Energy Diagrams Worksheet
Energy diagrams are a valuable tool for science students to understand the relationship between entities and subjects in complex systems. By visualizing the energy changes that occur during a process or reaction, these worksheets provide a clear and concise overview of the subject matter. Whether you are a high school student studying chemistry or a college student delving into thermodynamics, energy diagrams worksheets can enhance your understanding of key concepts and help you ace your exams.
Table of Images 👆
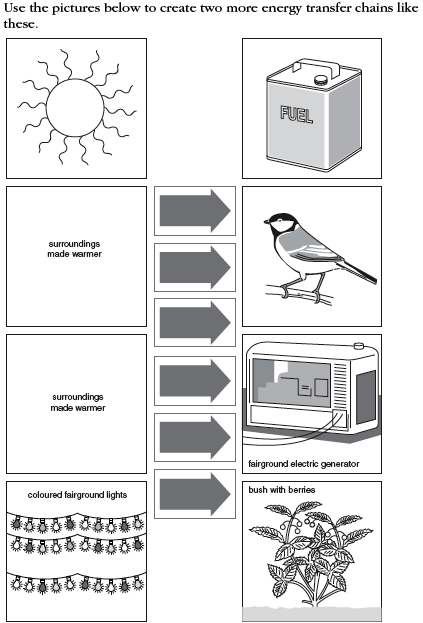
- Types of Energy Transfer Worksheet
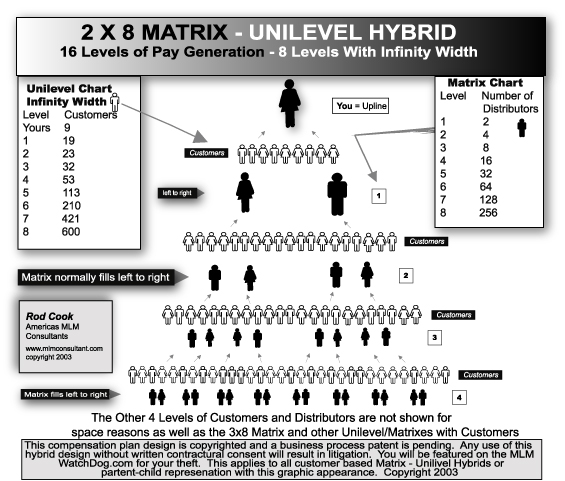
- MLM Compensation Plans Companies
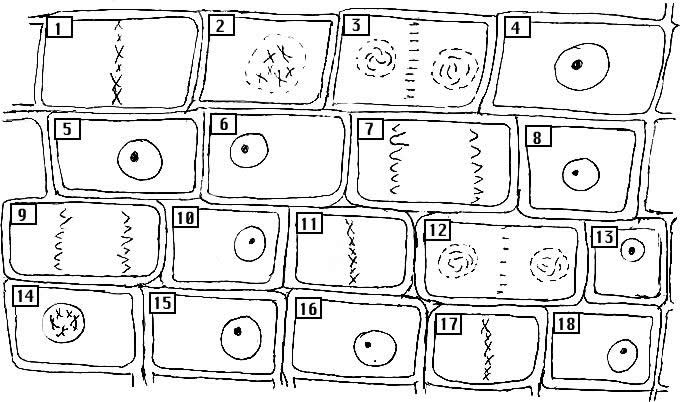
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answers
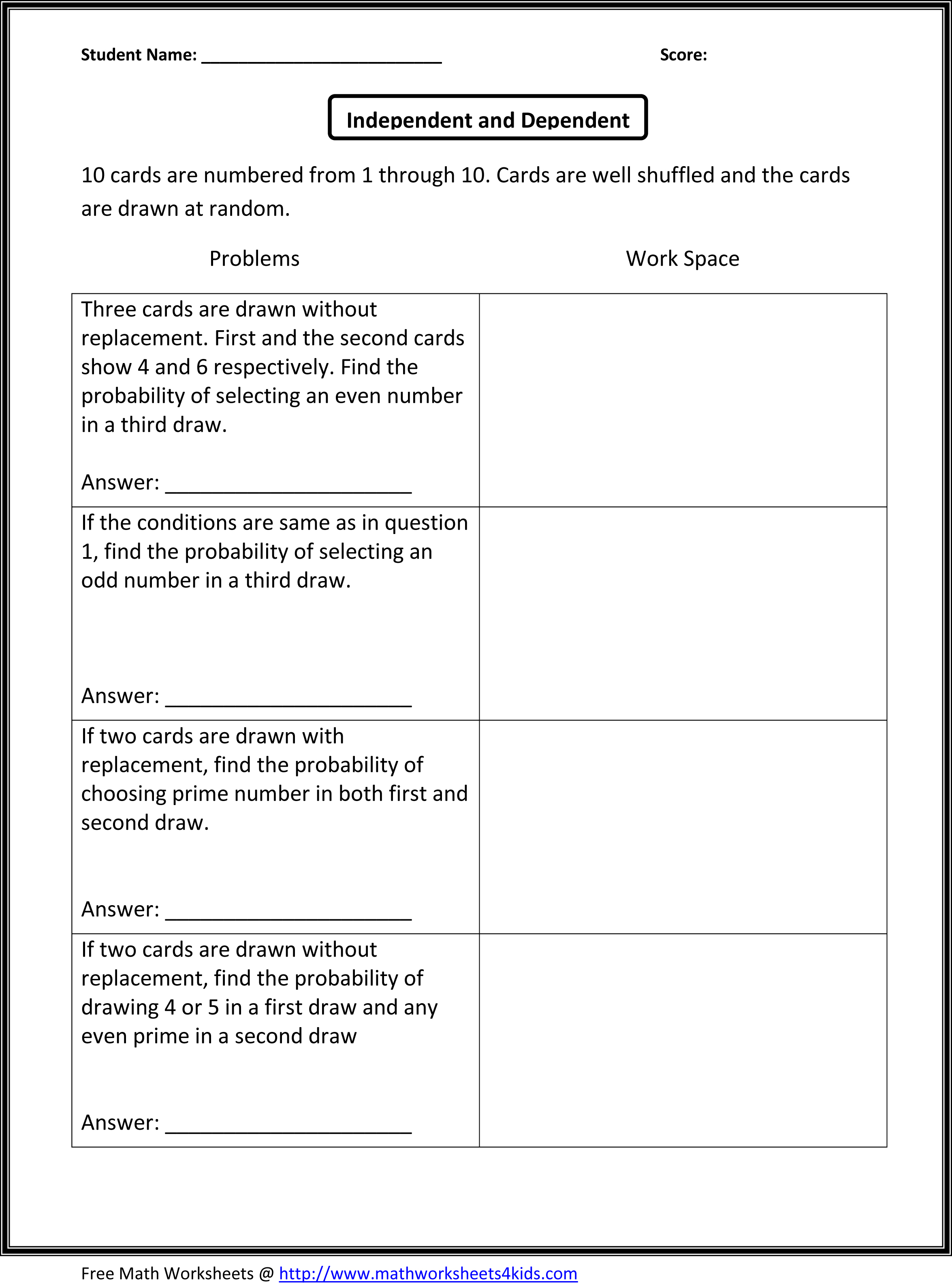
- 8th Grade Math Worksheets Ratios
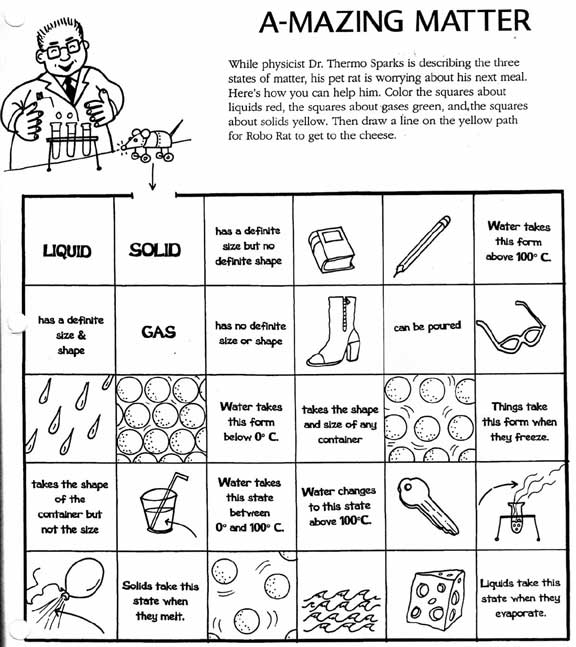
- Matter Solid-Liquid Gas Worksheet
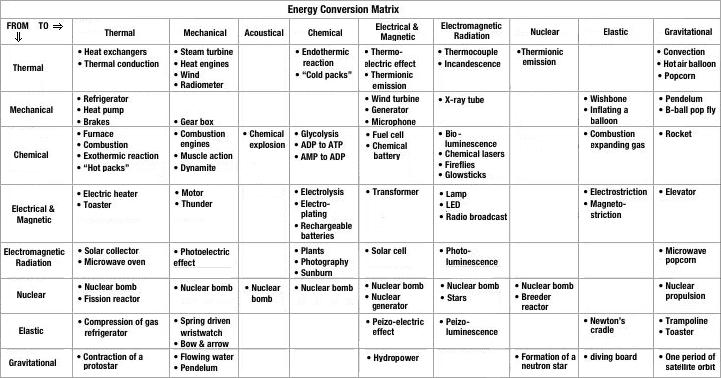
- Energy Conversion Examples
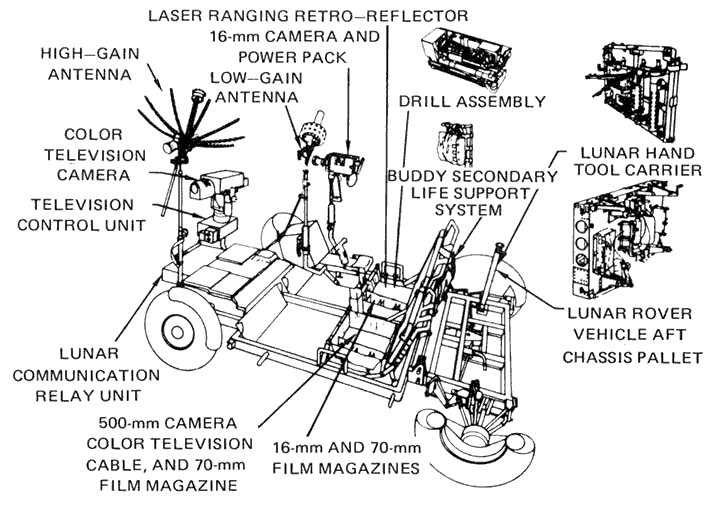
- Lunar Rover Diagram
- Specific Heat Calculations Worksheet Answers
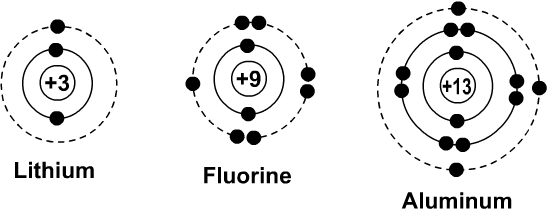
- Lithium Bohr-Rutherford Diagram
- Venn Diagram Compare
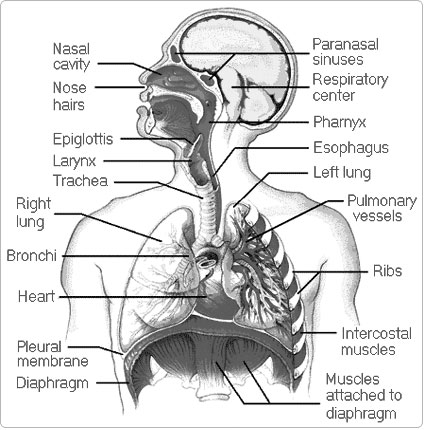
- Parts of the Human Respiratory System
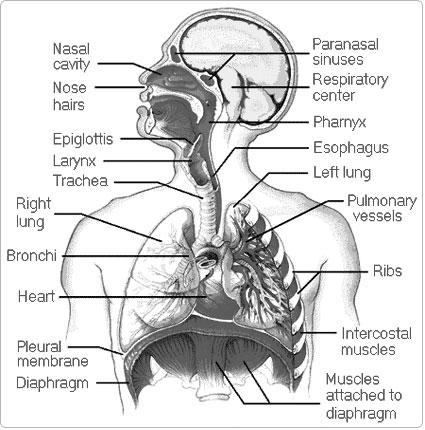
- Parts of the Human Respiratory System
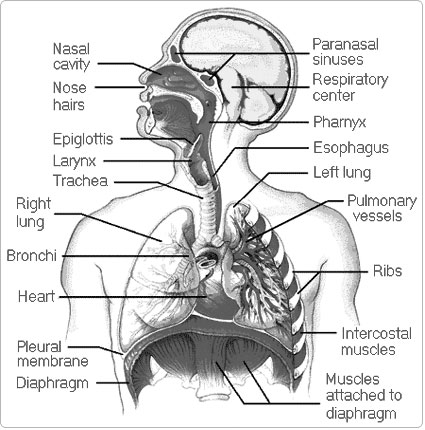
- Parts of the Human Respiratory System
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is an energy diagram?
An energy diagram is a visual representation that shows the changes in energy that occur during a specific process or reaction. It typically consists of a graph where the vertical axis represents energy and the horizontal axis represents the progress of the process. Peaks and valleys on the graph indicate energy levels at different stages of the process, helping to illustrate the energy changes involved in the reaction.
What are the main components of an energy diagram?
The main components of an energy diagram include the reactants at the starting energy level, the transition state at the peak energy level, the products at the ending energy level, and the enthalpy change or energy difference between the reactants and products. These components help visualize and analyze the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction or process.
How does an energy diagram depict energy changes?
An energy diagram visually represents energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction or process. It typically consists of a horizontal axis showing the progress of the reaction or process and a vertical axis representing energy content. Peaks correspond to energy maxima, such as activation energy, while valleys correspond to energy minima, such as the energy of products or reactants. The energy diagram illustrates the initial and final energy states, the energy changes that take place, and helps to visualize the relative energy levels of reactants, products, transition states, and intermediates involved in the reaction or process.
What is the role of the x-axis in an energy diagram?
The x-axis in an energy diagram represents the progress of a reaction or process from the starting point to the ending point. It typically shows the reaction coordinate or the extent of the process, helping to visualize how the energy of the system changes as the reaction proceeds. By providing a visual representation of the reaction pathway, the x-axis allows us to analyze the energy changes at different stages of the reaction and understand the overall energetics of the process.
How is the potential energy represented in an energy diagram?
Potential energy is typically represented as the vertical height of a curve in an energy diagram. The higher the curve, the greater the potential energy, and the lower the curve, the lower the potential energy. This allows for visualizing how potential energy changes as a system undergoes a physical or chemical process.
How is the kinetic energy represented in an energy diagram?
Kinetic energy is usually represented in an energy diagram as the highest point on the graph. This is because kinetic energy is at its maximum when the object is in motion. In a graph depicting potential and kinetic energy, the highest point on the graph represents the kinetic energy of the system.
What is the purpose of energy diagrams in chemistry?
Energy diagrams in chemistry are used to visualize and understand the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. They show the relative energy levels of reactants, products, and intermediates, as well as the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. Energy diagrams help chemists predict the feasibility and outcome of reactions, determine reaction mechanisms, and optimize reaction conditions to increase reaction rates or yield desired products.
How do energy diagrams illustrate chemical reactions?
Energy diagrams illustrate chemical reactions by showing the energy changes that occur as reactants are transformed into products. The diagram typically includes the energy of the reactants, the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed, and the energy of the products. It visually represents how the reaction progresses from the initial state to the transition state to the final products, providing insight into the overall energetics of the reaction and whether it is exothermic or endothermic. Additionally, energy diagrams can help to identify intermediates, catalysts, and the overall feasibility of the reaction based on the energy profiles depicted.
What information can be obtained from an energy diagram?
An energy diagram provides information about the relative energy levels of reactants, transition states, and products in a chemical reaction or physical process. It illustrates the energy changes that occur during the reaction, showing the energy required to break bonds (activation energy) and the energy released when new bonds form. Additionally, it can reveal whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic based on the energy of the products compared to the reactants. Overall, an energy diagram helps in understanding the energetics of a reaction and predicting its feasibility and rate.
How can energy diagrams be used to determine reaction rates?
Energy diagrams can be used to determine reaction rates by illustrating the energy changes that occur during a reaction. The height of the energy barrier, known as the activation energy, determines how easily reactants can transform into products. The lower the activation energy, the faster the reaction rate. By analyzing the energy diagram, one can identify the activation energy and predict the rate of reaction based on how it compares to the available energy of the reactants.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments