DNA Replication Worksheet Middle School
This blog post will discuss a useful tool called worksheets that can greatly assist middle school students in understanding the concept of DNA replication. Worksheets are designed to provide structured practice and consolidate knowledge on a specific subject, such as DNA replication, allowing students to engage with the material more effectively and improve their understanding of the topic.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA Replication Worksheet Key
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- Character Analysis Worksheets High School
- DNA Replication Steps Worksheet
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Function Worksheet
- Worksheets DNA Coloring Page
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy DNA
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
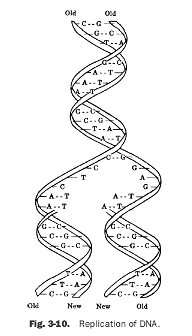
What is DNA replication?
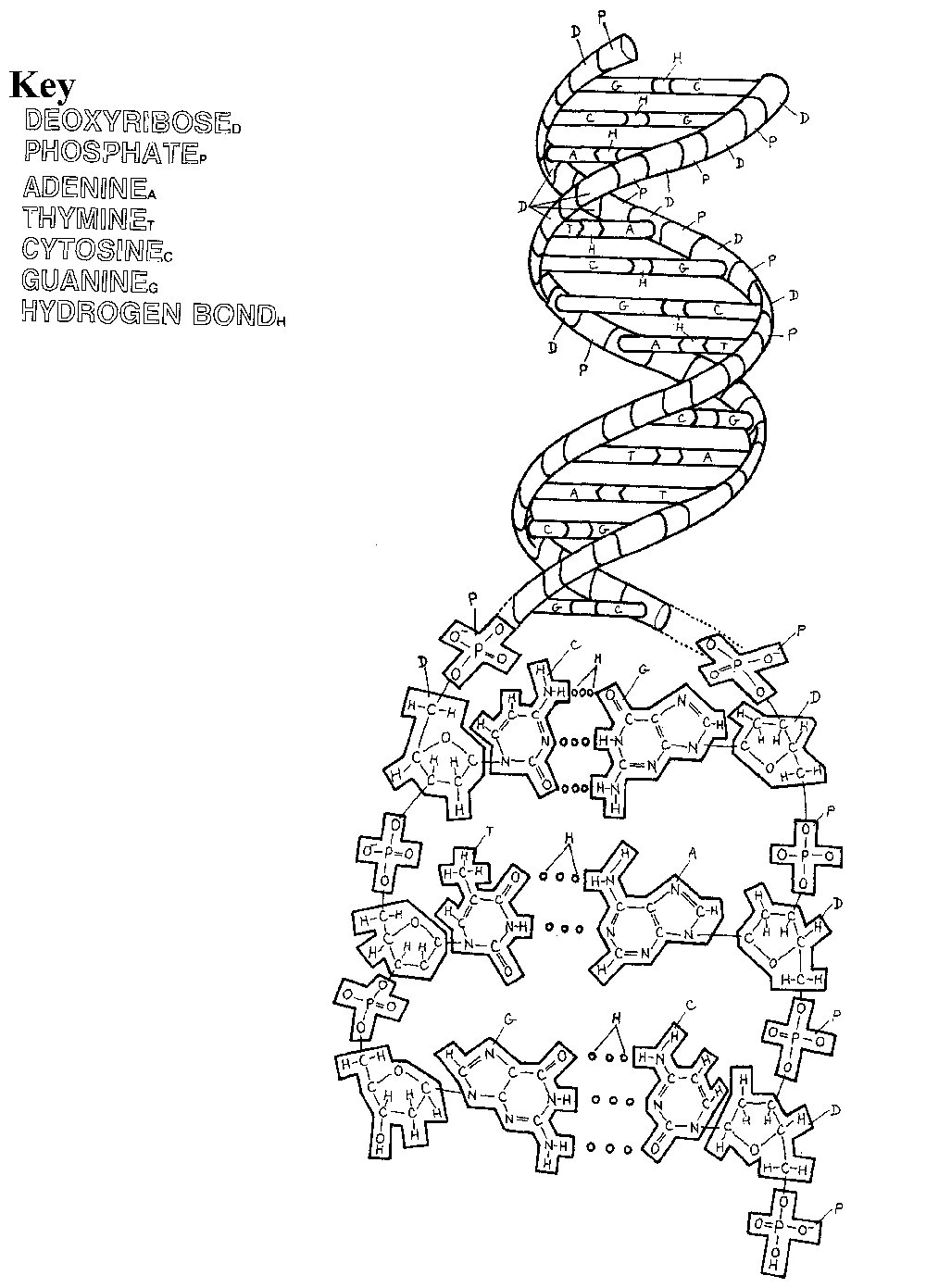
DNA replication is the biological process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. This intricate process involves the unwinding of the double helix structure of DNA, followed by the synthesis of new complementary strands through the pairing of nucleotides. DNA replication is essential for cell division and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Why is DNA replication important?
DNA replication is crucial for various reasons. It ensures that genetic information is faithfully passed on to daughter cells during cell division, allowing for the continuation of life and growth. Additionally, accurate DNA replication is essential for maintaining genetic stability and preventing mutations that could lead to genetic diseases or cancer. DNA replication also allows for the repair of damaged DNA, ensuring the survival and proper functioning of cells.
Where does DNA replication occur in the cell?
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. It is a crucial process for cell division and the transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.
What is the first step of DNA replication?
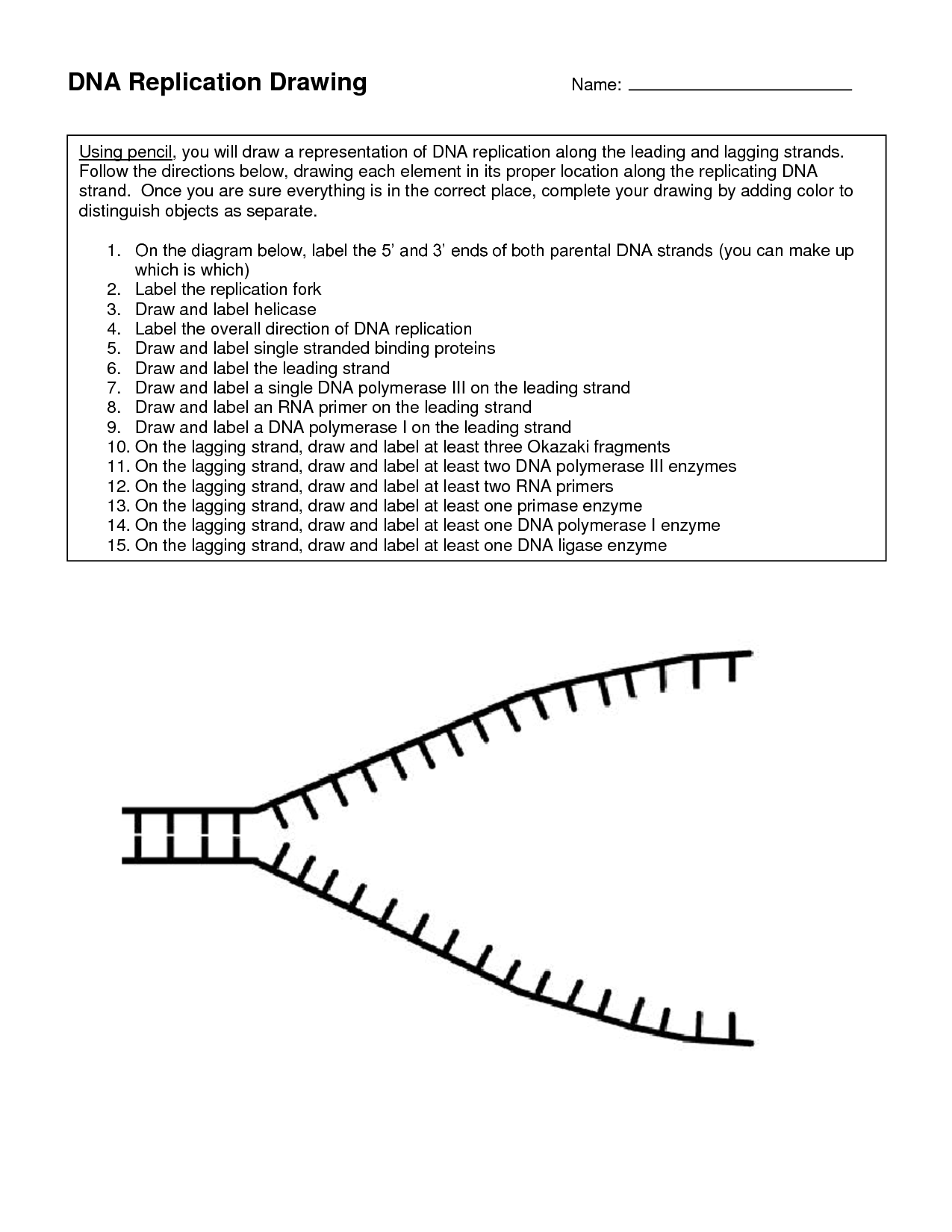
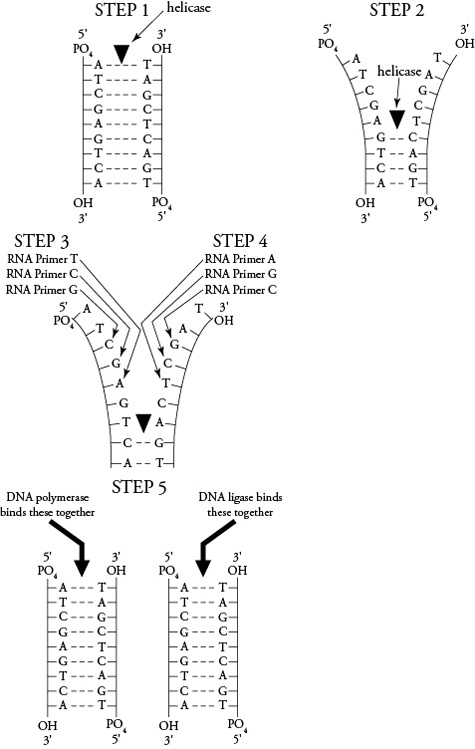
The first step of DNA replication is the unwinding of the double helix structure of the DNA molecule by an enzyme called helicase, which breaks hydrogen bonds between the base pairs and separates the two strands of the DNA.
What enzyme is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix?
The enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix is called DNA helicase. DNA helicase functions by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs of the DNA strands, allowing the two strands to separate and unwind to expose the genetic information for processes such as replication or transcription.
What are the two strands of DNA called during replication?
During replication, the two strands of DNA are called the leading strand and the lagging strand.
What is the role of DNA polymerase during replication?
DNA polymerase plays a crucial role during replication by catalyzing the synthesis of a new complementary DNA strand using the original DNA strand as a template. It adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, proofreads for errors, and ensures the accurate and faithful replication of the genetic information. This enzyme helps maintain the integrity of the genetic material and is essential for cell division and passing on genetic information to offspring.
How are errors or mistakes in DNA replication corrected?
DNA replication errors or mistakes are corrected through a process called DNA repair. There are mechanisms in place within the cell to detect errors in replicated DNA and fix them. One common mechanism is through the use of DNA polymerases that have proofreading capabilities to identify and correct errors as they occur during replication. Additionally, cells have specialized repair pathways such as mismatch repair, nucleotide excision repair, and base excision repair to correct different types of DNA damage. These repair mechanisms help maintain the integrity of the genetic information passed on during cell division.
What is the end result of DNA replication?
The end result of DNA replication is two identical DNA molecules, each composed of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This process ensures that each newly formed cell receives a complete and accurate copy of the genetic information stored in the original DNA molecule.
How does DNA replication ensure the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next?
DNA replication ensures the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next by accurately copying the DNA molecule during cell division. This process involves unwinding the double helix structure of the DNA, synthesizing new complementary strands using each original strand as a template, and then reassembling the double helix with the newly synthesized strands. The fidelity of this process is maintained by proofreading mechanisms and DNA repair processes that help to prevent errors or mutations from being passed on to the next generation, thereby preserving the integrity of the genetic information.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments