Energy Phase Change Worksheet
Are you a science teacher or a parent looking for a comprehensive worksheet on energy phase change? Look no further! This blog post will discuss an informative and engaging worksheet that focuses on the entity and subject of energy phase change. Whether you are teaching a class or guiding your child through the concept, this worksheet will provide the perfect opportunity for learning and understanding.
Table of Images 👆
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
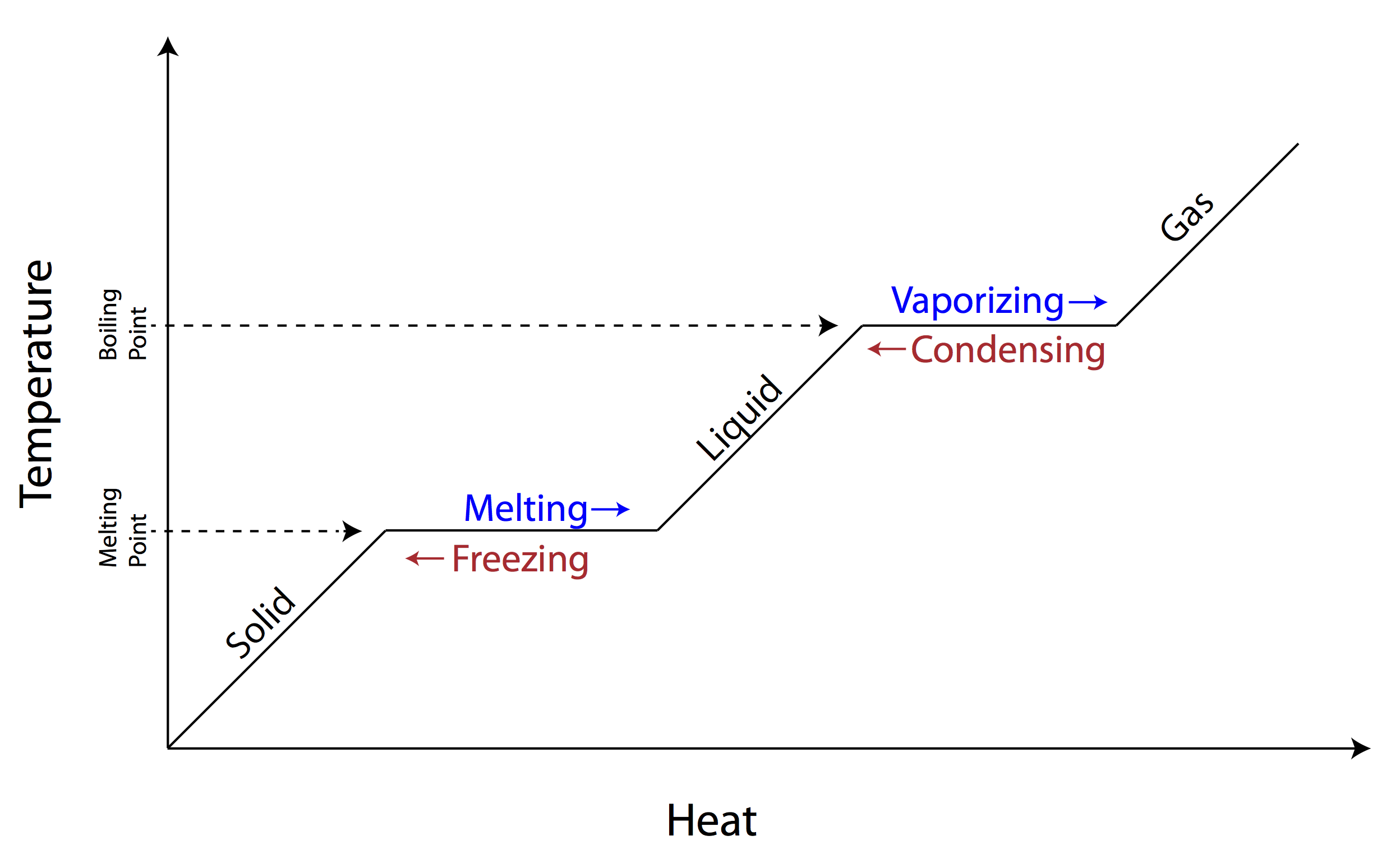
What is a phase change?
A phase change refers to the physical transformation of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as from solid to liquid (melting), liquid to gas (vaporization), or vice versa. These changes occur due to variations in temperature and pressure, causing the substance's particles to rearrange and move differently.
What is the difference between latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization?
Latent heat of fusion is the heat required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point, while latent heat of vaporization is the heat required to change a substance from liquid to gas at its boiling point. In other words, latent heat of fusion is the energy needed to break the bonds holding particles together in a solid, while latent heat of vaporization is the energy needed to overcome the intermolecular forces keeping particles in a liquid state.
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is the process by which a liquid, such as water, converts into a gas or vapor state due to the heat and energy from its surroundings. This transformation occurs when the molecules at the surface of the liquid gain enough kinetic energy to break free from the cohesive forces holding them in the liquid state, resulting in the molecules escaping into the surrounding air as vapor.
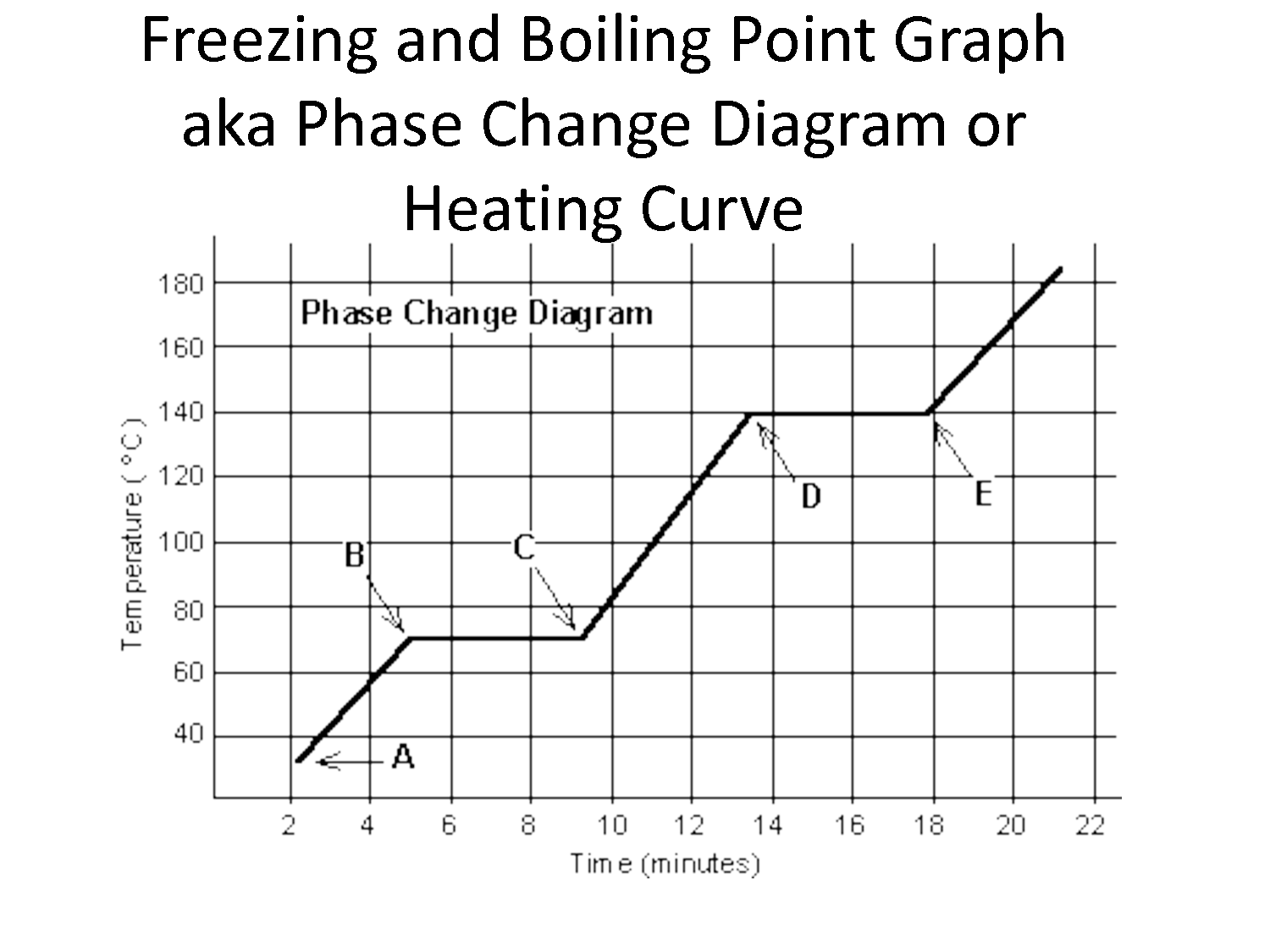
What happens to the temperature during a phase change?
During a phase change, such as from a solid to a liquid or a liquid to a gas, the temperature remains constant despite adding heat to the system. This is because the energy being added is being used to break intermolecular forces rather than increase the kinetic energy of the particles, resulting in a temporary plateau on the temperature-time graph known as a plateau.
What is the boiling point of water?
The boiling point of water is 100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit at standard atmospheric pressure.
What is sublimation?
Sublimation is a process where a substance transitions directly from a solid to a gas without passing through the liquid phase. This occurs when the substance's vapor pressure exceeds its atmospheric pressure at a certain temperature. Examples of sublimation include dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) turning into carbon dioxide gas without melting, and mothballs gradually disappearing as they release vapors into the air.
What is the process of condensation?
Condensation is the process where water vapor in the air cools and changes into liquid water, forming clouds or droplets. When the air cools, it loses its ability to hold water vapor, causing the vapor to condense and eventually form clouds or droplets on surfaces. This process is essential for the water cycle and plays a crucial role in the formation of precipitation.
What is the freezing point of water?
The freezing point of water is 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit).
What is the relationship between pressure and boiling point?
The relationship between pressure and boiling point is direct. As pressure increases, the boiling point of a substance also increases. This is because at higher pressures, it requires more energy for the particles to overcome the external pressure and change from liquid to gas phase. Conversely, at lower pressures, the boiling point decreases because less pressure is needed for the particles to escape into the gas phase. This relationship is defined by the Clausius-Clapeyron equation, which shows how pressure influences the temperature at which a substance changes its phase from liquid to gas.
How does the addition of heat affect a substance during a phase change?
When heat is added to a substance during a phase change, such as melting or boiling, the temperature of the substance remains constant until all of the substance has completed the phase change. This is because the added heat is being used to break the intermolecular forces holding the particles together, rather than increasing the kinetic energy of the particles and raising the temperature. Once the phase change is complete and all of the substance has converted to the new phase, the temperature will start to rise again as the added heat begins to increase the kinetic energy of the particles.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments