DNA Replication Worksheet Answers 16
Worksheets are an essential tool for students seeking to solidify their understanding of complex subjects. When it comes to the topic of DNA replication, having access to reliable and accurate answers to worksheet exercises is crucial. Whether you are a biology student, a science enthusiast, or an educator looking for valuable resources, having access to DNA Replication Worksheet Answers can greatly enhance your learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- Pearson Education Biology Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Punnett Square Practice Problems Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Diagram
- Enlightenment Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
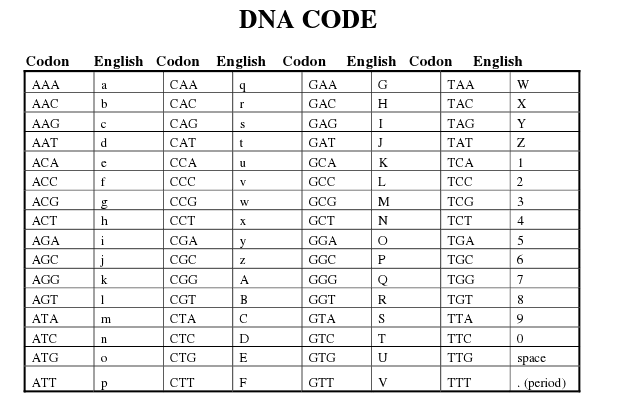
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
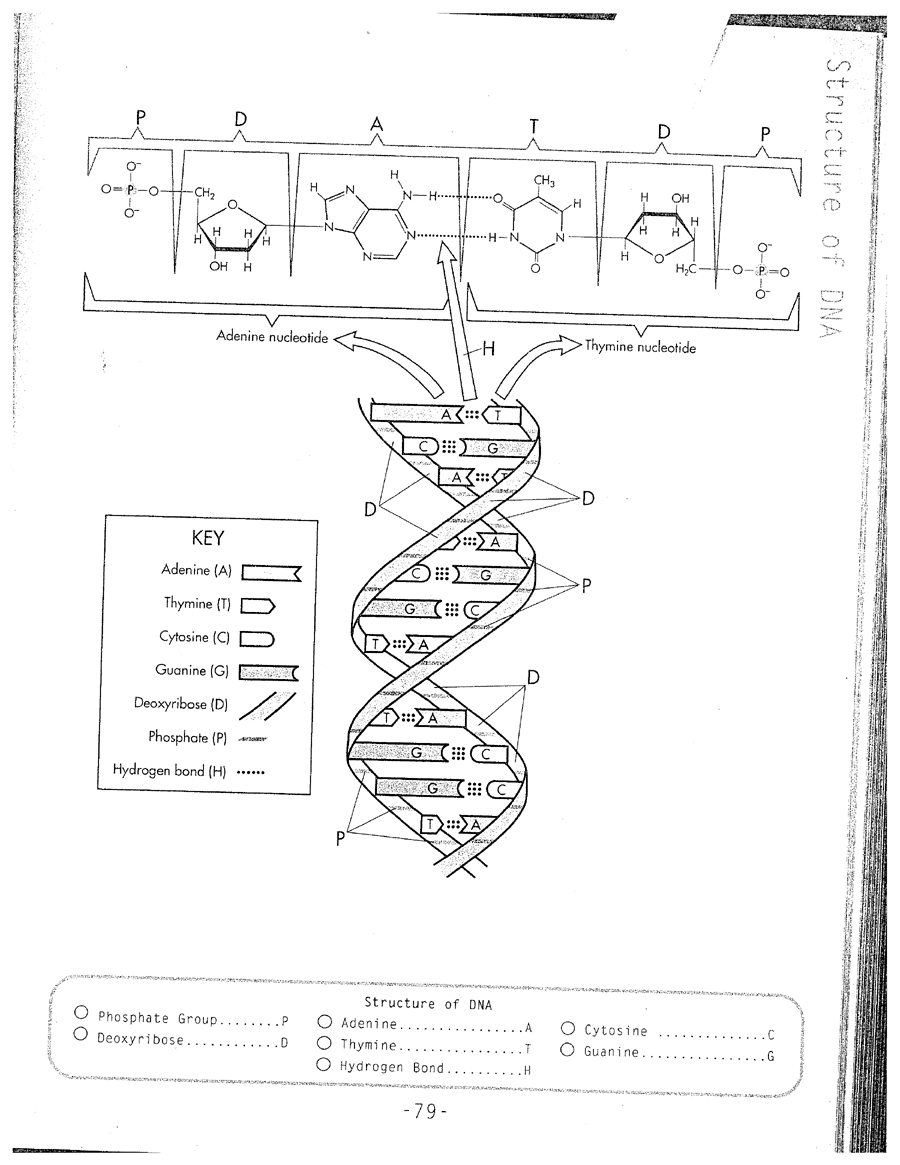
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the biological process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and growth, as well as for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. During DNA replication, the double-stranded DNA molecule unwinds and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand, resulting in two identical double-stranded DNA molecules.
DNA replication is the process by which a DNA molecule makes an exact copy of itself.
DNA replication is the process in which a DNA molecule duplicates itself to produce an identical copy.
Where does DNA replication occur in the cell?
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and in the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell.
DNA replication occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Yes, DNA replication takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, the process occurs within the nucleus where the DNA is housed, while in prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, DNA replication occurs in the cytoplasm since prokaryotes lack a true nucleus. This crucial process allows for the accurate copying of genetic material to ensure proper cell division and functioning in both cell types.
What is the purpose of DNA replication?
The purpose of DNA replication is to accurately duplicate the genetic information contained within a cell's DNA before it divides. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions, allowing for growth, development, and maintenance of the organism. DNA replication also serves as a mechanism for repair and adaptation, as errors in DNA can be corrected and variations can arise through mutation.
The purpose of DNA replication is to ensure that each new cell receives an accurate and complete copy of the genetic information stored in the DNA molecule.
The purpose of DNA replication is to produce an identical copy of the DNA molecule for cell division, ensuring that each new cell receives an accurate and complete set of genetic information.
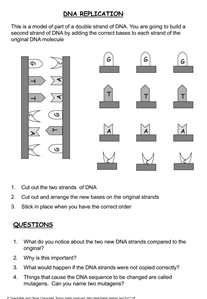
What are the three main steps of DNA replication?
The three main steps of DNA replication are initiation, where the DNA molecule unwinds and the replication fork is formed, elongation, where new DNA strands are synthesized by DNA polymerase using the existing strands as templates, and termination, where the replication process is completed and two identical daughter DNA molecules are produced.
The three main steps of DNA replication are initiation, elongation, and termination.
DNA replication starts with initiation, where the DNA unwinds and the double helix separates. Next is elongation, where new nucleotides are added to the growing strands of DNA. Lastly, termination occurs when replication is complete and the newly synthesized DNA molecules are fully formed.
What is the role of DNA helicase?
DNA helicase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication and repair processes. It is responsible for unwinding the double-stranded DNA helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the base pairs, thus allowing other enzymes, such as DNA polymerase, to access the DNA strands for replication or repair. This unwinding process is essential for the accurate and efficient copying of genetic information, ensuring the fidelity of DNA replication and maintenance of genome integrity.
DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs.
DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs, powering the separation of the two strands and allowing for processes such as DNA replication and repair to occur.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments