Easy Sound Wave Worksheet
Are you searching for a simple and informative worksheet to help your students understand sound waves? Look no further! This easy sound wave worksheet is designed to provide a clear and concise overview of the topic, making it perfect for middle school or high school students studying physics or general science. By focusing on the key concepts of sound waves, this worksheet is sure to engage and educate your students in an engaging and effective manner.
Table of Images 👆
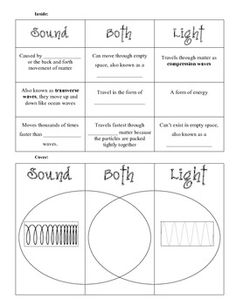
- Light and Sound Waves
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- 2nd Grade Science Sound Worksheets
- Sound and Vibration Worksheets
- Long Vowel Sounds Worksheets
- Sound Wave Science Projects
- Printable Science Worksheets
- Sound and Light Worksheets 4th Grade
- Bill Nye Earthquakes Worksheet
- First Grade Homophone Worksheet
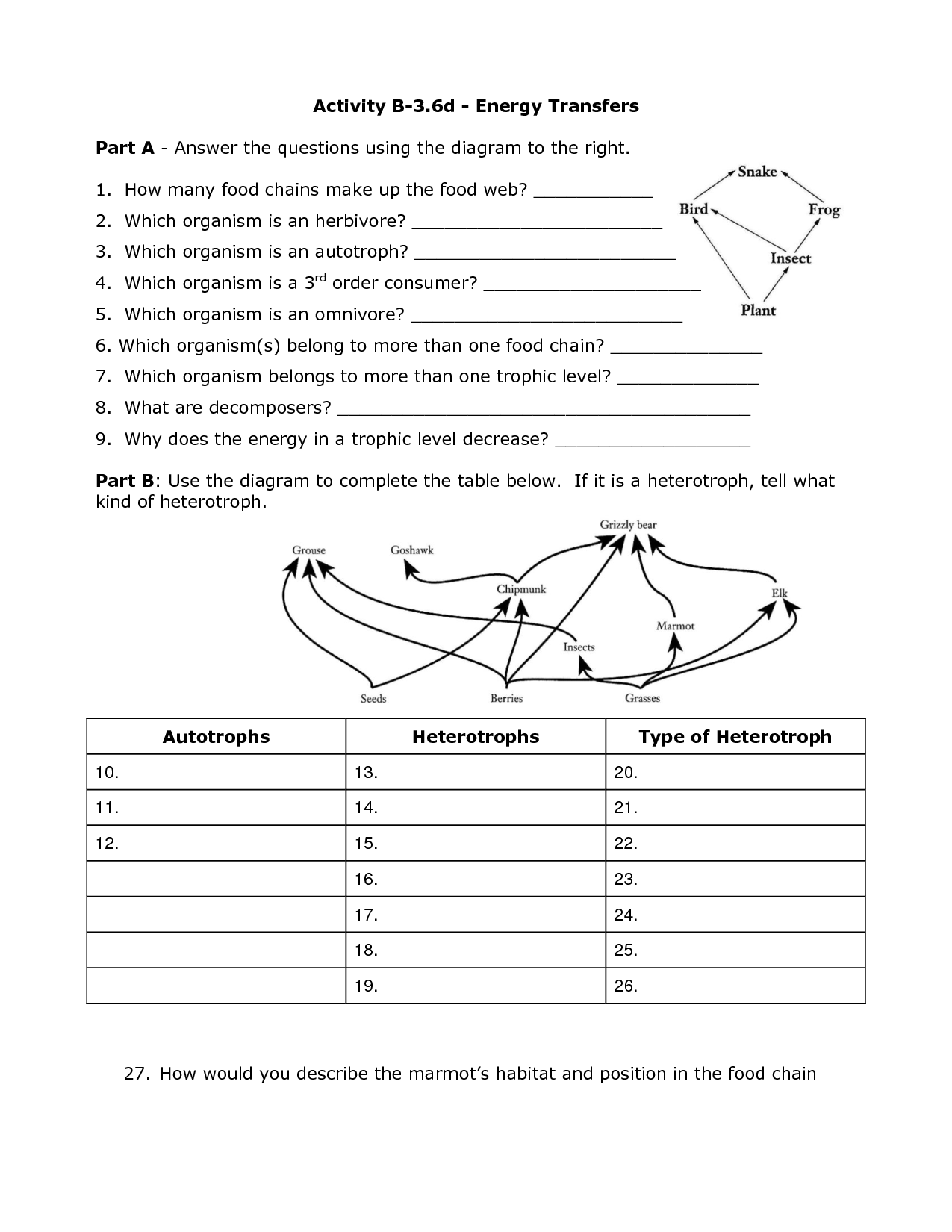
- Food Web Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Ear Diagram Worksheet
- Bill Nye Waves Worksheet
- Science Worksheets Light
- Christmas Word Jumbles Printables
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
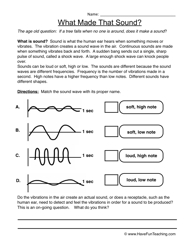
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a longitudinal wave that carries energy through a medium by the vibration of particles. These vibrations create mechanical disturbances that travel through air, water, or solids and can be perceived by our ears as sound. Sound waves have characteristics such as frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed that determine the pitch and volume of the sound we hear.
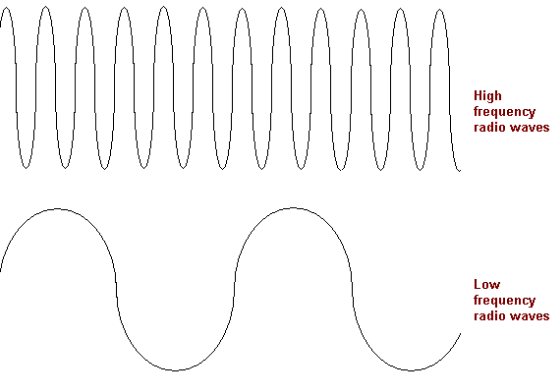
How is the frequency of a sound wave related to its pitch?
The frequency of a sound wave is directly related to its pitch, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher pitch and lower frequencies corresponding to lower pitch. Essentially, the pitch of a sound is determined by how fast or slow the sound wave vibrates, with faster vibrations resulting in a higher pitch and slower vibrations resulting in a lower pitch.
What is the amplitude of a sound wave?
The amplitude of a sound wave is the measure of the maximum displacement of particles from their rest position as the wave moves through a medium. It represents the loudness or intensity of the sound wave, with greater amplitude corresponding to a louder sound and larger displacement of particles.
How is the amplitude of a sound wave related to its volume?
The amplitude of a sound wave is directly related to its volume. Essentially, the greater the amplitude of a sound wave, the louder the volume of the sound produced. This is because higher amplitudes result in more energy being transferred, causing the air particles to move with greater force and creating a louder sound. Conversely, lower amplitudes produce quieter sounds.
What is the wavelength of a sound wave?
The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive points of the same phase, such as two peaks or two troughs, in the waveform of the sound wave. Sound waves are longitudinal waves, which means that the particles in the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave propagation. The wavelength of a sound wave is inversely proportional to its frequency, with longer wavelengths corresponding to lower frequencies, and shorter wavelengths corresponding to higher frequencies.
How is the wavelength of a sound wave related to its frequency?
The wavelength of a sound wave is inversely proportional to its frequency; meaning that as the frequency of a sound wave increases, its wavelength decreases and vice versa. This relationship is mathematically expressed by the equation: wavelength = speed of sound / frequency. This means that sound waves with higher frequencies (like those of a higher pitch) have shorter wavelengths, while sound waves with lower frequencies (such as those of a lower pitch) have longer wavelengths.
What is the speed of sound in a medium?
The speed of sound in a medium depends on factors such as the medium's density, elasticity, and temperature. In general, sound travels faster in denser and stiffer materials and slower in lighter and more elastic materials. The speed of sound in air at room temperature is approximately 343 meters per second.
How does the speed of sound vary in different mediums?
The speed of sound varies in different mediums due to differences in the material's density and elasticity. In general, sound travels faster in solids, such as metals, than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases. This is because the particles in solids are closer together, allowing sound waves to propagate more quickly. Additionally, the elasticity of a medium affects the speed of sound; materials that are more elastic will transmit sound waves more efficiently, resulting in a faster speed of sound.
What is the difference between a compressional wave and a transverse wave?
The main difference between compressional waves and transverse waves lies in the direction of the oscillation of the medium particles. In compressional waves, the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave's propagation, causing areas of compression and rarefaction. In contrast, transverse waves cause the particles of the medium to move perpendicular to the direction of the wave's propagation, resulting in crests and troughs. Examples of compressional waves include sound waves, while examples of transverse waves include light waves.
How do sound waves travel through different mediums?
Sound waves travel through different mediums by causing the particles in the medium to vibrate. When a sound wave is created, it compresses and rarefies the particles in the medium, causing them to bump into each other and transfer energy along the wave. In solids, the particles are closely packed and can transmit sound waves quickly, whereas in liquids and gases, the particles are further apart, causing sound waves to travel at a slower pace. The speed of sound also varies depending on the density and elasticity of the medium.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments