DNA Transcription Coloring Worksheet 84
The DNA Transcription Coloring Worksheet 84 is a valuable resource for students studying genetics or biology. This engaging worksheet focuses on the process of DNA transcription, offering a unique approach to learning by incorporating a coloring activity. By providing a hands-on way to understand this complex biological process, this worksheet is tailored to appeal to visual learners in middle school, high school, or even college-level students.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of DNA transcription?
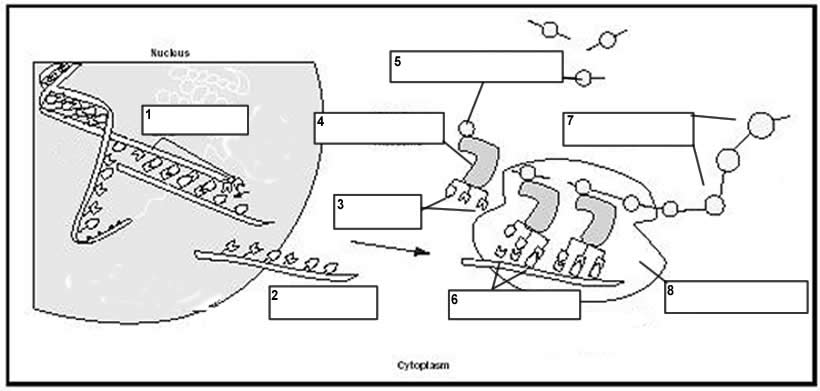
The purpose of DNA transcription is to create a complementary RNA copy of a specific gene from a DNA template. This process is essential for protein synthesis as the RNA copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesized. By transcribing specific genes into mRNA, cells can regulate gene expression and produce the proteins necessary for various cellular functions and processes.
What enzyme is responsible for DNA transcription?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for DNA transcription. It catalyzes the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template during transcription in the process of gene expression.
What is the role of the promoter region in DNA transcription?
The promoter region in DNA transcription is responsible for initiating the process of transcription. It acts as a binding site for RNA polymerase, which is the enzyme responsible for transcribing the DNA into RNA. The promoter region contains specific sequences that are recognized by transcription factors, which help recruit RNA polymerase to the correct location on the DNA strand to start transcription. Essentially, the promoter region serves as a signal to indicate where transcription should begin and helps regulate the expression of genes by controlling when and how often they are transcribed into RNA.
What is the template strand in DNA transcription?
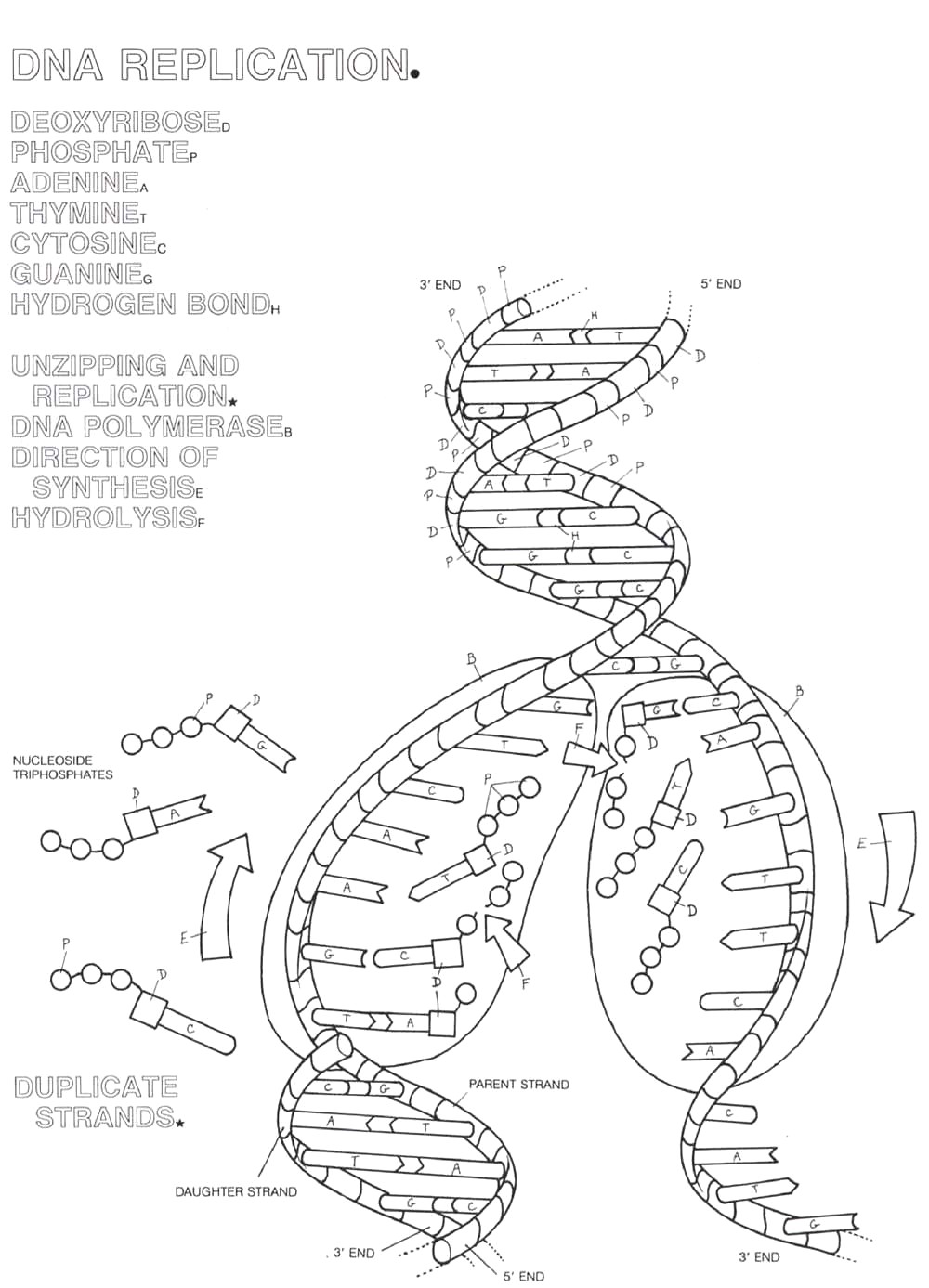
The template strand in DNA transcription is the strand of DNA that serves as a guide for the complementary base pairing during the synthesis of mRNA. This strand is used by RNA polymerase to create a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the template DNA strand.
What are the three steps involved in DNA transcription?
The three steps involved in DNA transcription are initiation, where the RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of the DNA; elongation, where the RNA polymerase synthesizes a complementary RNA strand using the DNA template; and termination, where the RNA polymerase reaches a termination sequence and releases the newly formed RNA strand.
What is the function of RNA polymerase in DNA transcription?
RNA polymerase plays a crucial role in DNA transcription by catalyzing the synthesis of an RNA strand from a DNA template. It recognizes a specific region on the DNA called the promoter and unwinds the DNA double helix to expose the template strand. Then, it joins complementary RNA nucleotides together to form an RNA transcript that is complementary to the DNA template. This process is essential for the transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA, which can then be used for protein synthesis.
How is the coding strand different from the template strand in DNA transcription?
The coding strand, also known as the sense strand, has the same sequence as the mRNA transcript except with thymine (T) instead of uracil (U). It is not directly involved in transcription but serves as a reference for protein synthesis. The template strand, on the other hand, is the complementary strand to the coding strand and is used as a template for mRNA synthesis during transcription. The RNA polymerase reads the template strand and synthesizes an mRNA molecule that is complementary to it.
What is the significance of transcription factors in DNA transcription?
Transcription factors are essential proteins that regulate the process of DNA transcription by binding to specific DNA sequences and either promoting or inhibiting the recruitment of RNA polymerase to initiate the transcription of a particular gene. They help in controlling the rate of gene expression and play a crucial role in determining which genes are active in a particular cell at a specific time. Transcription factors are therefore key players in coordinating and regulating the complex process of gene transcription, ultimately influencing various cellular processes and functions.
What is the difference between primary transcript and mature mRNA in DNA transcription?
The primary transcript is the initial RNA molecule transcribed from a gene during transcription in the nucleus, containing both exons and introns. The mature mRNA, on the other hand, is the processed and edited version of the primary transcript, where introns have been spliced out and exons have been joined together. This mature mRNA is then ready to be exported to the cytoplasm for translation into a protein.
What is the role of RNA processing in DNA transcription?
RNA processing is an essential step that occurs during and after DNA transcription. It involves a series of modifications such as adding a 5' cap, splicing out introns, and adding a poly-A tail to the pre-mRNA transcript to generate a mature mRNA molecule. These modifications are critical for stabilizing the mRNA, facilitating its transport out of the nucleus, and directing the protein synthesis machinery during translation. Overall, RNA processing ensures that the genetic information encoded in the DNA is accurately and efficiently transcribed into functional proteins.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments