Earth Science Worksheets 8th Grade
Earth Science Worksheets are a great resource for 8th graders who want to enhance their knowledge and understanding of various topics related to our planet. With a wide range of engaging and informative exercises, these worksheets provide the perfect opportunity for students to explore concepts such as geology, meteorology, and environmental science in a structured and accessible way.
Table of Images 👆
- 2nd Grade Cloud Worksheets
- 7th Grade Life Science Lab Safety Rules
- Earth Science Printable Worksheets
- Topographic Maps Worksheets 8th Grade
- Plate Tectonics Worksheet 7th Grade
- 8th Grade Science Test Worksheets
- Solar System Test 7th Grade
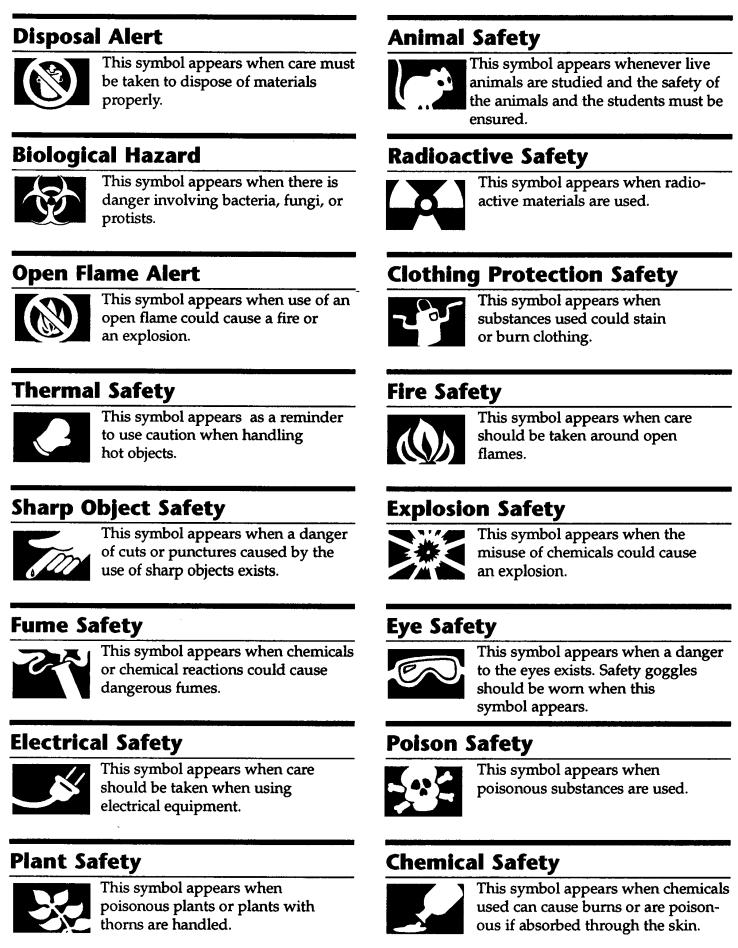
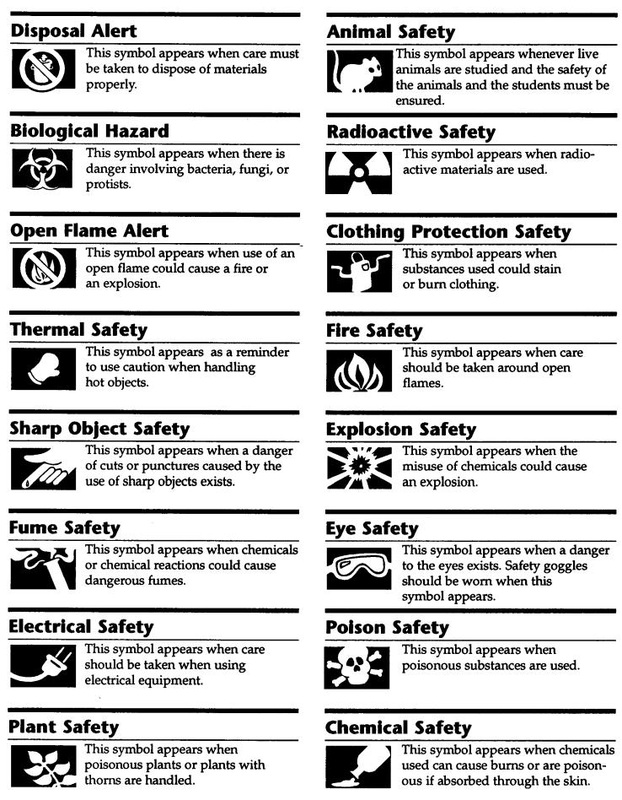
- Science Lab Safety Symbols Worksheets
- Plate Tectonics Worksheet Answers
- Science Lab Safety Symbols Worksheets
- Density Jokes Science
- Bill Nye Atoms Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Atoms Worksheet Answers
More 8th Grade Worksheets
8th Grade Spelling Worksheets8th Grade Worksheets Homeschooling
8th Grade Vocabulary Worksheets
Rotations Worksheet 8th Grade
What is the main source of energy that drives Earth's weather systems?
The main source of energy that drives Earth's weather systems is the sun. Solar radiation heats the Earth's atmosphere and surface, creating differences in temperature and pressure that drive atmospheric circulation, leading to the formation of weather patterns and systems.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its importance in the Earth's ecosystem.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is vital for life on Earth as it is the main way in which oxygen is produced in the atmosphere, providing the necessary oxygen for aerobic respiration in organisms. In addition, photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain, as plants use the glucose they produce as energy to grow and reproduce, which in turn sustains other organisms that consume plants for energy. Overall, photosynthesis plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere and supporting all living organisms on Earth.
How are minerals formed? Provide a detailed explanation of at least two ways.
Minerals are formed through various processes, including solidification from a molten state and precipitation from a solution. In the case of solidification from a molten state, when magma cools and solidifies, it can create minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica. On the other hand, precipitation from a solution occurs when dissolved substances in water, such as salts or ions, reorganize and crystalize, forming minerals like halite and calcite. These chemical and physical processes contribute to the formation of the wide array of minerals found in the Earth's crust.
Explain the difference between weathering and erosion and provide examples of each.
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth's surface due to exposure to natural elements like rain, wind, and temperature changes. Some examples of weathering include the physical process of frost shattering and the chemical process of acid rain dissolving limestone formations. Erosion, on the other hand, is the process of transporting the weathered materials through the action of agents such as water, wind, ice, or gravity. Examples of erosion include rivers carrying sediments downstream, wind wearing away rock formations in deserts, and glaciers moving rock debris across landscapes.
What is the composition of Earth's atmosphere and how does it support life on our planet?
Earth's atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of other gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and argon. This composition is crucial for supporting life on our planet as oxygen is essential for the respiration of organisms, while nitrogen is necessary for the growth and development of plants. The atmosphere also helps regulate the Earth's temperature by trapping heat through the greenhouse effect, making the planet habitable for a wide range of species. Additionally, the atmosphere acts as a protective shield by filtering out harmful solar radiation and meteoroids, creating a stable environment for life to thrive.
Describe the rock cycle and the different processes involved in it.
The rock cycle is a continuous process that transforms rocks from one type to another over time. It includes three main processes: 1) Igneous rocks are formed from molten magma cooling and solidifying either beneath the Earth's surface (intrusive rocks) or on the surface (extrusive rocks); 2) These rocks can be weathered and eroded into sediments, which then get deposited and lithified to form sedimentary rocks; 3) Through heat and pressure deep within the Earth's crust, both igneous and sedimentary rocks can undergo metamorphism to become metamorphic rocks. This cycle is driven by forces like plate tectonics, erosion, and volcanic activity, showcasing the dynamic nature of Earth's geology.
How do earthquakes occur and what factors contribute to their severity?
Earthquakes occur when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, typically along faults in the rock. The shifting tectonic plates cause stress to build up until it's released in the form of seismic waves. Factors that contribute to the severity of earthquakes include the depth of the focus (where the earthquake originates), the magnitude of the release of energy, the proximity to populated areas, the type of rock and geology of the area, and the structures and buildings in the affected area.
What are fossils and how do they provide evidence of Earth's past environments and life forms?
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms found in rocks or sediment. They provide valuable evidence of Earth's past environments and life forms by revealing the types of plants and animals that lived during a specific time period, as well as information about climate, habitats, and evolutionary relationships. By studying fossils, scientists can reconstruct past ecosystems and track changes in biodiversity over millions of years, shedding light on the history of life on Earth.
Explain the process of plate tectonics and its impact on Earth's landforms and natural disasters.
Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that move and interact with each other. These plates can converge, diverge, or slide past one another, leading to various geological phenomena. When plates collide, they can create mountain ranges and volcanoes. When they separate, they cause the formation of new crust and ocean basins. Additionally, the movement of plates can trigger earthquakes and tsunamis, as well as volcanic eruptions. Overall, plate tectonics play a crucial role in shaping Earth's landforms and influencing natural disasters.
Describe the water cycle and the different stages involved in it.
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, describes the continuous movement of water in various forms between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. The cycle includes several stages: evaporation occurs when heat from the sun causes water to change from liquid to vapor; condensation happens when water vapor cools and becomes liquid in the form of clouds; precipitation occurs when condensed water falls back to the Earth's surface as rain, snow, sleet, or hail; infiltration happens when precipitation seeps into the ground and becomes groundwater or runoff; transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor into the atmosphere. This cycle is crucial for the distribution of water on Earth and plays a vital role in supporting life.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments