Electricity Worksheets 5th Grade Science
Electricity worksheets are an essential resource for 5th grade science students to explore and understand the intricacies of this fascinating subject. With a focus on engaging content and interactive exercises, these worksheets provide an opportunity for students to strengthen their understanding of electricity-related concepts, such as circuits, conductors, and electrical safety.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Motion Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Matter Solid-Liquid Gas Worksheet
- Science Experiment Worksheet Scientific Method
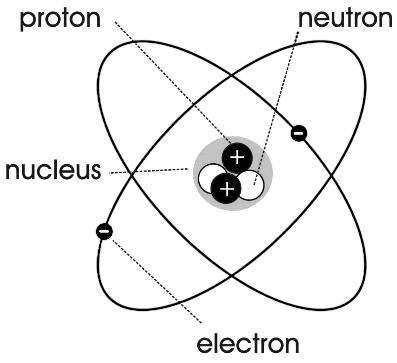
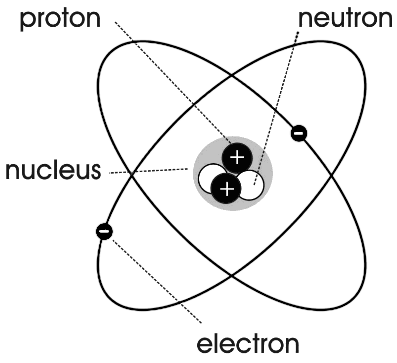
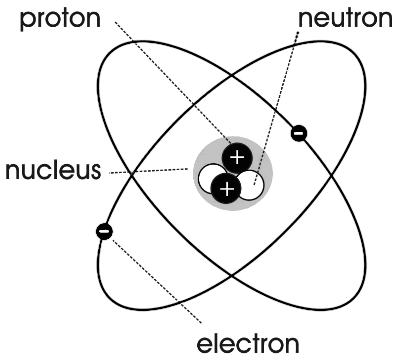
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
- 3rd Grade Word Search Puzzles Printable
- Nicki Minaj
- 2015 the Science Penguin Scientific Method 2 Warm Up
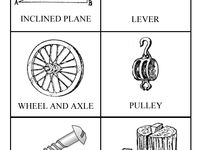
- Simple Machine Science Doodles
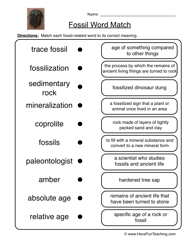
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- 2nd Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, usually electrons, through a conductor. This flow of charged particles generates a force that can be harnessed to power a wide range of electrical devices and systems, enabling them to perform various functions that have become essential in modern society.
How is electricity produced?
Electricity is typically produced by spinning turbines that are connected to generators. There are various methods to spin these turbines, such as burning fossil fuels like coal or natural gas, harnessing the power of flowing water in hydroelectric plants, capturing the energy of the sun through solar panels, utilizing wind turbines to convert wind energy into electricity, or through nuclear fission in nuclear power plants. When the turbines spin, they create an electromagnetic field that generates electricity which can be fed into the power grid for distribution to homes and businesses.
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is a complete loop through which electricity can flow, typically consisting of a power source (such as a battery), conductors (wires), and electrical components (such as resistors, capacitors, and light bulbs). The circuit allows the flow of electrons to power devices and perform various functions by creating a pathway for the electricity to travel.
What is a conductor and give an example?
A conductor is a material that allows the flow of electrical current. One example of a conductor is copper, which is commonly used in electrical wiring due to its high conductivity and reliability in carrying electricity.
What is an insulator and give an example?
An insulator is a material that does not easily allow the flow of electricity or heat. It has high resistance to the flow of electrons, preventing the transfer of electrical charge or thermal energy. An example of an insulator is rubber, which is commonly used to coat electrical wires to prevent electric shocks and short circuits.
What is static electricity?
Static electricity is the build-up of electric charge on the surface of an object. This charge is generated when two materials rub against each other and one material loses electrons, becoming positively charged, while the other material gains electrons, becoming negatively charged. The imbalance of charges creates static electricity that can cause objects to stick together, generate sparks, or give a mild shock.
How does a switch work in a circuit?
A switch works by opening or closing a gap in a circuit, allowing or interrupting the flow of electricity. When the switch is in the "on" position, it completes the circuit, allowing electricity to flow through and power the connected device. Conversely, when the switch is in the "off" position, it breaks the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity and turning off the device. This simple mechanism gives users control over the flow of electricity in a circuit, enabling devices to be powered on or off as needed.
What is a battery and how does it produce electricity?
A battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of one or more cells that contain chemicals that react to produce an electrical current. When the battery is connected to a circuit, a chemical reaction occurs within the cells, causing electrons to flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal, generating an electric current. This flow of electrons is what we refer to as electricity produced by the battery.
What is an electromagnet and how does it work?
An electromagnet is a type of magnet that operates using electricity. It consists of a coil of wire through which an electric current flows, creating a magnetic field around it. The strength of the magnetic field can be controlled by adjusting the amount of current flowing through the wire. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field disappears. Electromagnets are widely used in various devices and technologies, such as electric motors, speakers, MRI machines, and cranes for lifting heavy objects.
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
In series circuits, the components are connected in a single path so that the current flows through each component one after the other. In parallel circuits, the components are connected in different branches so that the current is divided among them. The voltage in series circuits is divided among the components, while in parallel circuits, all components have the same voltage. Additionally, if one component fails in a series circuit, the entire circuit is disrupted, whereas in a parallel circuit, other components can still function independently.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






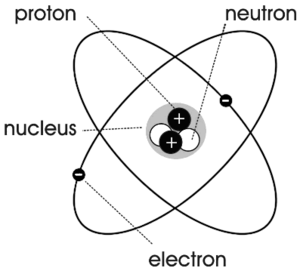
















Comments