DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
The DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive and clear understanding of the entity and subject of DNA structure. Designed for students studying biology, genetics, or biochemistry, this worksheet offers an organized and detailed overview of the key components that make up the structure of DNA. Whether you are a teacher seeking a useful resource for your classroom or a student searching for a reliable study guide, this answer key offers a concise and accurate description of the various aspects of DNA structure.
Table of Images 👆
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
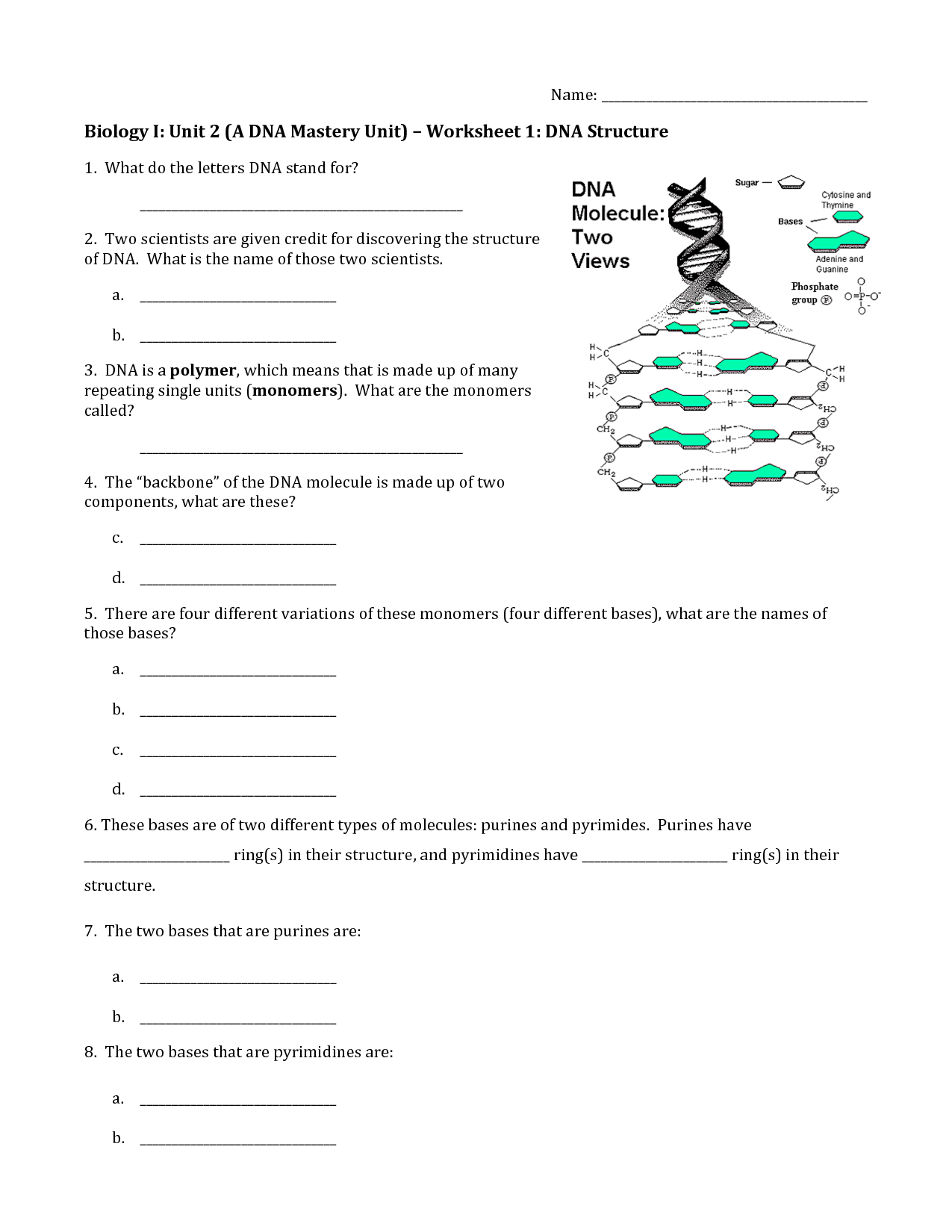
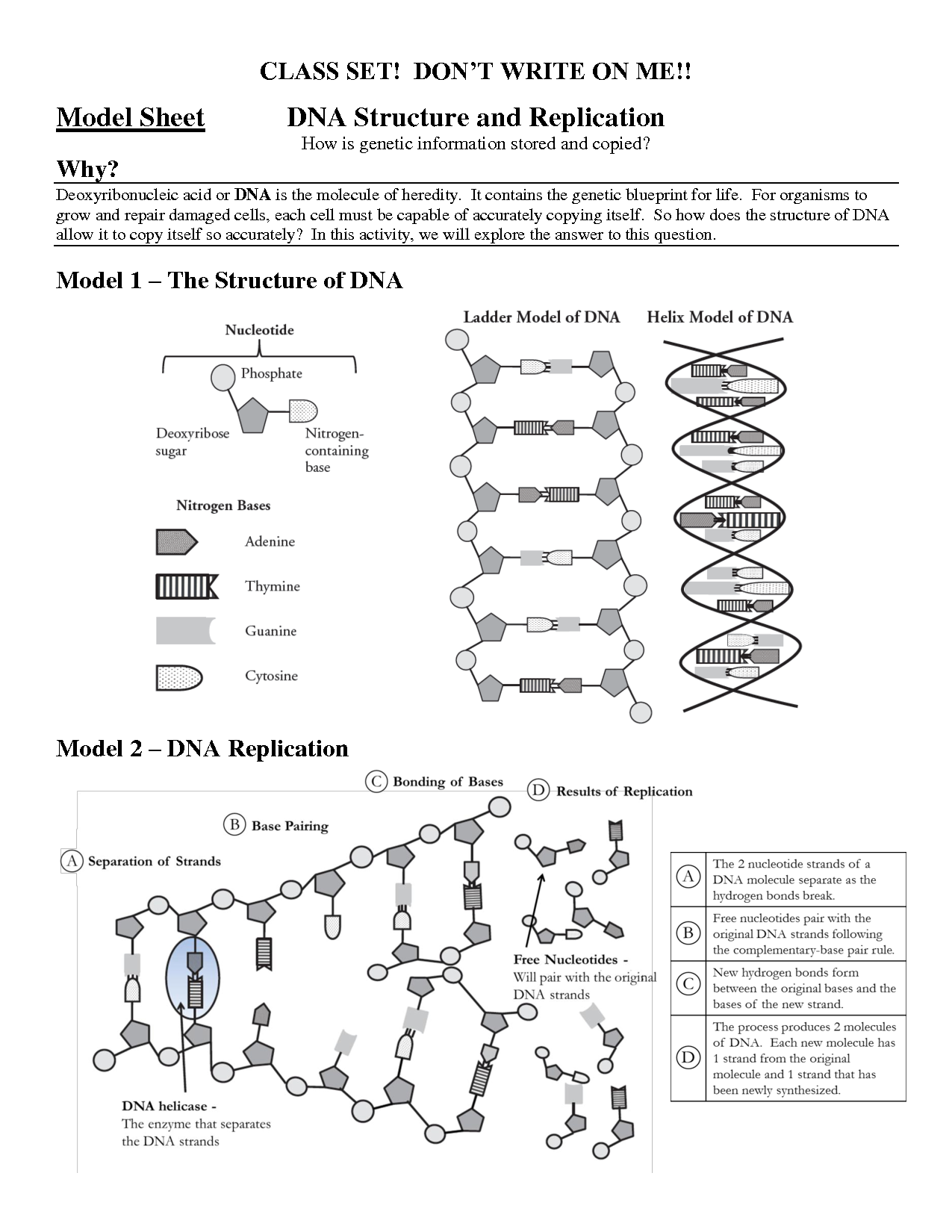
What is the shape of DNA? - Double helix
Yes, the shape of DNA is a double helix. This means that the DNA molecule consists of two strands twisting around each other in a spiral formation. This structure was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, and it plays a crucial role in storing and transmitting genetic information in living organisms.
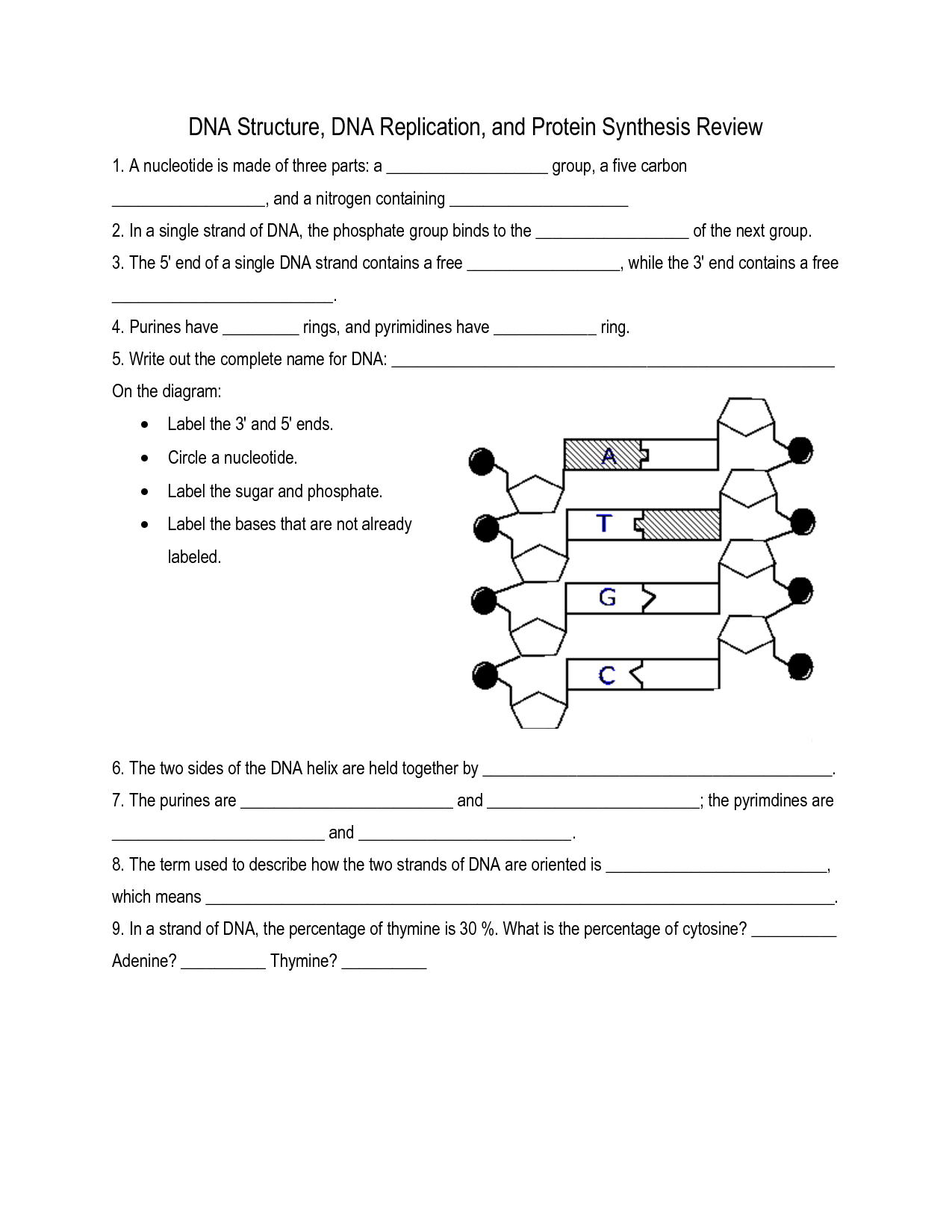
What are the building blocks of DNA? - Nucleotides
Yes, the building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). These nucleotides are arranged in a specific sequence to form the double helix structure of DNA, which carries genetic information in living organisms.
What does DNA stand for? - Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic acid
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA? - Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine.
What bonds hold the two strands of DNA together? - Hydrogen bonds
Yes, hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA together. These bonds form between specific base pairs: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). The hydrogen bonds between these base pairs help stabilize the structure of the DNA molecule.
What is the role of the sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA? - Provides a structural support for the nitrogenous bases
The sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA provides a structural support for the nitrogenous bases, helping to stabilize the overall structure of the double helix. It also serves as a foundation for the attachment of the nucleotide bases, which contain the genetic information encoded in the sequence of the bases along the backbone.
Where is DNA found in a eukaryotic cell? - Nucleus
DNA is found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, where it is organized into chromosomes and plays a crucial role in the storage and transmission of genetic information.
What is the function of DNA replication? - To make an identical copy of the DNA
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. This ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information during cell division, allowing for accurate transmission of genetic material from one generation to the next.
What is the significance of the complementary base pairing in DNA? - It allows for the accurate replication and transcription of genetic information
The complementary base pairing in DNA, where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine, is significant as it ensures accurate replication and transcription of genetic information. During replication, each base pairs with its complementary partner, resulting in two identical DNA molecules. During transcription, the DNA sequence is copied into RNA with the help of complementary base pairing. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity of genetic information and ensuring the fidelity of protein synthesis.
How does DNA encode genetic information? - Through the sequence of its nitrogenous bases, which determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins.
Yes, DNA encodes genetic information through the sequence of its nitrogenous bases. The four bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine determine the genetic code by forming codons that specify individual amino acids in proteins. By reading the sequence of bases in DNA, cells can accurately transcribe and translate this information into functional proteins that carry out various biological functions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments