DNA Worksheet Printable
If you're a biology enthusiast or a student looking for a comprehensive resource to enhance your understanding of DNA, you may be interested in exploring interactive DNA worksheets. These worksheets provide a structured and engaging approach for learning about the building blocks of life and how they function within an organism. Whether you're studying for an exam or simply seeking to broaden your knowledge, incorporating DNA worksheets into your learning routine can be a valuable asset.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA RNA Structure Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Page for Kids
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
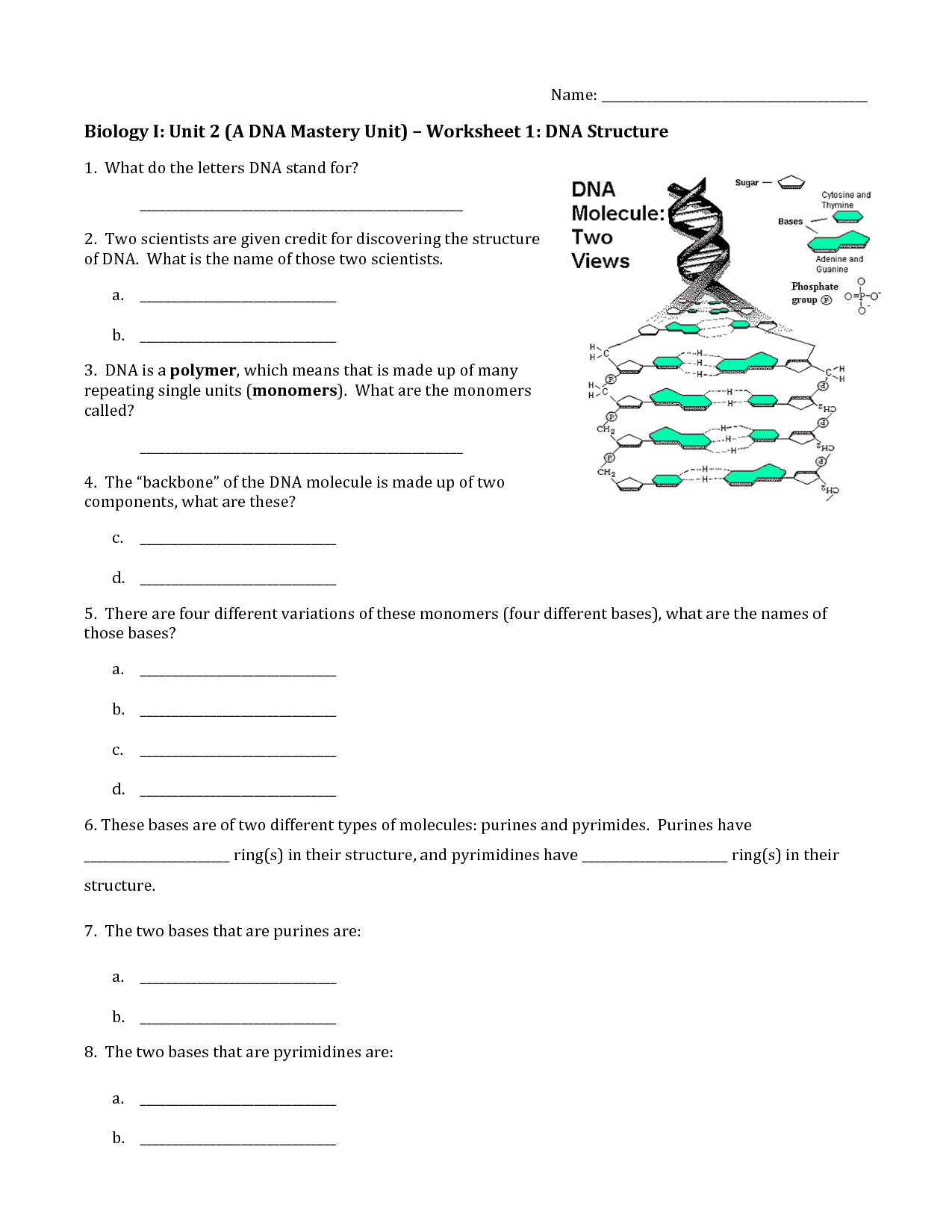
- DNA Structure Worksheet
- The Genetic Code Worksheet DNA RNA
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
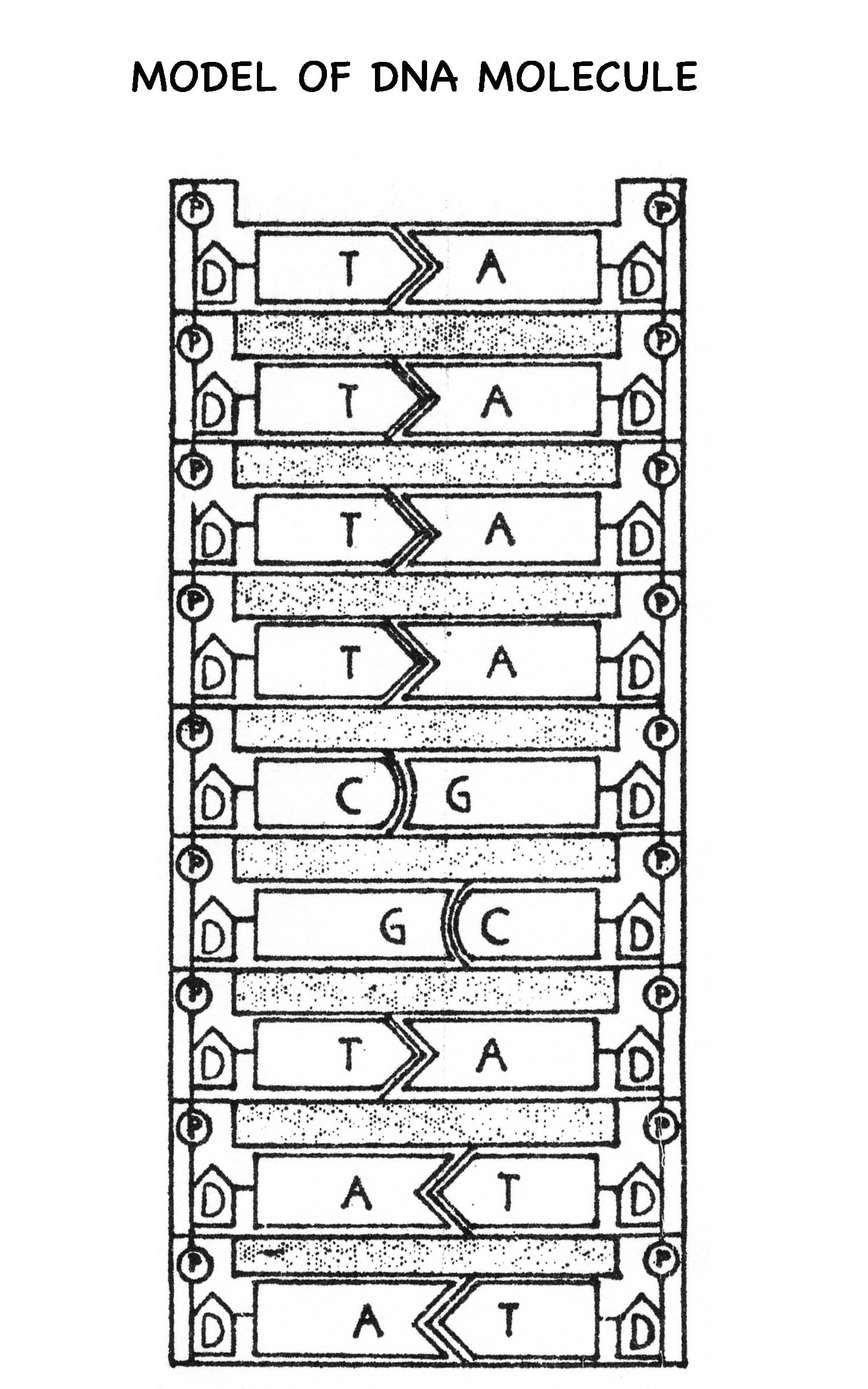
- DNA Model Worksheet
- DNA Extraction Worksheet
- DNA Fingerprinting Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Worksheets DNA Coloring Page
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Function Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
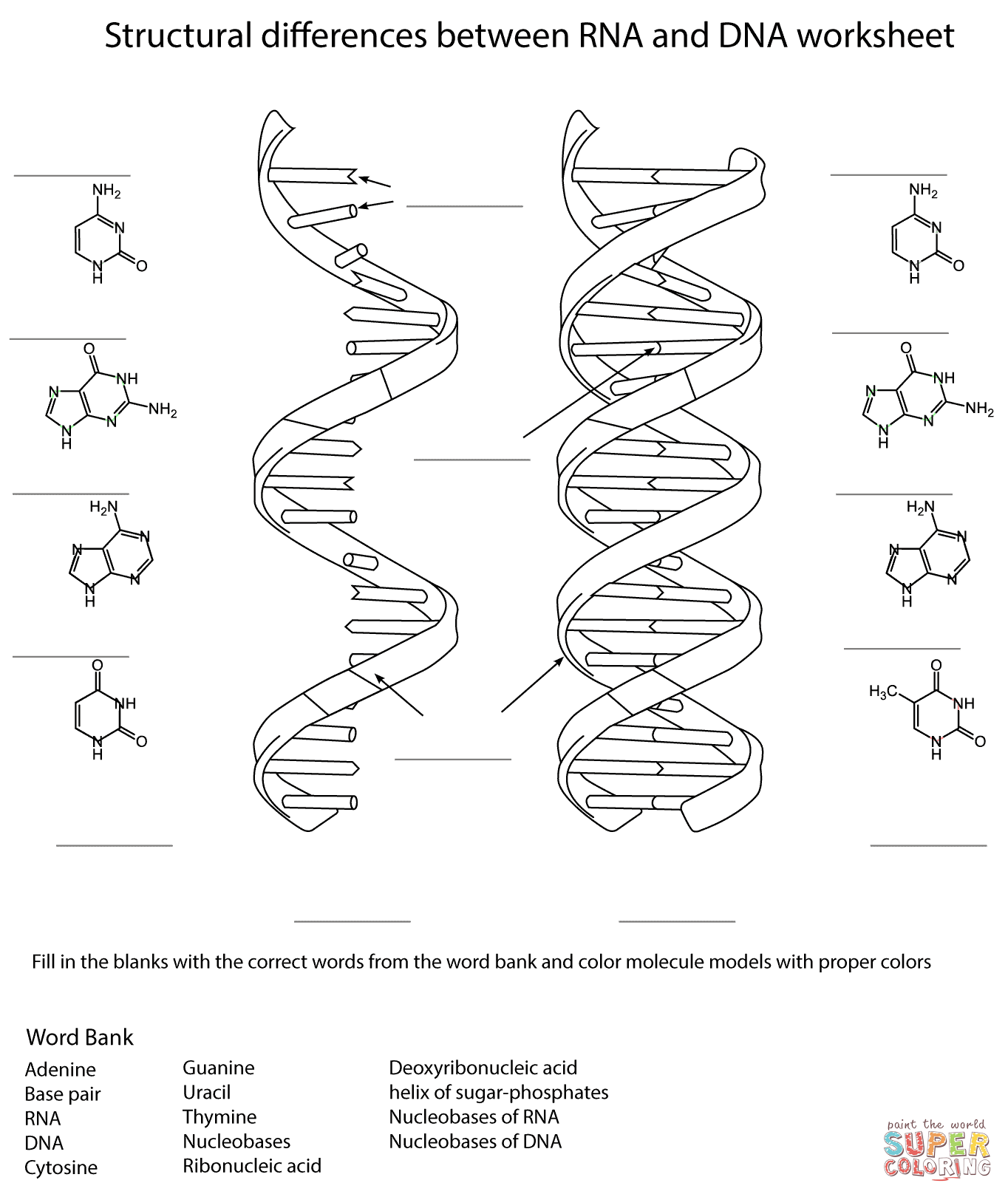
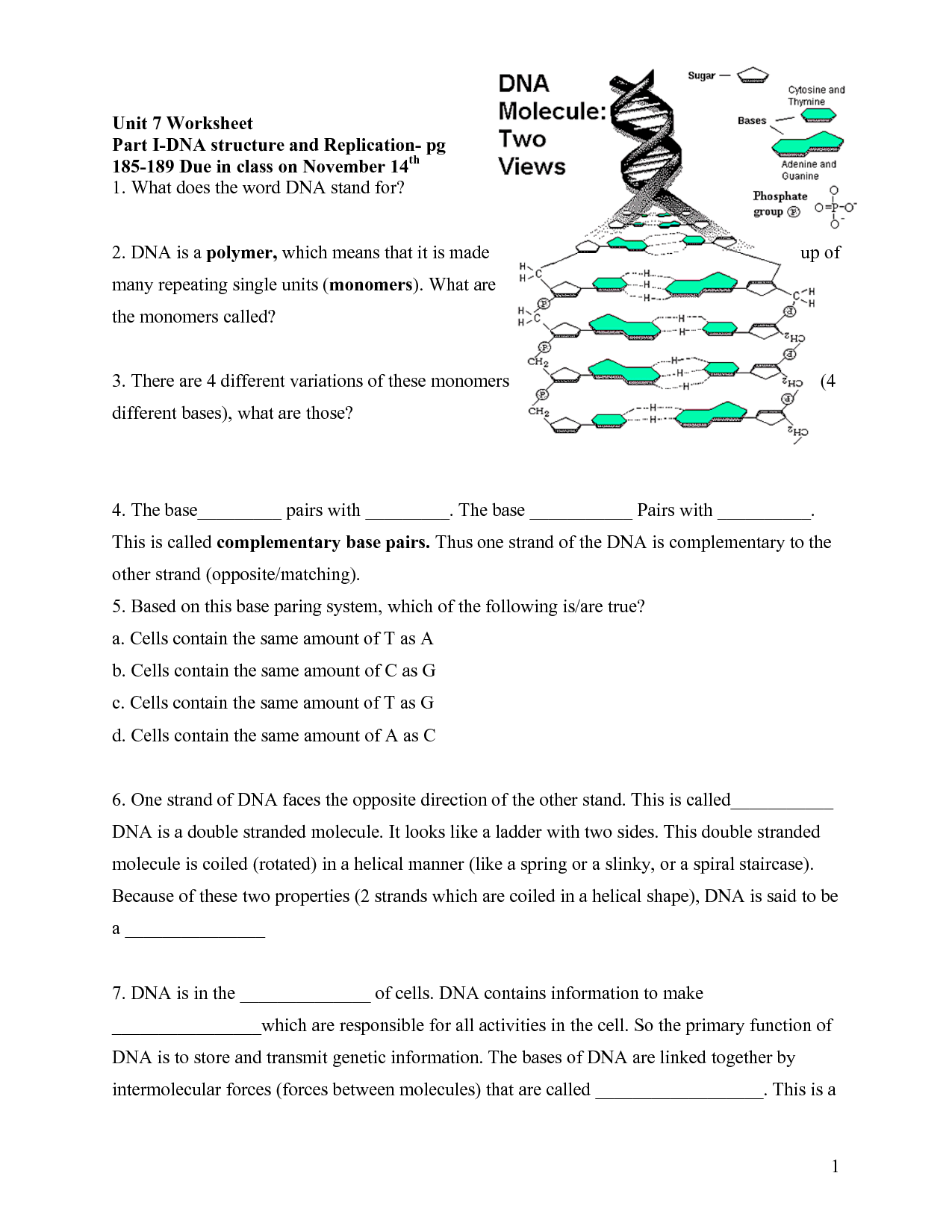
What is the structure of DNA?
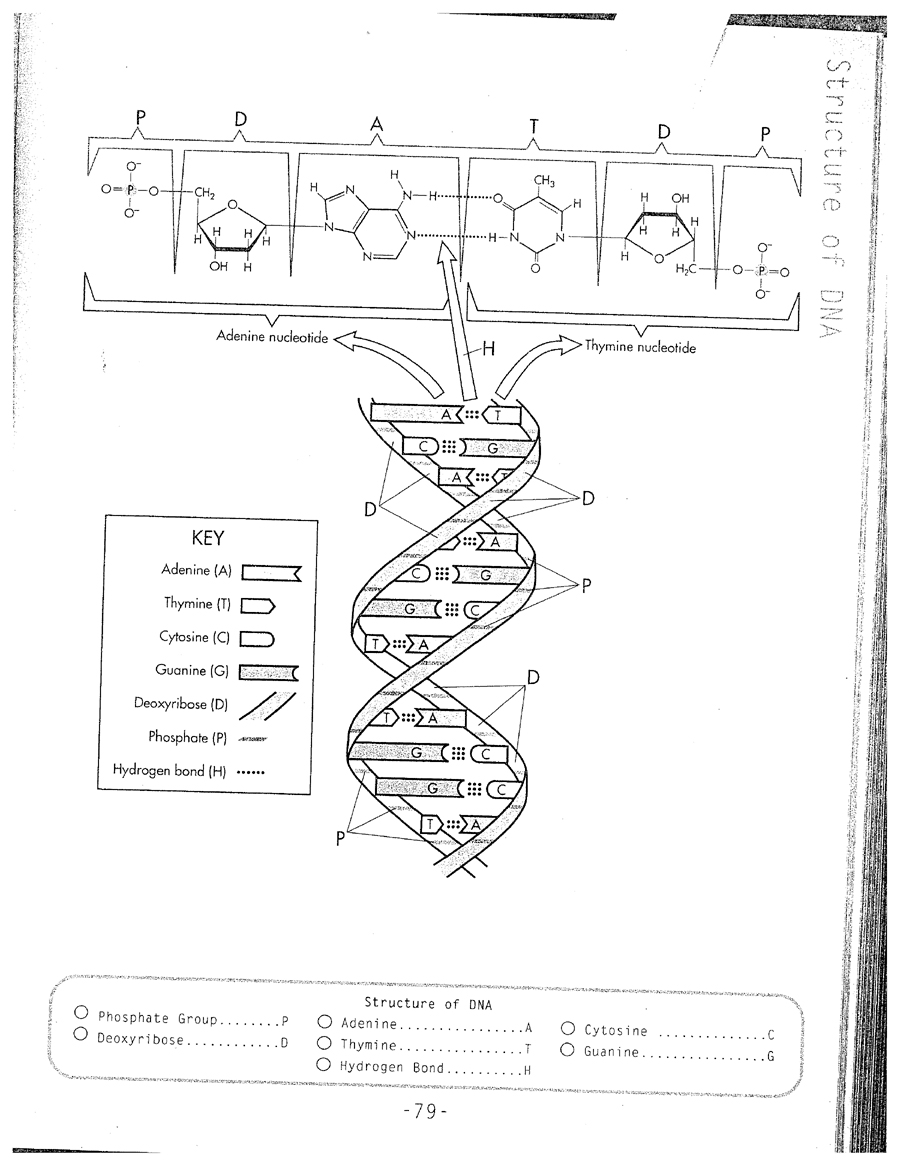
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double helix structure composed of two complementary strands that are made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or thymine (T). The nucleotide bases on opposite strands pair up in a specific way - adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine - which allows the genetic information to be accurately replicated during cell division.
What is the function of DNA?
The main function of DNA is to store and transmit genetic information that directs the development, growth, and functioning of living organisms. DNA carries the instructions needed for an organism to build, maintain, and reproduce itself, as well as to control and regulate its activities and functions.
How is DNA replicated?
DNA replication is a process where the double-stranded DNA molecule is unwound and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. Enzymes known as DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the growing new strand, following the base pairing rules (A with T and G with C). This results in two identical DNA molecules that each contain one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other to form the rungs of the DNA double helix, with A always pairing with T and C always pairing with G.
How is DNA different from RNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is double-stranded and contains the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is single-stranded and contains the bases adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Additionally, DNA serves as the genetic material in most organisms and is found in the cell nucleus, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and can be found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of a cell.
What is the role of enzymes in DNA replication?
Enzymes play a critical role in DNA replication by facilitating the process of unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new DNA strands, and proofreading for accuracy. Enzymes such as helicase unwind the double helix, polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides, and exonuclease proofreads the newly synthesized DNA for errors. These enzymes work together to ensure that DNA is accurately and efficiently replicated during cell division.
How does DNA determine an individual's traits?
DNA determines an individual's traits through its unique sequence of nucleotides, which encode instructions for building proteins. These proteins control various processes in the body that ultimately determine an individual's physical characteristics, such as eye color, height, and blood type. The specific combination of genes inherited from an individual's parents influences the expression of these traits, resulting in the diverse range of characteristics seen in humans.
What is a gene?
A gene is a specific sequence of DNA that contains the instructions for making a particular protein or performing a specific function in an organism. Genes are the basic units of heredity and play a crucial role in determining an individual's traits and characteristics.
What is genetic mutation and how does it occur?
A genetic mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence of a gene. It can occur due to various factors such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, or environmental factors. Mutations can affect the function of a gene, leading to changes in the protein it encodes or affecting the regulation of gene expression. These changes can have different effects on an organism, ranging from no impact to causing genetic disorders or increasing susceptibility to certain diseases.
How is DNA used in forensic science?
DNA is used in forensic science to identify individuals, determine familial relationships, and link suspects to crime scenes. By analyzing the unique DNA profiles of individuals, forensic scientists can match DNA found at a crime scene to potential suspects or victims. This powerful tool has revolutionized criminal investigations by providing irrefutable evidence that can be used in court to secure convictions or exonerate the innocent.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments