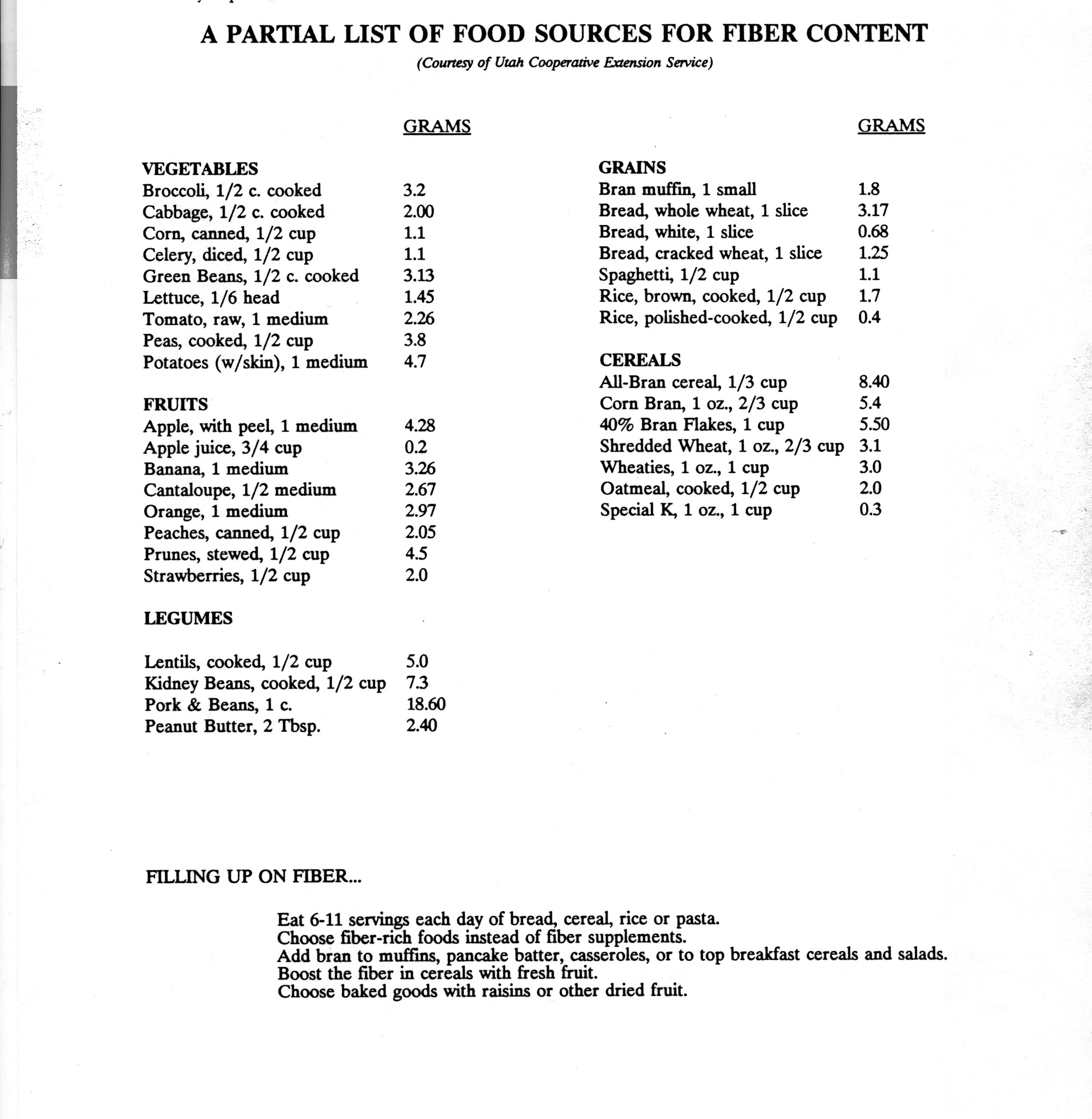
- High-Fiber Foods List
- Vitamins and Minerals Worksheet
- Printable Food and Nutrition Worksheets
- Measuring Cups and Spoons Worksheets
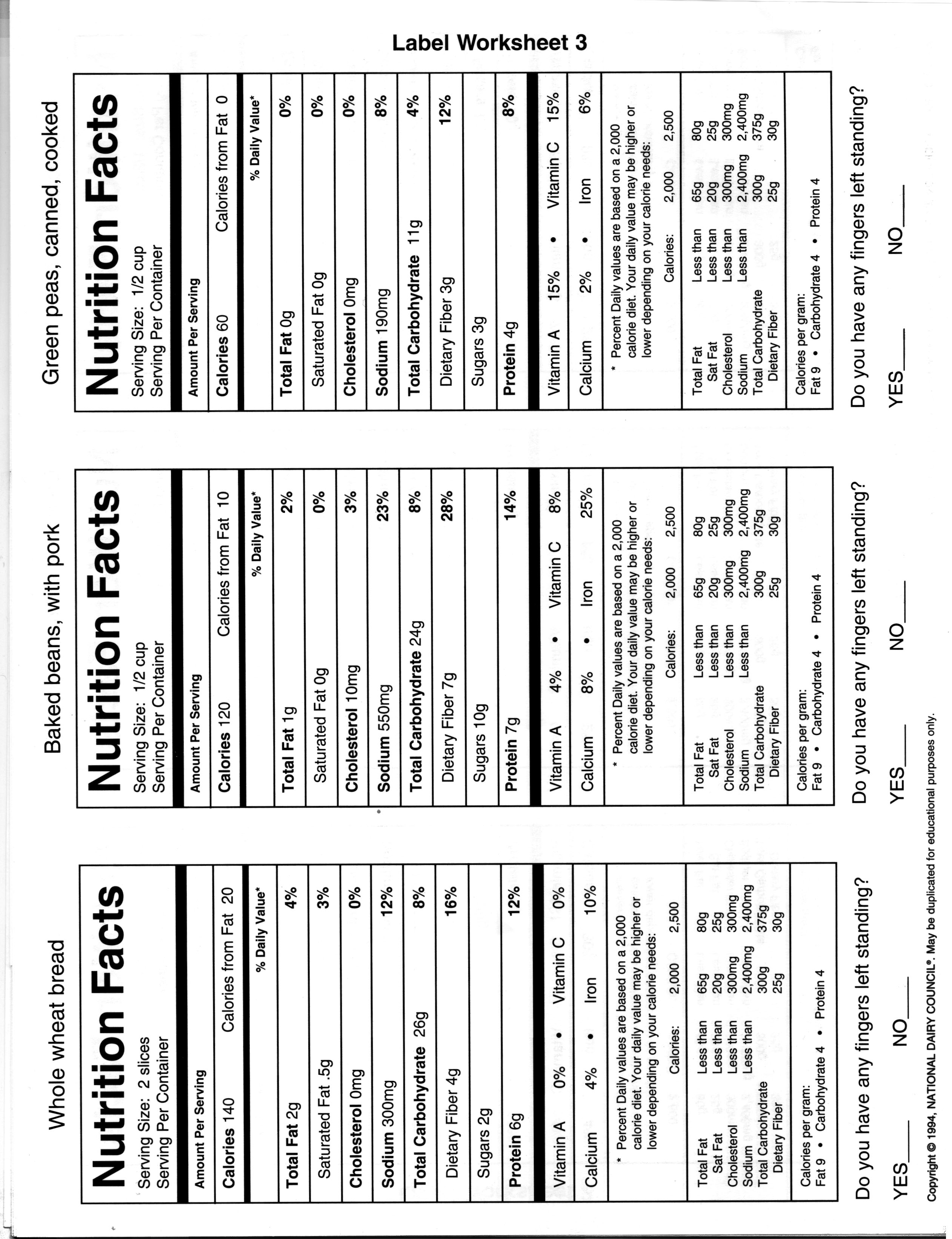
- Food Label Worksheet
- Carbohydrate Nutrition Worksheets
- Measuring Cups and Spoons Worksheets
- Food Nutrition Labels Worksheet
- Food Label Worksheet
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
What is fiber?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate found in plant-based foods that the body cannot digest or absorb. It passes through the digestive system largely intact, adding bulk to stools and helping to promote regular bowel movements. Additionally, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, lowering cholesterol, and assisting with weight management. It can be found in foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
What are the different types of fiber?
There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble fiber, which dissolves in water and can help lower cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels, and insoluble fiber, which does not dissolve in water and promotes healthy digestion by adding bulk to the stool. Both types of fiber are important for overall health and should be included in a balanced diet.
Why is fiber important for a healthy diet?
Fiber is important for a healthy diet because it aids in digestion, promotes regularity, and helps prevent constipation. It also helps control blood sugar levels, lowers cholesterol, and can contribute to weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness. Additionally, fiber can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome and reduce the risk of developing certain chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and some types of cancer.
What are some examples of high-fiber foods?
Some examples of high-fiber foods include fruits like apples, berries, and pears, vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and kale, whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats, legumes like lentils, black beans, and chickpeas, as well as nuts and seeds such as almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. These foods can help promote digestive health, regulate blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight.
How does fiber help with digestion?
Fiber helps with digestion by adding bulk to the stools, which helps to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation. It also promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which aids in digestion and nutrient absorption. Additionally, fiber can help to regulate blood sugar levels and lower cholesterol, contributing to overall digestive health.
What are the health benefits of consuming fiber?
Consuming fiber has numerous health benefits, including promoting a healthy digestive system by preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Fiber also helps to lower cholesterol levels, control blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of developing various chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, fiber can aid in weight management by increasing feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake.
Can fiber help with weight management? How?
Yes, fiber can help with weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness and aiding in digestion. Foods high in fiber take longer to digest, which can help control hunger and prevent overeating. Additionally, fiber-rich foods often have fewer calories than processed or high-fat foods, making them a good choice for those trying to manage their weight. Fiber can also help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce cholesterol, and improve overall gut health, all of which can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight.
How much fiber should one consume in a day?
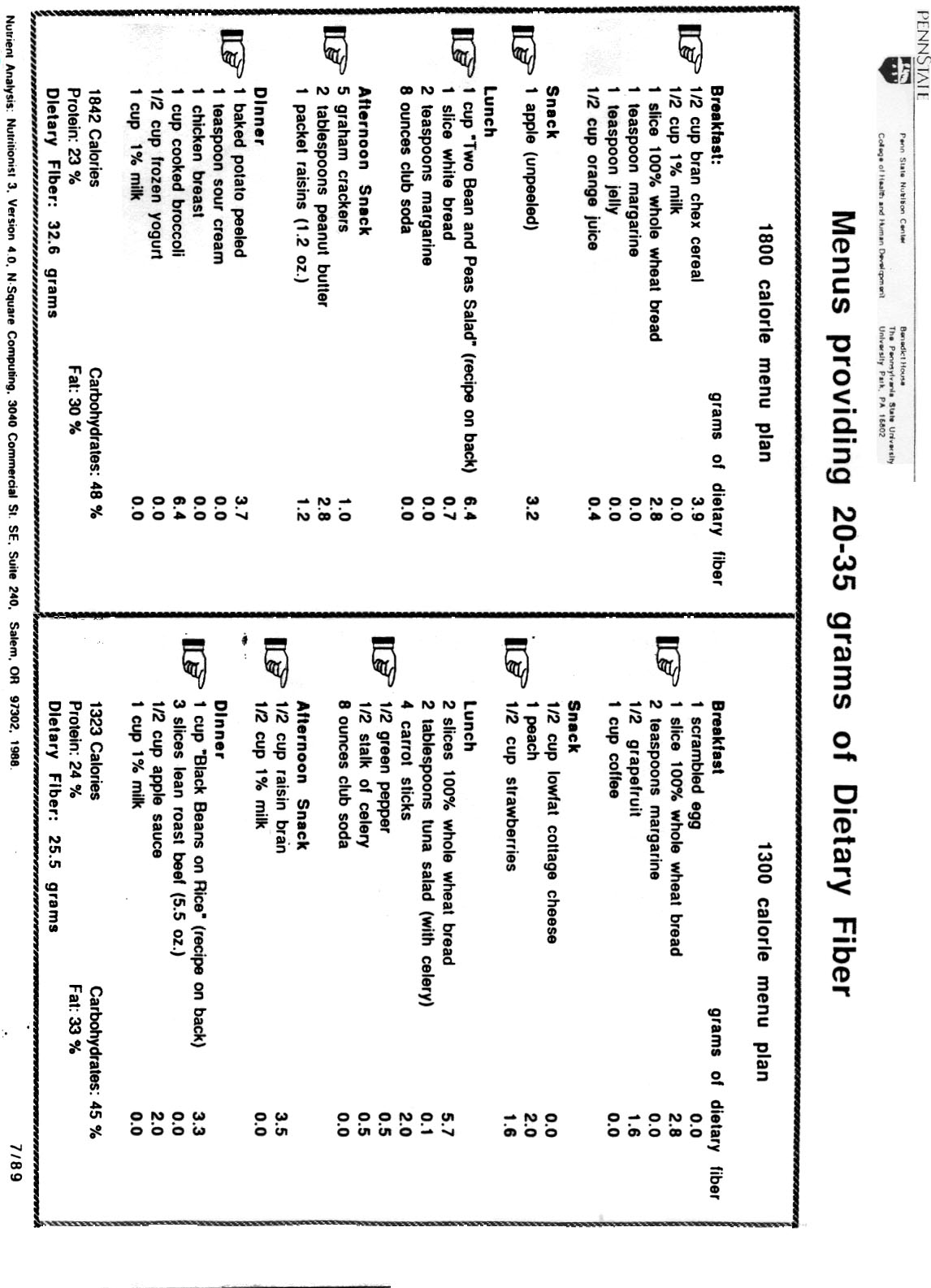
It is generally recommended to consume around 25-30 grams of fiber per day for adults. This can help promote healthy digestion, support weight management, and reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases. However, individual fiber needs may vary based on factors such as age, gender, and level of physical activity, so it's best to consult with a healthcare provider or a dietitian to determine the most appropriate fiber intake for your specific needs.
Are there any potential side effects of consuming too much fiber?
Consuming too much fiber can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. It can also interfere with the absorption of certain minerals and medications. Additionally, excessive fiber intake without enough fluids can cause dehydration. It is important to consume fiber in moderation and gradually increase intake to avoid these potential side effects.
How can you increase your daily fiber intake?
You can increase your daily fiber intake by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds into your meals and snacks. Aim to include high-fiber foods such as berries, broccoli, oats, quinoa, lentils, and chia seeds in your diet. Additionally, choosing whole grains over refined grains, consuming plenty of water, and gradually increasing fiber intake to allow your body to adjust can also help you reach your daily fiber goals.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments