Evolution Worksheets Biology
If you're a biology student or teacher looking for specialized resources to enhance your understanding or teaching of evolution, look no further. In this blog post, we will explore the world of evolution worksheets designed specifically for this subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Evolution Concept Map Worksheet
- Plant Kingdom Worksheet
- Holt Biology Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Answer Key
- Blank Neuron Worksheet Answers
- Darwins Finches Galapagos Islands
- Gregor Johann Mendel
- Draw Graffiti Bubble Letters
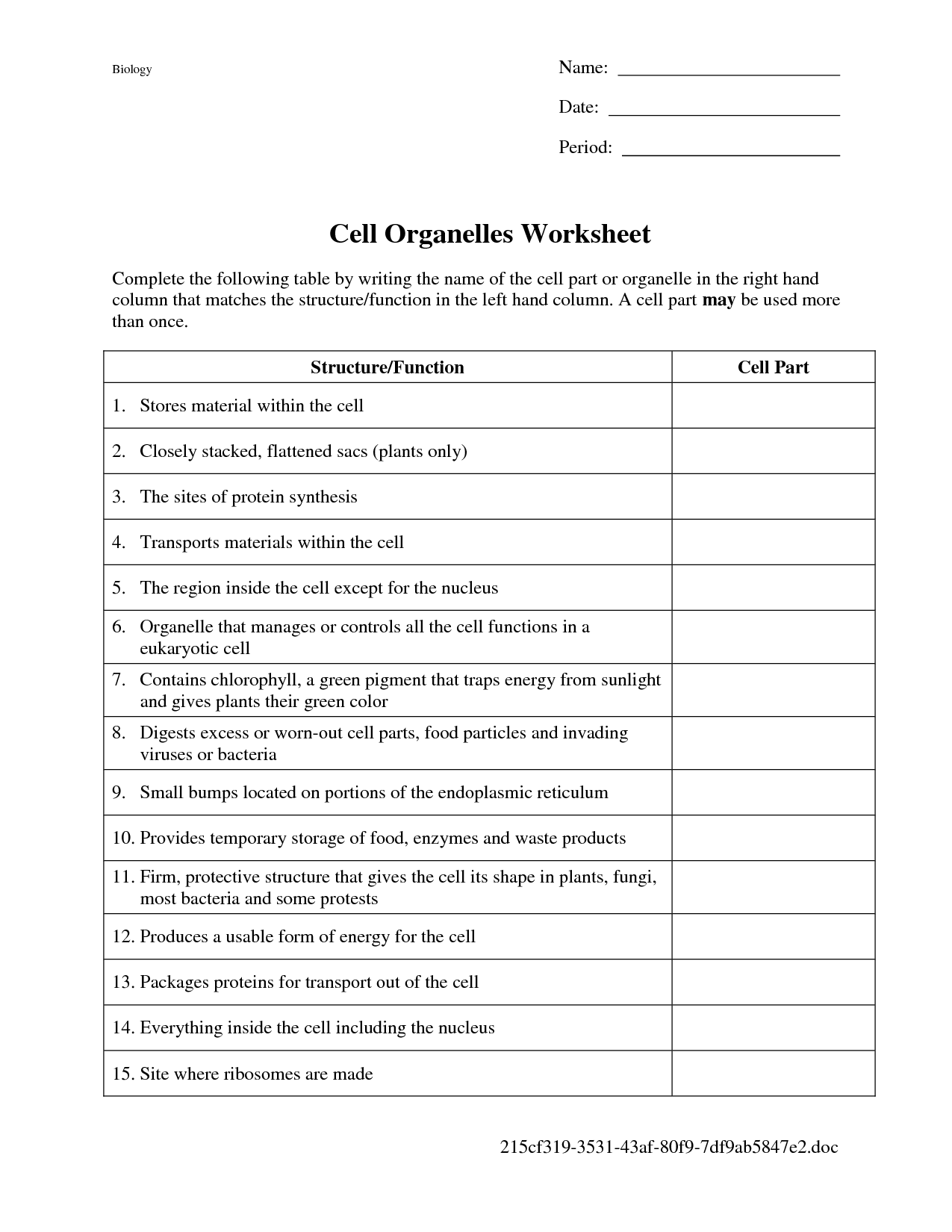
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Essay
- Plant Cell Not Labeled
More Biology Worksheets
Free Printable Biology WorksheetsCollege Biology Worksheets
7th Grade Biology Worksheets
Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
Karyotype Worksheet Answers Biology
What is evolution?
Evolution is a scientific theory that explains how species change over time through the process of natural selection. It suggests that living organisms have evolved from a common ancestor through gradual changes in their genetic makeup and physical traits, allowing them to adapt to their environment and increase their chances of survival and reproduction. This theory has been supported by a wide range of evidence from various fields of science, including genetics, paleontology, and comparative anatomy.
How does natural selection contribute to evolution?
Natural selection contributes to evolution by favoring the survival and reproduction of individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment. Over time, this process leads to the accumulation of genetic changes in a population, resulting in the emergence of new species and the diversity of life forms we see today. By acting as a mechanism for adaptation and change, natural selection plays a critical role in driving the evolutionary process.
What is the role of genetic variation in evolution?
Genetic variation is essential for evolution as it provides the raw material upon which natural selection acts. It introduces new traits and characteristics into a population, allowing individuals with advantageous variations to survive and reproduce more successfully, leading to changes in the gene pool over time. This process ultimately drives the evolution of species, enabling them to adapt to changing environments and increasing their chances of survival and reproduction.
How does genetic drift affect evolution?
Genetic drift refers to random changes in gene frequencies in a population over time, which can have a significant impact on evolution. It can lead to the loss of genetic diversity within a population, potentially reducing the overall fitness of a species. Genetic drift is particularly significant in small populations, where chance events can have a disproportionate effect on gene frequencies. Over generations, genetic drift can result in the fixation of certain alleles and the loss of others, ultimately shaping the genetic makeup of a population and influencing its evolutionary trajectory.
What are the different types of reproductive isolation mechanisms?
There are several types of reproductive isolation mechanisms that prevent mating or successful reproduction between different species or populations, including geographic isolation, temporal isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, and gametic isolation. Geographic isolation occurs when populations are physically separated by a barrier, while temporal isolation involves differences in timing of reproduction. Behavioral isolation occurs when differences in behaviors or signals prevent mating, mechanical isolation involves physical barriers preventing mating or fertilization, and gametic isolation is when the gametes of different species are incompatible. These mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining species boundaries and promoting speciation.
How does speciation occur?
Speciation occurs through a gradual process of reproductive isolation, where populations of a species become genetically distinct due to factors such as geographic separation, natural selection, genetic drift, or mutations. Over time, these barriers prevent interbreeding between populations, leading to the evolution of new species with unique characteristics and adaptations.
What is the difference between convergent and divergent evolution?
Convergent evolution occurs when different species independently evolve similar traits or characteristics due to similar environmental pressures, resulting in analogous structures. Divergent evolution, on the other hand, happens when two or more related species evolve different traits or characteristics over time due to different environmental pressures or adaptive needs, leading to distinct features or specialized functions.
How do fossils provide evidence for evolution?
Fossils provide evidence for evolution by showing the gradual changes in organisms over time. By studying the physical characteristics of fossilized organisms, scientists can trace the development of species and identify transitional forms that demonstrate the process of evolution. Fossils also provide important information about the age of different species and how they are related to one another, helping to build a comprehensive understanding of the history of life on Earth and how species have evolved and adapted to changing environments over millions of years.
What is the significance of transitional fossils in understanding evolutionary relationships?
Transitional fossils play a crucial role in understanding evolutionary relationships by providing tangible evidence of how species have evolved over time. These fossils exhibit characteristics that are intermediate between older and younger species, showcasing gradual changes and helping to bridge gaps in the evolutionary timeline. By studying transitional fossils, scientists can trace the paths of evolutionary change and infer relationships between different species, ultimately gaining valuable insights into the history and diversity of life on Earth.
How does the fossil record support the idea of common ancestry?
The fossil record supports the idea of common ancestry by showing that species found in older rock layers are less similar to present-day species, while species found in more recent rock layers share more similarities with present-day species. This gradual change in species over time provides evidence for the evolution of organisms from common ancestors. Additionally, the presence of transitional fossils, which exhibit traits of both ancestral and descendant species, further supports the concept of common ancestry by demonstrating the gradual changes that have occurred over millions of years.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments