Endocrine System Worksheet Answers
Are you a biology student seeking a comprehensive resource to reinforce your knowledge of the endocrine system? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the answers to an endocrine system worksheet that will help you solidify your understanding of this intricate and fascinating bodily system. Whether you are a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student reviewing for a quiz, these answers will serve as a valuable tool to test yourself and gauge your comprehension of key concepts within the endocrine system.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
The primary function of the endocrine system is to regulate and control the body's hormones, which are chemical messengers that help coordinate various bodily functions such as growth, metabolism, mood, and reproduction. The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream, where they travel to target cells and organs to elicit a specific response, helping to maintain overall balance and homeostasis within the body.
Name three major glands of the endocrine system.
The three major glands of the endocrine system are the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands.
How does the endocrine system regulate metabolism?
The endocrine system regulates metabolism by secreting hormones that control processes such as the rate at which the body uses energy (basal metabolic rate), the breakdown of nutrients for energy production, and the storage of excess energy as fat. Hormones such as insulin, glucagon, adrenaline, and thyroid hormones play key roles in regulating metabolism by influencing how cells absorb nutrients, metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and maintain energy balance throughout the body.
What is the role of hormones in the endocrine system?
Hormones play a crucial role in the endocrine system by acting as chemical messengers that regulate and coordinate various physiological processes within the body. These hormones are secreted by endocrine glands and travel through the bloodstream to target cells or organs, where they initiate responses that help maintain homeostasis, growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, and other essential functions in the body.
How do hormones travel throughout the body?
Hormones travel throughout the body primarily via the bloodstream. Produced by endocrine glands, hormones are released into the blood and then circulate to target cells or organs where they initiate specific physiological responses. Hormones can also travel through the lymphatic system or bodily fluids to reach their target sites and regulate various functions in the body.
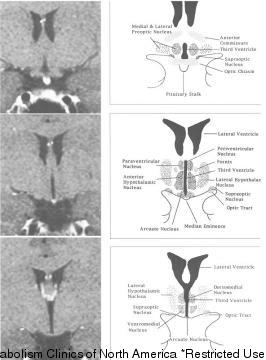
What is the master gland of the endocrine system and what does it control?
The master gland of the endocrine system is the pituitary gland, located in the brain. It controls and regulates the function of other endocrine glands in the body by secreting hormones that stimulate or inhibit their activity. The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in growth, metabolism, reproductive function, and stress response, making it a key regulator of various bodily processes.
Explain the feedback loop involved in hormone regulation.
Feedback loops in hormone regulation involve the endocrine system's way of maintaining balance through a self-regulating mechanism. When hormone levels in the bloodstream deviate from the desired range, the hypothalamus detects this imbalance and releases specific hormones to either stimulate or inhibit the pituitary gland's hormone production. The pituitary gland then secretes hormones that act on target organs to either release more hormones to correct the imbalance or reduce hormone production to restore equilibrium. Once hormone levels return to the optimal range, the hypothalamus senses this and reduces its signal to the pituitary gland, thereby closing the loop. This feedback loop ensures that the body's hormone levels are finely tuned to support various physiological processes and maintain overall homeostasis.
What is the difference between an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland?
The main difference between an endocrine gland and an exocrine gland is in how they secrete their products. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, which then travel to target organs or tissues. In contrast, exocrine glands secrete their products through ducts onto the body surfaces or into body cavities. Examples of endocrine glands include the thyroid and adrenal glands, while examples of exocrine glands include sweat glands and salivary glands.
How does the endocrine system influence growth and development?
The endocrine system influences growth and development by releasing hormones that regulate various physiological processes such as cell growth, metabolism, and maturation of tissues and organs. Hormones like growth hormone, thyroid hormone, and sex hormones play key roles in stimulating growth and development during different stages of life, helping individuals reach their full physical and sexual maturity. Imbalances or abnormalities in the endocrine system can lead to growth disorders or developmental delays.
What are some common disorders of the endocrine system?
Some common disorders of the endocrine system include diabetes, thyroid disorders (such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism), adrenal gland disorders (such as Cushing's syndrome and Addison's disease), polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and pituitary gland disorders (such as acromegaly and hyperprolactinemia). These disorders can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications if left untreated, making early diagnosis and proper management essential.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments