DNA and Genes Worksheet
In the world of genetics, understanding DNA and genes is essential. Whether you are a student studying biology or a science enthusiast curious about how our genetic code shapes who we are, a DNA and Genes worksheet can be a valuable tool. This worksheet provides an interactive and engaging way to explore the intricacies of DNA structure, gene expression, and the role they play in heredity and biological processes. Suitable for curious learners of all ages, this worksheet offers a comprehensive overview of the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Virtual Lab DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Genes Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Double Helix Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Code Chart Worksheet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Review Worksheet Answers
- Simple Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms. It is composed of two strands twisted into a double helix, with each strand made of a sequence of nucleotides containing the genetic code. DNA carries the blueprint for an organism's traits and characteristics, and is passed down from one generation to the next through the process of reproduction.
What is the structure of DNA?
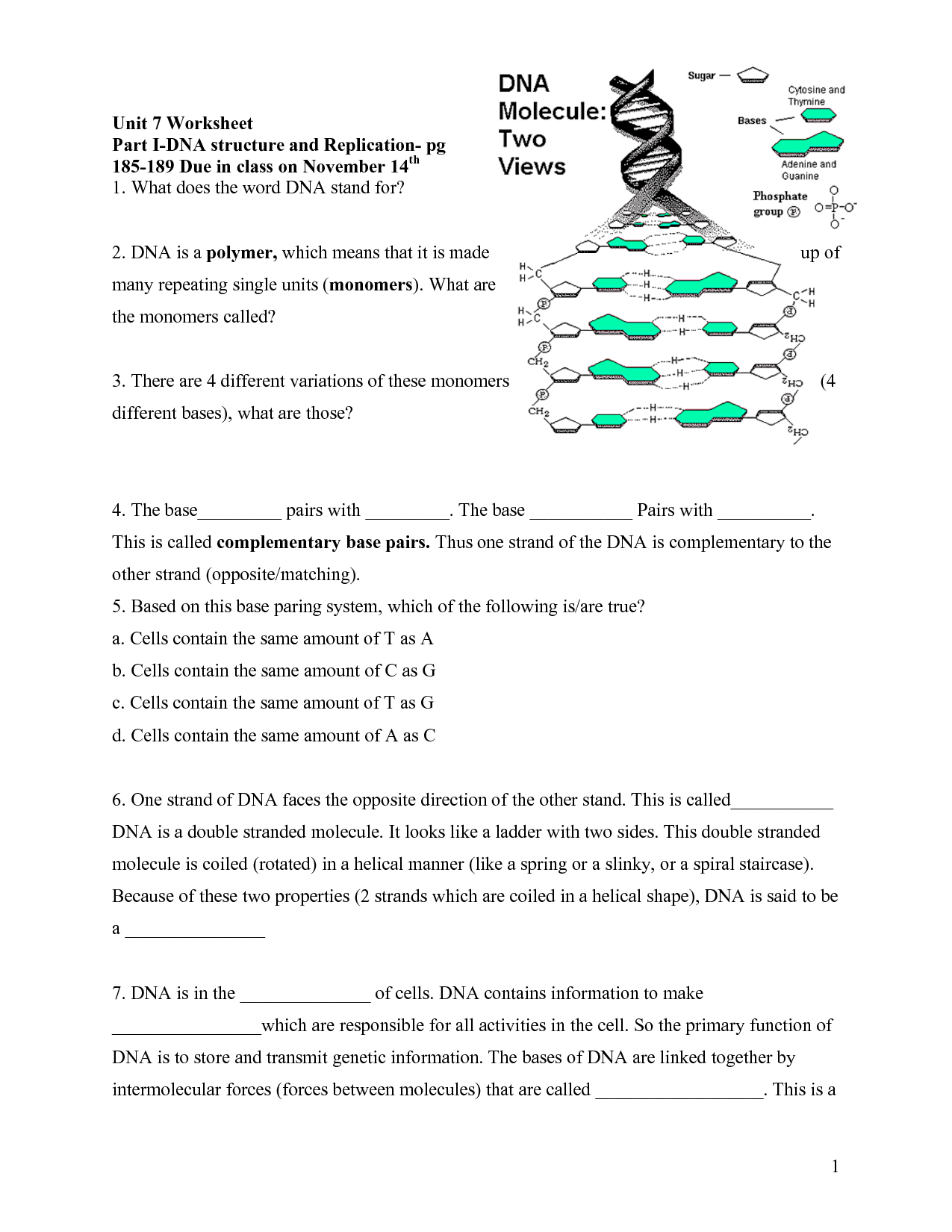
DNA is a double helix structure composed of two complementary strands made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine. This structure allows for the genetic information stored in DNA to be accurately replicated and transmitted during cell division.
What are genes?
Genes are segments of DNA that carry the instructions for creating specific proteins within a cell. These proteins play a vital role in determining the characteristics and functions of organisms. Genes are inherited from parents and serve as the blueprint for growth, development, and overall functioning of living organisms.
How are genes related to DNA?
Genes are segments of DNA that contain instructions for building proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells in our body. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms. Genes are made up of specific sequences of DNA that determine traits and characteristics passed down from generation to generation. Each gene codes for a specific protein or set of proteins that play a role in various biological processes.
What is the function of genes?
Genes are responsible for carrying and passing on hereditary information from one generation to the next, determining various physical and biological traits of an organism. They serve as the blueprint for the production of proteins that carry out specific functions in the body, playing a crucial role in the growth, development, and overall functioning of living organisms.
How are genes expressed?
Genes are expressed through a process known as gene expression, in which the information stored in a gene is used to create a functional product, such as a protein. This process involves two main steps: transcription, where a gene's DNA is copied into a messenger RNA molecule, and translation, where the RNA is decoded to build the corresponding protein. Gene expression is tightly regulated by various mechanisms, including transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and signaling pathways, to ensure that genes are only expressed when needed by the cell or organism.
What is the role of DNA replication in genes?
DNA replication plays a critical role in genes by ensuring that genetic information is accurately copied and transferred to new cells during cell division. This process is essential for the inheritance of genetic traits and the maintenance of genetic stability. Additionally, DNA replication allows for the production of RNA molecules, which serve as templates for protein synthesis. Without DNA replication, cells would not be able to reproduce, leading to the loss of genetic information and potentially harmful mutations.
How do genes influence traits and characteristics?
Genes influence traits and characteristics by carrying the coded instructions for specific proteins that determine an organism's physical and functional traits. These instructions regulate processes such as growth, development, metabolism, and biological functioning, ultimately shaping an individual's phenotypic traits based on the interactions between genes and the environment. Genetic variations and mutations can lead to differences in traits within a population, highlighting the significant role genes play in influencing an organism's characteristics.
What is the relationship between genes and heredity?
Genes play a crucial role in heredity as they are the units of inheritance that are passed down from parents to offspring. Genes contain the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, determining traits such as eye color, height, and predisposition to certain diseases. Essentially, genes are the blueprint for an individual's characteristics, and they are transmitted through generations, influencing an individual's heredity.
How does variation in genes contribute to evolution?
Variation in genes contributes to evolution by providing the raw material upon which natural selection can act. In a population, individuals with different genetic variations may have diverse traits that affect their survival and reproductive success. Through natural selection, beneficial traits that provide a competitive advantage are more likely to be passed on to future generations, leading to the accumulation of advantageous genetic variations over time and driving evolutionary change.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



































Comments