Energy in a Cell Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are a valuable tool for students and educators alike, providing a structured format for learning and reinforcing subject matter. When it comes to understanding the intricate workings of energy in a cell, having access to accurate and reliable answers to worksheet questions can be hugely beneficial. Whether you're a student looking to strengthen your understanding or a teacher in need of comprehensive resources, finding the right energy in a cell worksheet answers can make all the difference in your learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
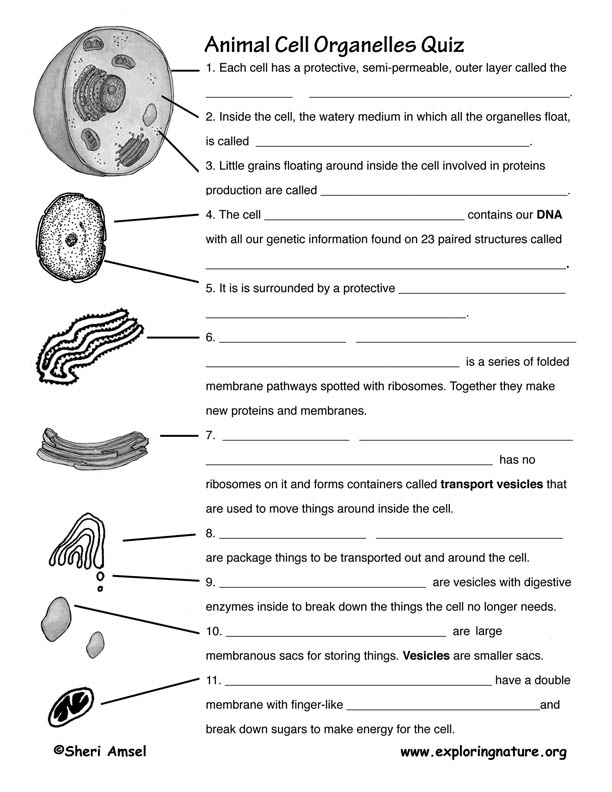
- Cell Organelle Quiz Worksheet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis and Genetics Answer Key Test
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis Worksheets with Answer Key
- POGIL Biology Answer Key
- Guided Reading and Study Workbook Chapter 2
- Cellular Respiration Flow Chart
- Significant Figures Worksheet and Answer Key
- Glencoe Chemistry Chapter Assessment Answers
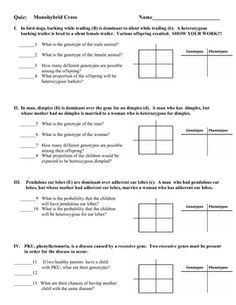
- Monohybrid Cross Practice Problems
- Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7 Review
- Health Worksheets for Middle School Students
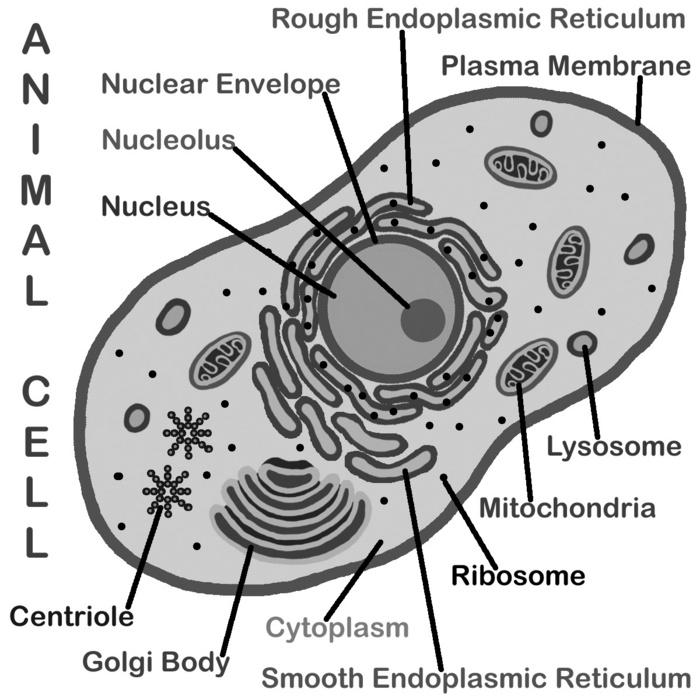
- Plant Cell Coloring Key Labeled
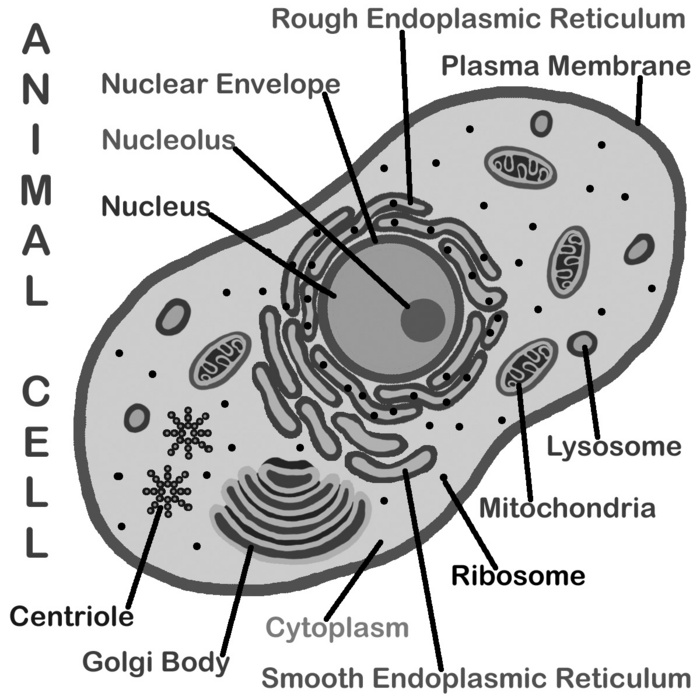
- Plant Cell Coloring Key Labeled
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is cellular energy?
Cellular energy is the energy produced and used by cells to carry out various cellular processes, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. It is primarily generated through the process of cellular respiration, which involves the breakdown of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy currency of cells. Cellular energy is essential for sustaining life and powering the myriad of biochemical reactions that occur within cells.
Cellular energy refers to the energy produced and used by cells to carry out various processes and functions.
Cellular energy is the energy produced and used by cells to fuel their activities and functions, including growth, maintenance, division, communication, and movement. This energy is primarily generated through the process of cellular respiration, where organic molecules are broken down to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy currency of cells. ATP is then utilized by cells to drive essential biochemical reactions and processes that sustain life.
What is the primary molecule used for cellular energy?
The primary molecule used for cellular energy is adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. It is the main form of energy currency in cells and is produced through processes such as cellular respiration and photosynthesis. ATP provides the necessary energy for various cellular activities, including metabolism, muscle contraction, and active transport.
The primary molecule used for cellular energy is adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Yes, the primary molecule used for cellular energy is adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is often referred to as the "energy currency" of cells because it stores and transfers energy within cells for various biochemical reactions and processes, such as muscle contraction, active transport, and biosynthesis.
How is ATP produced in cells?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced in cells through a process called cellular respiration, which involves glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. During glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, glucose and other molecules are broken down to produce electron carriers (NADH and FADH2). These electron carriers then transfer electrons to the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane, generating a proton gradient. The flow of protons back through ATP synthase drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation and is the most efficient way for cells to produce ATP.
ATP is produced through cellular respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria. During this process, glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to release ATP.
Yes, that is correct. Through a series of reactions that include glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, glucose is oxidized to produce ATP in the mitochondria. This process efficiently converts the energy stored in glucose molecules into usable ATP for the cell's energy needs.
What are the main stages of cellular respiration?
The main stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate molecules, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH. The pyruvate then enters the citric acid cycle, where it is further broken down, releasing more NADH and FADH2. In the final stage, oxidative phosphorylation, the NADH and FADH2 molecules produced in the earlier stages donate electrons to the electron transport chain, leading to the production of a much larger amount of ATP through chemiosmosis.
The main stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Cellular respiration is a complex process that occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate to produce a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle then further metabolizes pyruvate to produce more ATP and high-energy electron carriers. Finally, oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the mitochondria, where these electron carriers donate their electrons to generate a large amount of ATP through the electron transport chain.
What is glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH in the process. It is the first step in cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of all living cells. Glycolysis is essential for energy production in the form of ATP and provides intermediates for other metabolic pathways.
Glycolysis is the initial stage of cellular respiration where glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
Yes, that is correct. Glycolysis is the process in which a molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, which produces a small amount of ATP and NADH. This pathway occurs in the cytoplasm and is the first step in both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments