Exponents and Polynomial Worksheets
Exponents and polynomial worksheets are effective tools for reinforcing mathematical concepts and skills for middle school and high school students. These worksheets focus on the entity of exponents and polynomials, providing students with opportunities to practice solving equations, simplifying expressions, and mastering various operations involving exponents and polynomials.
Table of Images 👆
- Algebra 1 Factoring Polynomials Worksheet with Answers
- Adding Polynomials Worksheet
- Adding Polynomials Worksheet
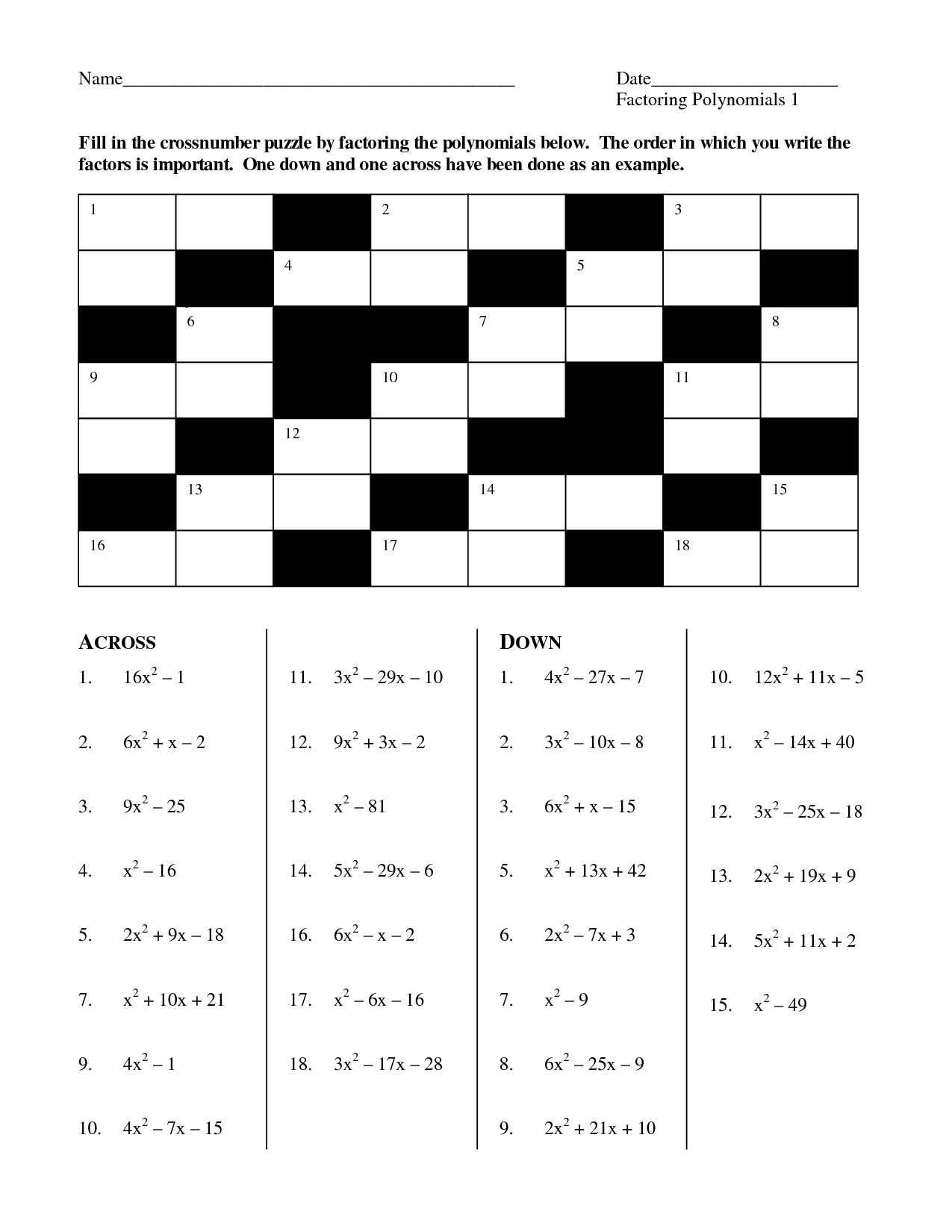
- Factoring Polynomials Worksheet
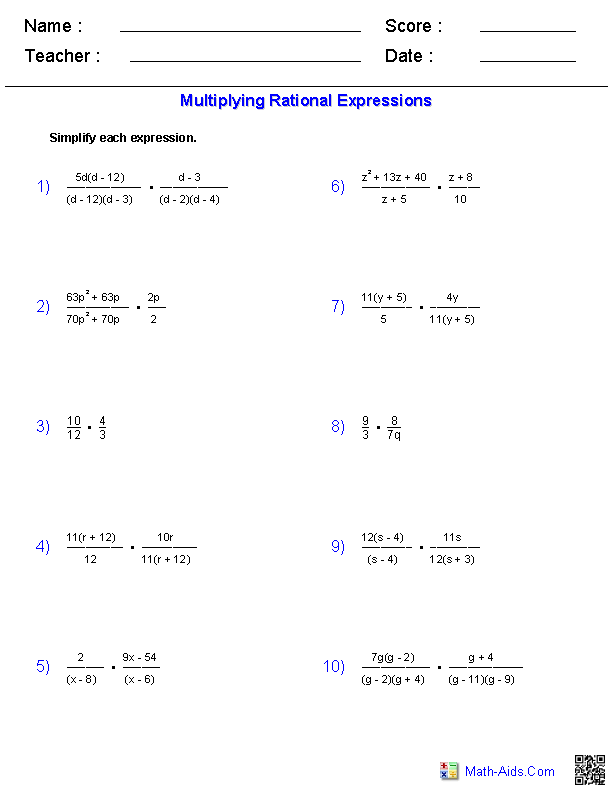
- Polynomials and Factoring Practice Worksheet Answers
- Multiplication of Exponents and Division Worksheets
- Algebra 1 Worksheets
- Algebra 1 Multiplying Polynomials Worksheet
- Algebra Functions Worksheets
- Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
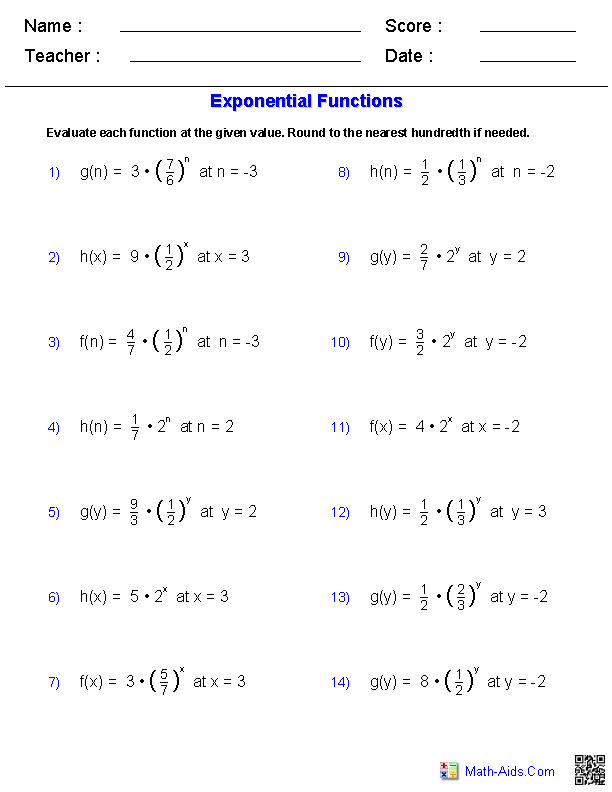
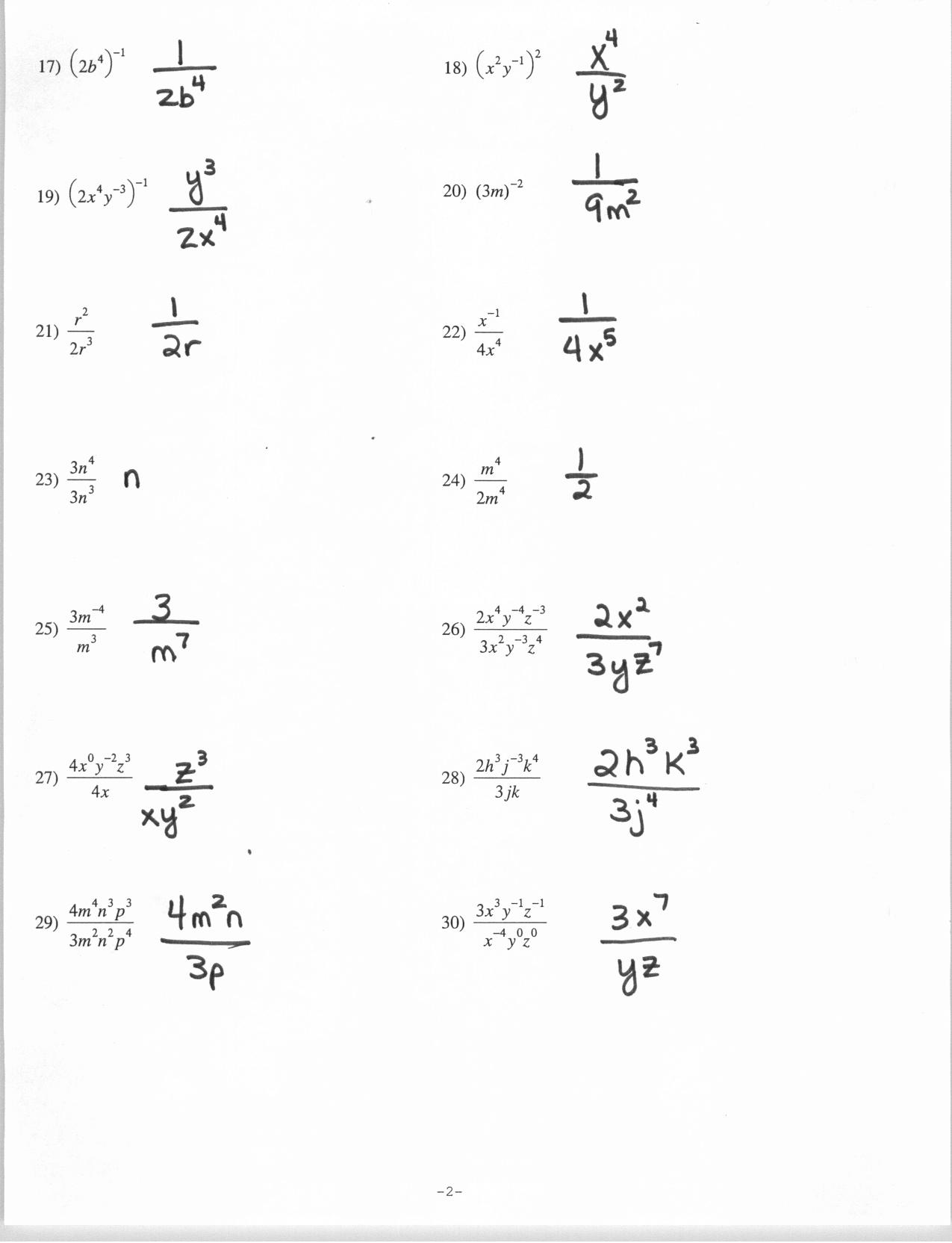
- Exponents Worksheets with Answers
- Rational Numbers as Exponents Worksheets
- Crossword Puzzle Fraction Worksheets
- Algebra 2 Factoring Review Worksheet Answers
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Scientific Notation
- 6th Grade Long Division Worksheets
- Algebra Exponent Rules Worksheet
- Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is an exponent?
An exponent is a numeral that represents the power to which a base number is raised. It indicates how many times the base number is multiplied by itself. For example, in 2^3, the base number is 2 and the exponent is 3, meaning 2 is multiplied by itself 3 times.
How do you calculate the value of a number raised to an exponent?
To calculate the value of a number raised to an exponent, you simply raise the number to the power of the exponent. This is done by multiplying the number by itself the number of times specified by the exponent. For example, if you have 2^3, you would multiply 2 by itself three times (2 * 2 * 2), resulting in 8.
What is the difference between a positive and negative exponent?
A positive exponent indicates that the base number is multiplied by itself a certain number of times, while a negative exponent indicates that the base number is divided by itself a certain number of times. In other words, a positive exponent represents repeated multiplication, while a negative exponent represents repeated division.
How do you simplify expressions with exponents?
To simplify expressions with exponents, follow the rules of exponents. This includes combining like terms, multiplying coefficients, and applying the properties of exponents such as product rule (adding the exponents when multiplying like bases), quotient rule (subtracting the exponents when dividing like bases), and power rule (raising a base to another exponent). Ensure to simplify each term in the expression and consolidate where possible to simplify the overall expression with exponents.
How do you add or subtract expressions with exponents?
To add or subtract expressions with exponents, you need to ensure that the bases (the numbers being raised to a power) are the same. If the bases are the same, you can simply add or subtract the coefficients in front of the bases while keeping the base and exponent the same. If the bases are not the same, you cannot directly add or subtract them. In that case, you may need to simplify each expression individually first, then apply the addition or subtraction. Remember to follow the rules of exponents, such as adding coefficients when the bases are the same and keeping the base and exponent unchanged.
How do you multiply terms with exponents?
To multiply terms with exponents, you add the exponents if the bases are the same. For example, if you have x^2 multiplied by x^3, you would add the exponents to get x^5. If the bases are different, you simply multiply the terms together without changing the exponents. Keep in mind these rules when multiplying terms with exponents.
How do you divide terms with exponents?
When dividing terms with exponents, subtract the exponent of the divisor from the exponent of the dividend to simplify the expression. For example, when dividing \(x^4\) by \(x^2\), subtract the exponent 2 from 4 to get \(x^{4-2} = x^2\). Remember to divide the coefficients separately if they are present.
What is a polynomial?
A polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of variables, coefficients, and exponents, combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The variables can only have non-negative integer exponents and the coefficients can be any real number. Polynomials are commonly used in algebra to represent functions and solve equations.
How do you classify polynomials by degree?
Polynomials are classified by degree based on the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. For example, a polynomial with a highest power of 1 is classified as a linear polynomial, degree 2 is a quadratic polynomial, degree 3 is a cubic polynomial, and so on. The degree of the polynomial represents the complexity and number of terms in the expression.
How do you perform operations on polynomials?
To perform operations on polynomials, you can add, subtract, multiply, or divide them. When adding or subtracting polynomials, combine like terms by adding or subtracting coefficients of the same variables. When multiplying polynomials, distribute each term of the first polynomial with each term of the second polynomial and then simplify by combining like terms. Division by a polynomial is more complex and involves long division or synthetic division techniques. Always follow the rules of arithmetic and algebra when performing operations on polynomials.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments