Energy Flow Worksheets
Are you a science teacher looking to engage your students in interactive activities that promote a deeper understanding of energy flow? Look no further than energy flow worksheets! Designed specifically for middle and high school students, these worksheets offer a holistic approach to teaching the concept of energy transfer between organisms, emphasizing the roles of both the entity and the subject.
Table of Images 👆
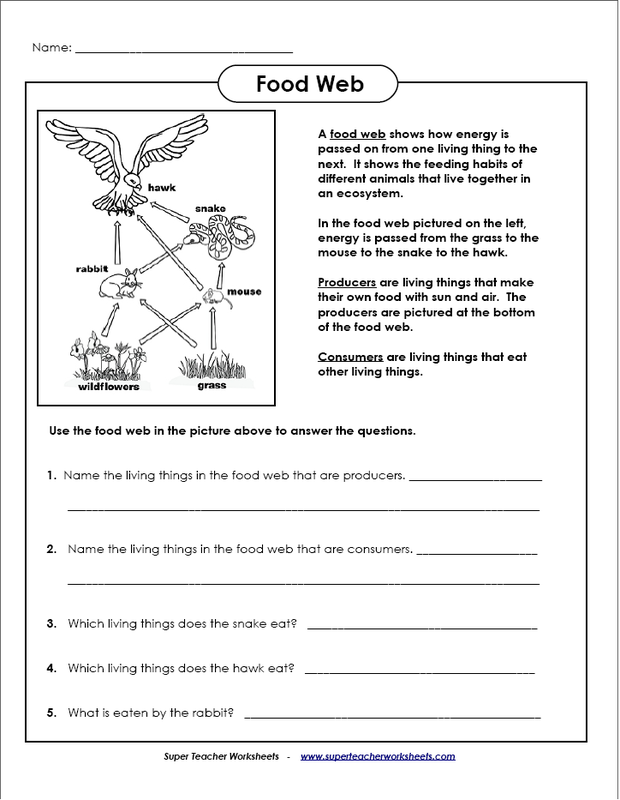
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Introduction to Energy Worksheet Answer Key
- Energy Flow in Ecosystems Worksheet
- Ecosystem Worksheet Answer Key
- Energy Flow through an Ecosystem Worksheet Answers
- Energy Flow Ecosystem Worksheet
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Energy Flow in Ecosystems Worksheet Answers
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
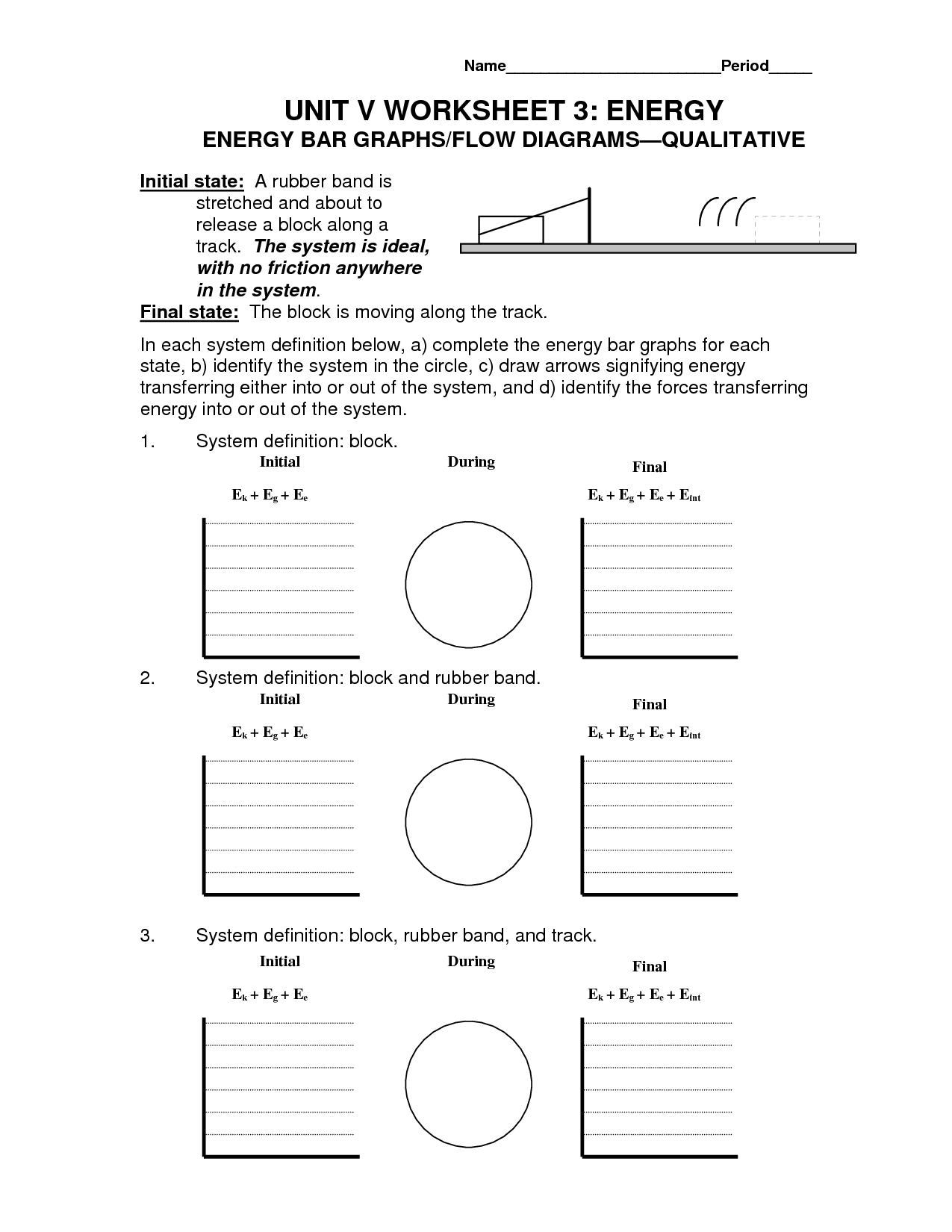
- Energy Bar Graphs Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Thermal Energy Transfer Worksheet Answers
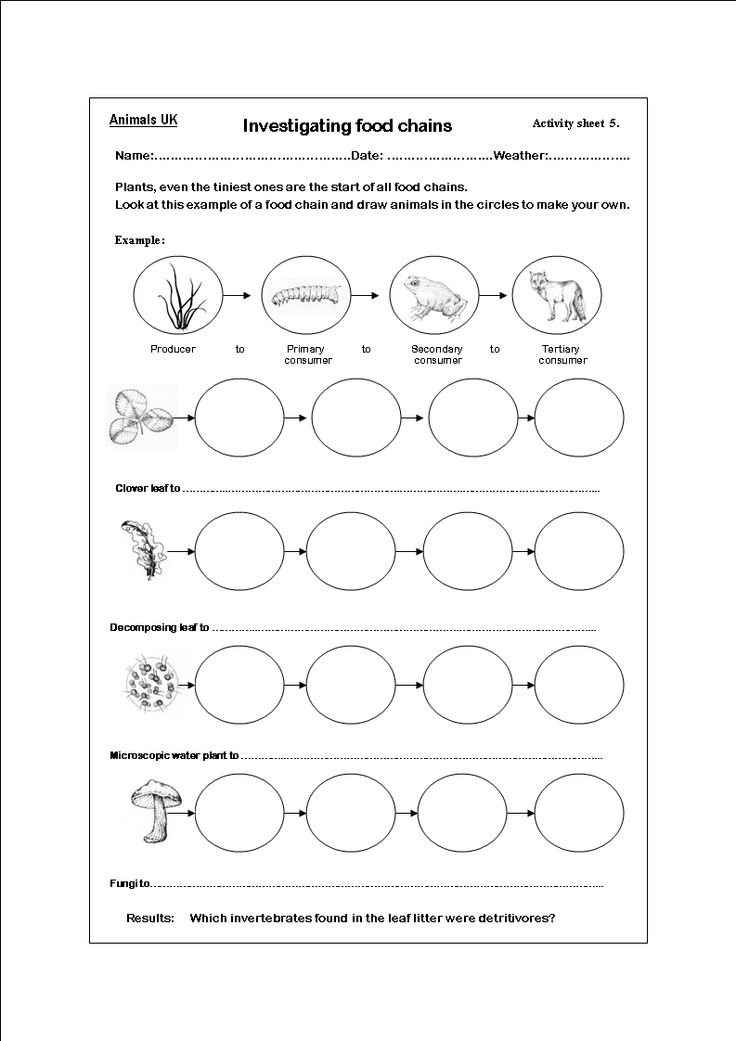
- Worksheets On Food Chains
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources Worksheet
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is the concept of energy flow?
Energy flow refers to the transfer of energy through a system, such as an ecosystem or a food chain, as it moves from one organism to another or between different components of the system. This transfer is essential for sustaining life and maintaining the balance of energy within an ecosystem. Energy flow typically follows a one-way direction, with energy being captured by producers (such as plants) through photosynthesis and then passed on to consumers (such as animals) as they consume other organisms. Ultimately, energy flow is crucial for all living organisms to carry out their biological processes and functions.
How does energy flow through ecosystems?
Energy flows through ecosystems in a unidirectional manner, starting with primary producers like plants that convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred through the food chain as various organisms consume each other, with energy being lost at each trophic level through respiration, heat loss, and waste production. Ultimately, decomposers break down organic matter and release the remaining energy back into the environment, completing the energy flow cycle within the ecosystem.
What are primary producers?
Primary producers are organisms, usually plants or algae, that can produce their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. They form the base of the food chain by converting inorganic substances into organic compounds, which are then consumed by other organisms in the ecosystem. In aquatic environments, phytoplankton are the primary producers, while plants fulfill this role on land.
What is the role of consumers in energy flow?
Consumers play a crucial role in the energy flow by utilizing energy resources to power their homes, vehicles, and various appliances. They are the end users of energy generated through various sources such as fossil fuels, renewable energy, and nuclear power. By consuming energy, consumers drive demand for energy sources, influencing energy production and distribution. Additionally, consumers have the power to make sustainable choices, such as opting for renewable energy and energy-efficient products, which can help reduce the overall environmental impact of energy consumption.
Describe the different trophic levels in an ecosystem.
Trophic levels in an ecosystem refer to the hierarchical levels of organisms based on their feeding relationships. They start with primary producers, such as plants, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores are the next trophic level, consuming the primary producers. Then come the primary predators, which feed on the herbivores. Lastly, there are secondary and tertiary predators, which feed on the primary predators. Each trophic level represents a transfer of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem, with organisms at higher levels often relying on those below them for food.
How do decomposers contribute to energy flow?
Decomposers play a crucial role in energy flow by breaking down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, into simpler molecules. Through this process of decomposition, they release nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for primary producers to use in photosynthesis. This nutrient recycling is essential for maintaining the flow of energy within an ecosystem, as it allows energy to be transferred from dead organic matter to living organisms, ultimately sustaining the entire food web.
Explain the concept of food chains and food webs.
Food chains and food webs are interconnected systems that depict the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. A food chain shows the transfer of energy from one organism to another in a linear pathway, with each organism feeding on the one below it. On the other hand, a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains, showing multiple pathways for energy flow between different organisms in an ecosystem. Both concepts illustrate the relationships and dependencies among different species in an ecosystem, highlighting the importance of maintaining balance and diversity for the overall health of the ecosystem.
Discuss how energy is transferred between trophic levels.
Energy is transferred between trophic levels through the consumption of organisms by those at higher levels. As organisms feed on each other, energy is passed along the food chain in the form of organic matter. This energy is used for various biological processes and is released as heat during metabolism. However, each transfer of energy between trophic levels results in a loss of energy due to inefficiencies in digestion, respiration, and other metabolic processes, with only a fraction of the energy being passed on to the next trophic level. This ultimately limits the number of trophic levels that can be sustained within an ecosystem.
What factors can impact energy flow in an ecosystem?
Several factors can impact energy flow in an ecosystem, such as the availability of resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients, as well as the presence of predators and competitors. Climatic conditions, disturbances like natural disasters or human activities, and the diversity and abundance of species in the ecosystem can also influence energy flow. Additionally, the efficiency of energy transfer between trophic levels, such as the conversion of plant biomass into animal biomass, and the decomposition of organic matter by decomposers play a crucial role in determining the overall energy flow within an ecosystem.
How does energy flow relate to the concept of energy pyramids?
Energy flow relates to the concept of energy pyramids in that energy is transferred and transformed as it moves through different trophic levels in an ecosystem. Energy pyramids illustrate this flow by showing how the amount of energy decreases as it moves up the pyramid from producers to primary consumers, and then to higher-level consumers. This is because energy is lost as heat during metabolism and other biological processes, resulting in less energy available at each successive trophic level. Energy pyramids help to visually represent the efficiency of energy transfer within an ecosystem and highlight the importance of maintaining balance and diversity within food webs to sustain energy flow and ecosystem stability.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments