DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Key
Understanding the structure and replication of DNA is a crucial aspect of biology education. For teachers and students seeking a comprehensive and reliable resource to reinforce this topic, the DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Key is an ideal solution. This worksheet delivers a concise and informative overview of DNA structure and replication, enabling students to grasp these concepts with ease.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the primary function of DNA?
The primary function of DNA is to store and transmit genetic information that determines the characteristics and traits of an organism. It contains the instructions needed for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living things.
Describe the double helix structure of DNA.
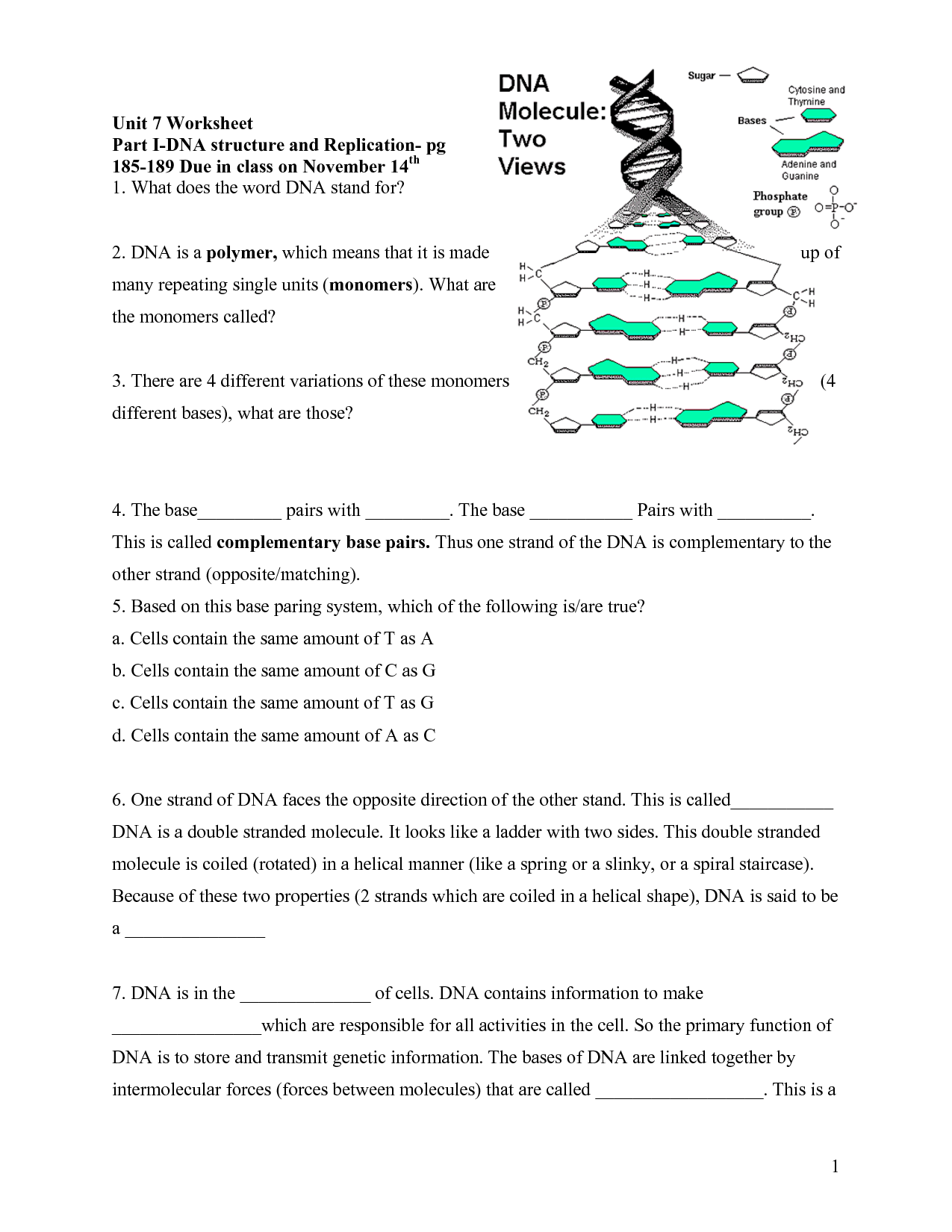
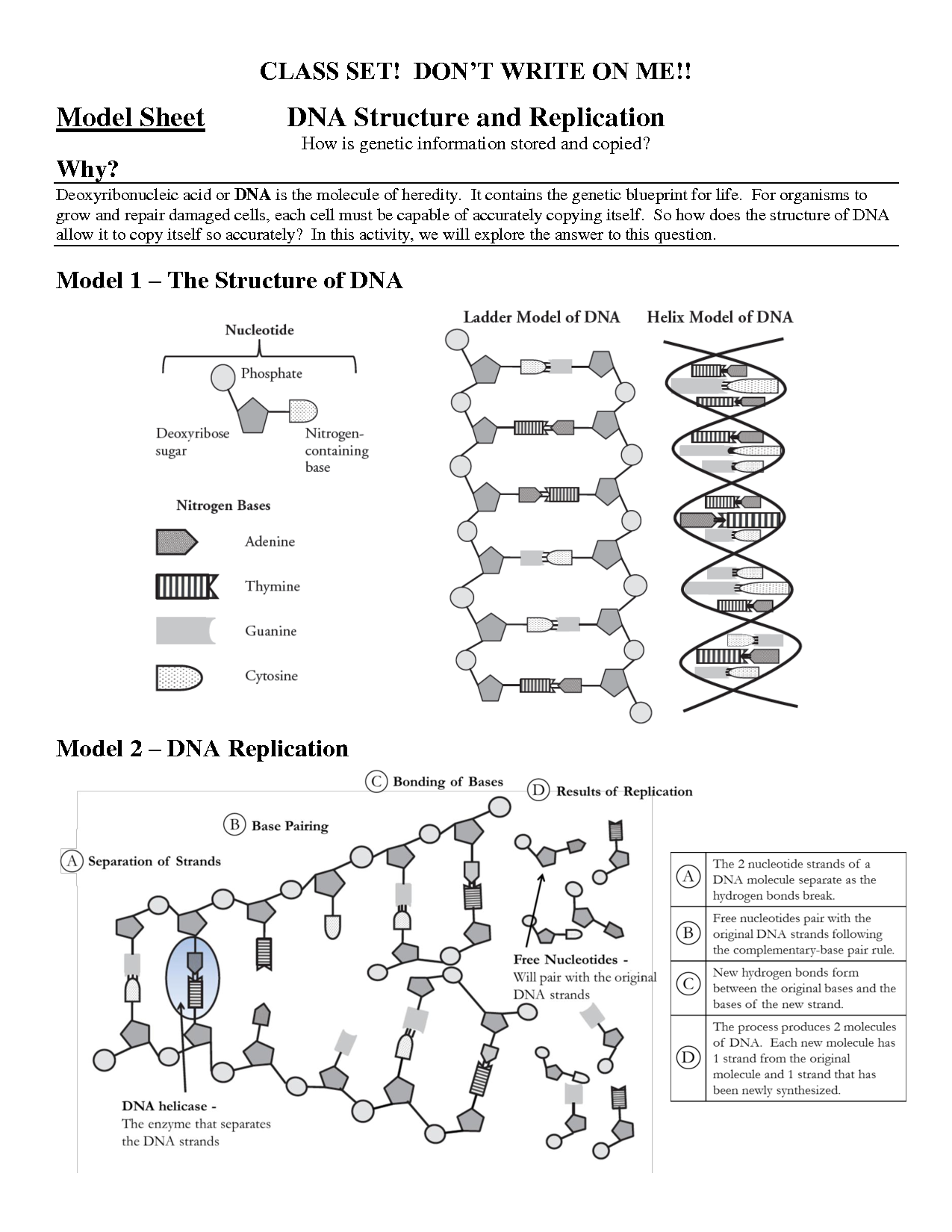
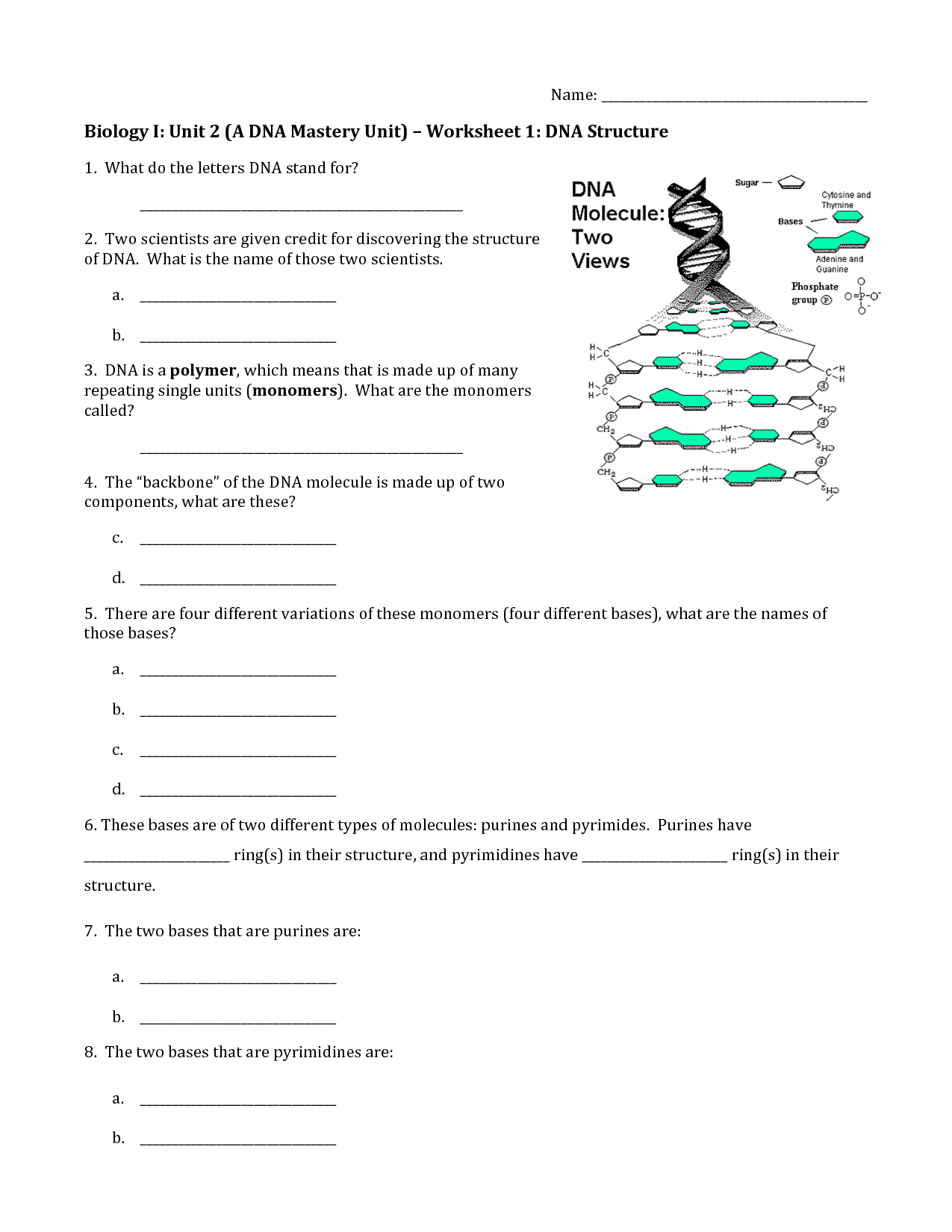
The double helix structure of DNA is a twisted ladder-like shape formed by two strands of nucleotides. These strands are composed of sugars and phosphate molecules, connected by pairs of nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between these base pairs, creating a stable structure. This helical shape allows the genetic information stored in DNA to be tightly packed and easily replicated during cell division.
Explain the complementary base pairing in DNA.
Complementary base pairing in DNA refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases between the two antiparallel strands of the DNA double helix. Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds, while guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. This base pairing ensures that the genetic information stored in DNA is accurately replicated during cell division, with each strand serving as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This precise pairing mechanism is crucial for maintaining the integrity of genetic information and ensuring the proper functioning of cells.
What are the building blocks of DNA called, and what does each one consist of?
The building blocks of DNA are called nucleotides, and each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine). These nucleotides link together in a specific sequence to form the double helix structure of DNA, which carries genetic information in living organisms.
How does DNA replication occur?
During DNA replication, the double helix of DNA unwinds, and the two strands separate. Each separated strand then serves as a template for the creation of a new complementary strand. Enzymes known as DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the growing new strand based on the template provided by the original strand. The result is two identical copies of the original DNA molecule, each containing one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in replication?
DNA polymerase is responsible for synthesizing new strands of DNA during replication. This enzyme adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of DNA, ensuring accurate copying of genetic information. It also has proofreading capabilities to detect and correct errors, maintaining the fidelity of the newly synthesized DNA. DNA polymerase plays a crucial role in ensuring that genetic information is faithfully passed on during cell division.
What is the significance of the leading and lagging strands in replication?
The leading and lagging strands play a crucial role in DNA replication. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, meaning that nucleotides are added one after another in a smooth, rapid manner. In contrast, the lagging strand is synthesized in fragments called Okazaki fragments, where DNA polymerase synthesizes short segments in the 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork. These fragments are later stitched together by DNA ligase. This process ensures accurate and efficient replication of both strands of DNA during cell division.
How does DNA repair mechanisms ensure the accuracy of DNA replication?
DNA repair mechanisms ensure the accuracy of DNA replication by constantly monitoring the DNA for any errors or damage. If a mistake is detected during replication, repair mechanisms such as base excision repair and mismatch repair can correct the error. This ensures that the new copy of DNA is a faithful replica of the original, minimizing mutations and maintaining the integrity of the genetic information.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase is an enzyme responsible for unwinding the double-stranded DNA molecule during DNA replication. It does this by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the two strands, allowing them to separate and expose the nucleotide bases for replication to occur. This process is essential for ensuring accurate and efficient DNA replication.
Why is DNA replication considered semi-conservative?
DNA replication is considered semi-conservative because each newly synthesized DNA molecule consists of one original (parental) strand and one newly synthesized (daughter) strand. During replication, the parental DNA molecule unwinds and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand, resulting in two daughter DNA molecules that each contain one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This process ensures that genetic information is accurately preserved and passed on to daughter cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments