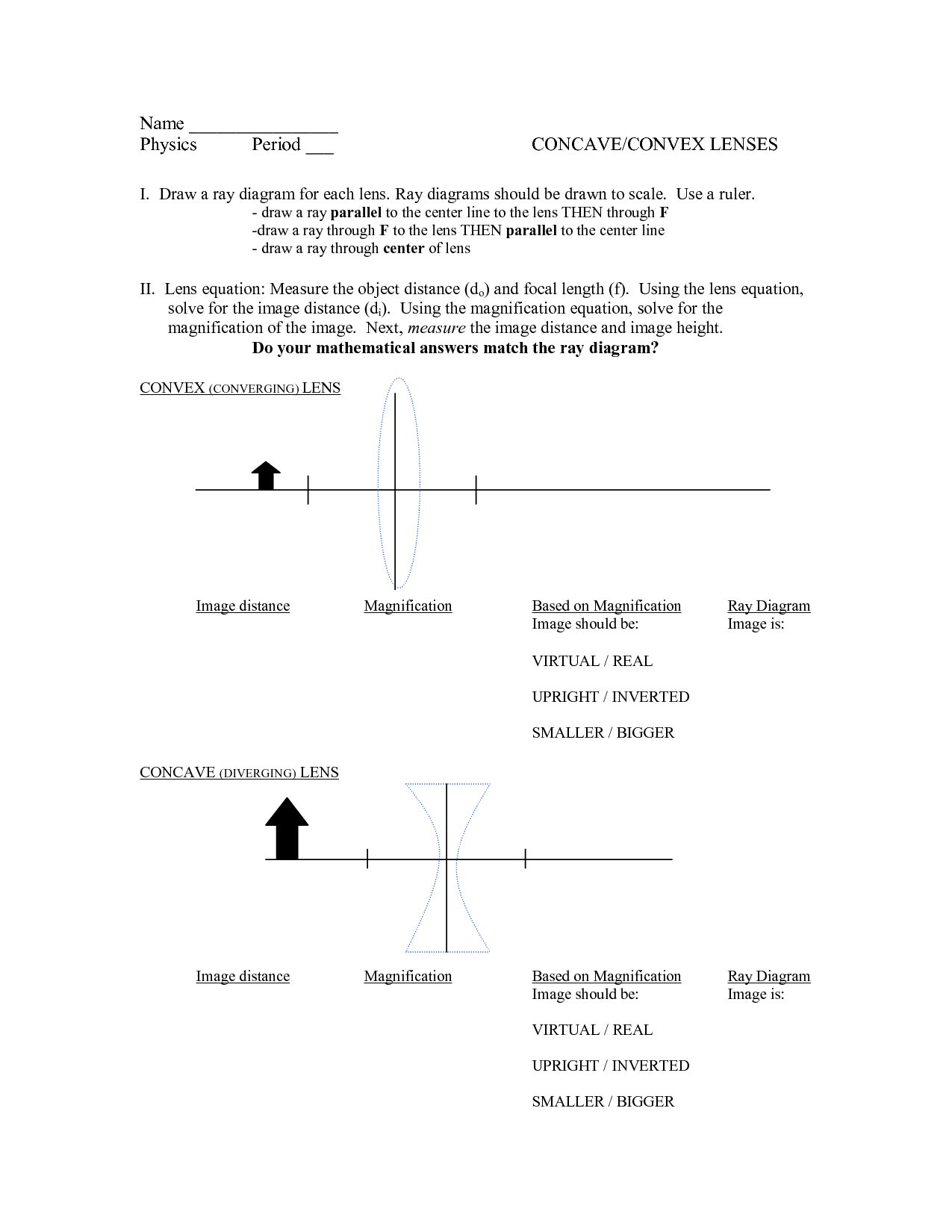
Diverging Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet
Are you a student studying optics or physics, looking for a helpful resource to practice ray diagrams with diverging lenses? Well, you're in luck! In this blog post, we will introduce you to a diverging lens ray diagram worksheet that will serve as an excellent tool for understanding and practicing this specific topic.
Table of Images 👆
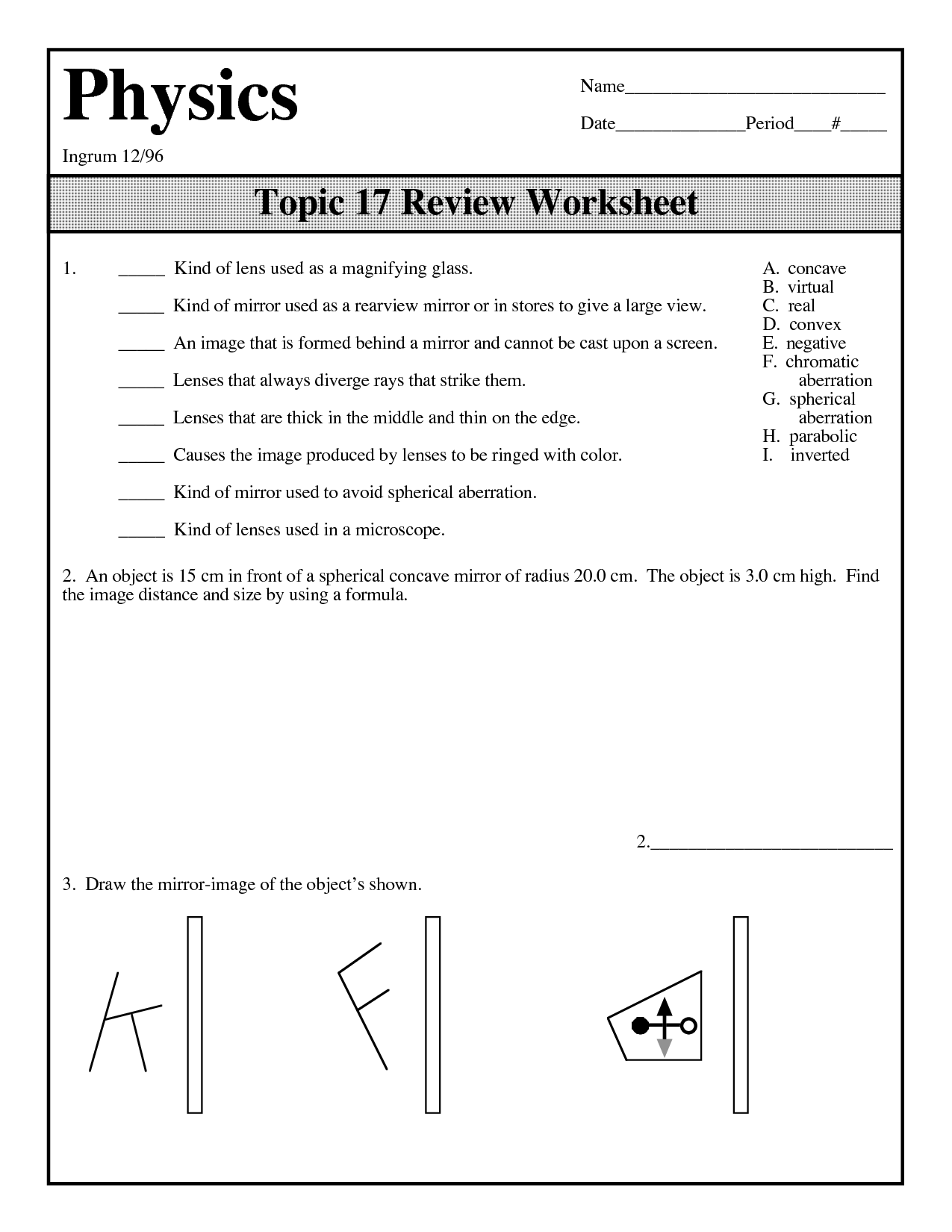
- Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Worksheet
- Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet
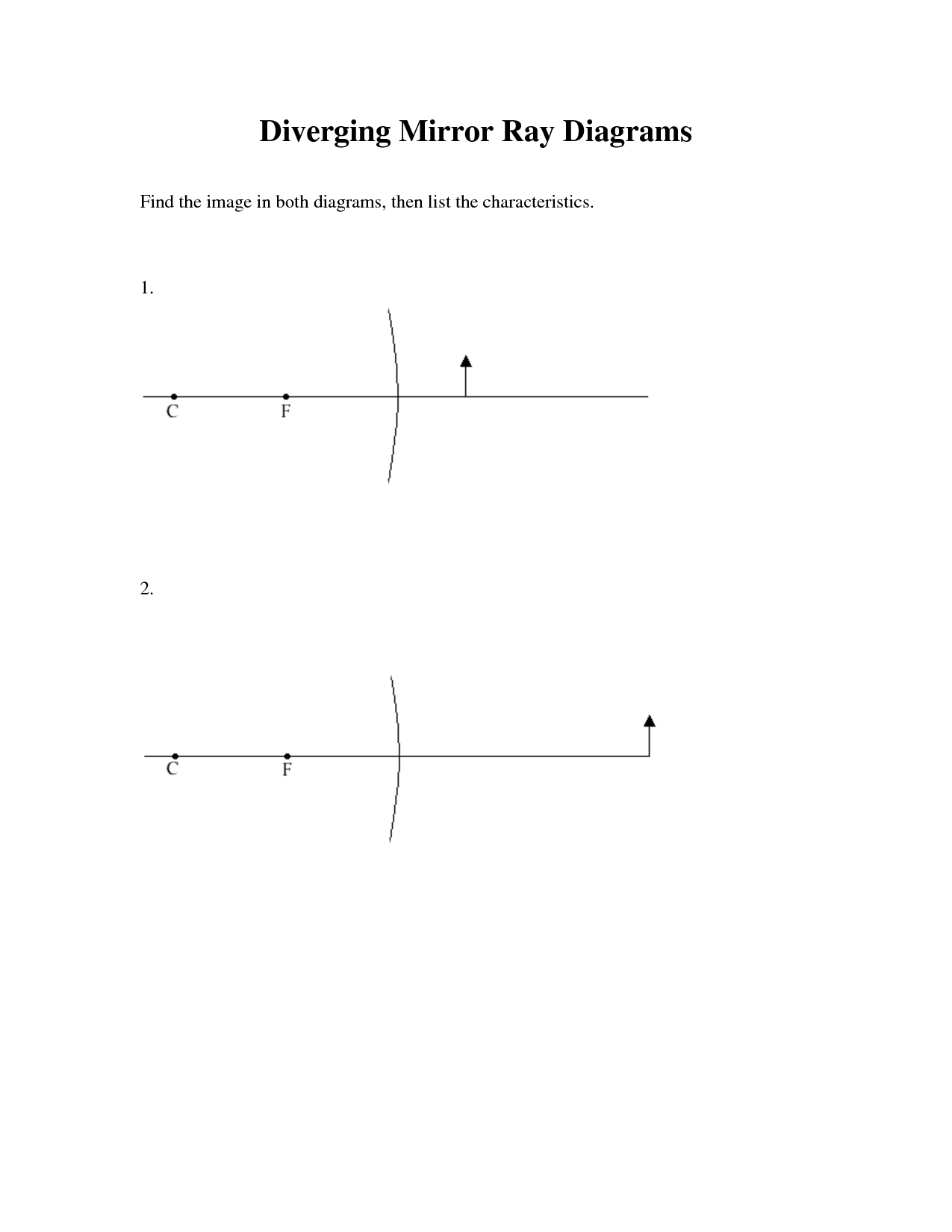
- Diverging Mirror Ray Diagram
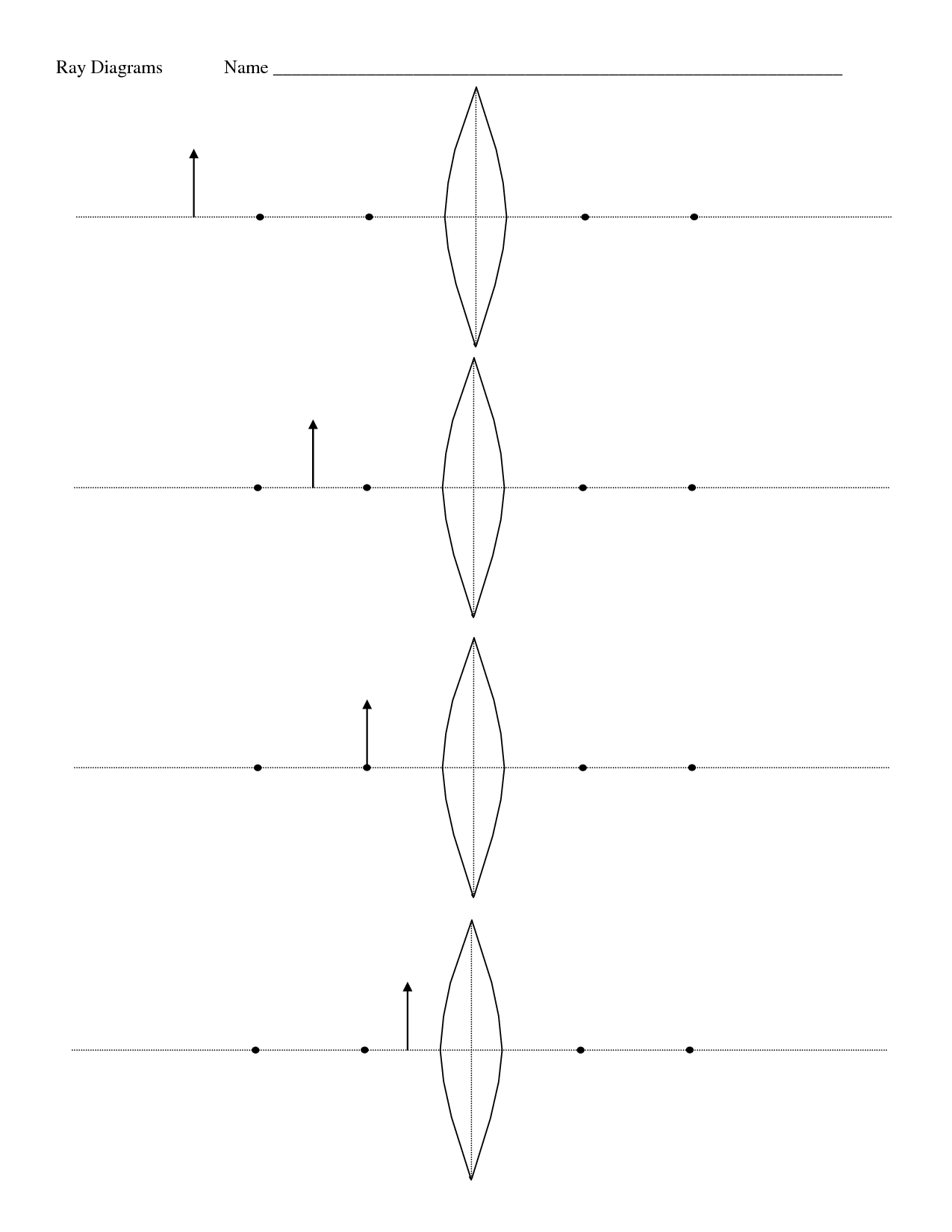
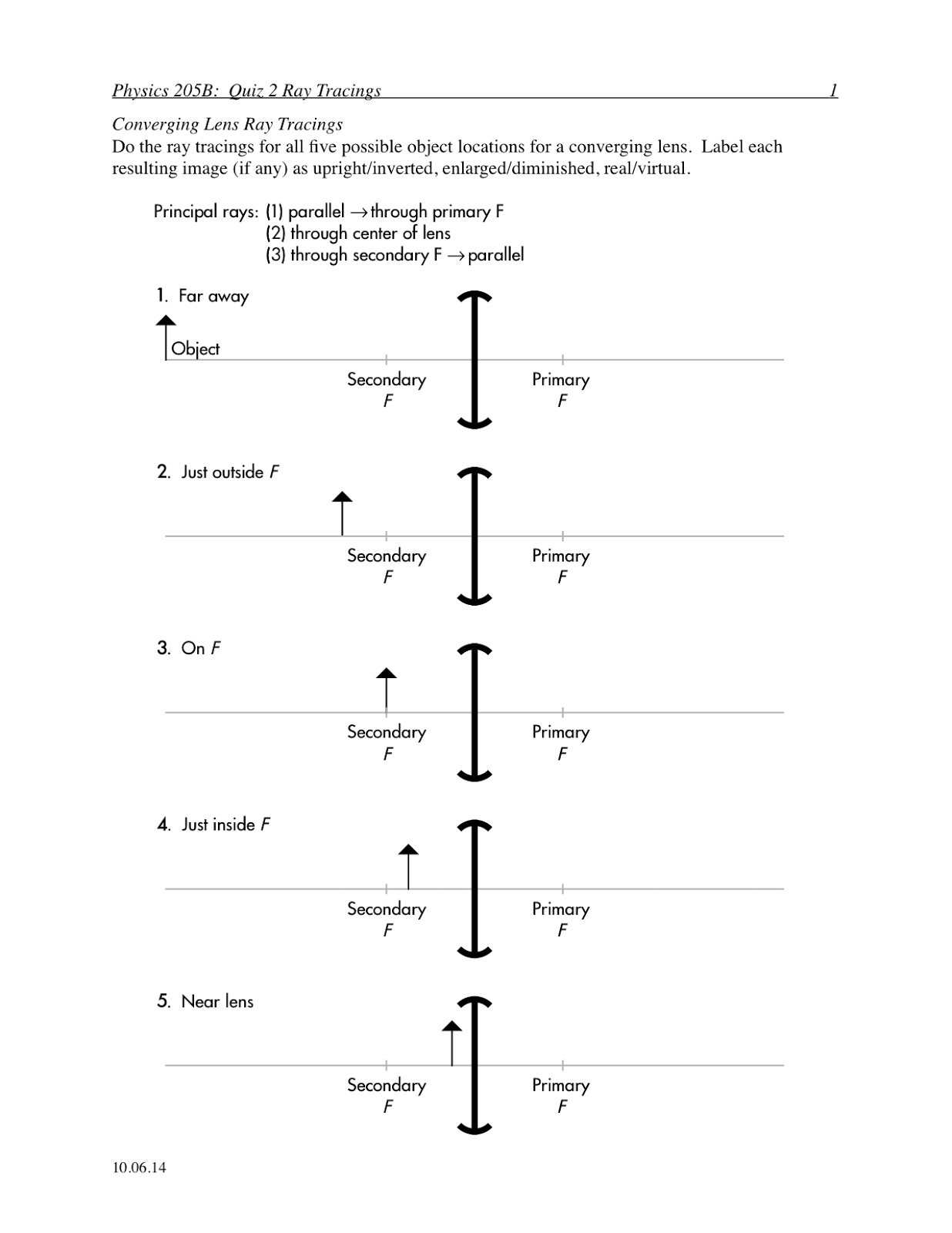
- Lens Ray Tracing Worksheet
- Convex Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet
- Ray Diagrams Lenses Diverging
- Lenses Ray Diagram Worksheet
- Converging Lenses Ray Diagrams
- Convex Lenses Practice Worksheet
- Concave and Convex Lenses Worksheet
- Mirror Ray Diagram Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a diverging lens?
A diverging lens is a lens that is thinnest in the center and thicker at the edges, causing parallel rays of light passing through it to spread out or diverge. This type of lens is concave in shape and causes light rays to refract in such a way that they appear to come from a virtual focus point located behind the lens. Diverging lenses are used to correct nearsightedness in eyeglasses and to reduce the effects of astigmatism in certain cases.
How does a diverging lens differ from a converging lens?
A diverging lens is thinner at the center than at the edges and causes light rays to spread out, resulting in the formation of a virtual image. On the other hand, a converging lens is thicker at the center than at the edges and causes light rays to converge towards a focal point, forming a real image. In summary, a diverging lens causes light rays to spread out, while a converging lens causes light rays to converge.
What is the focal length of a diverging lens?
The focal length of a diverging lens is a negative value.
How does the curvature of a diverging lens affect its behavior?
The curvature of a diverging lens affects its behavior by determining the amount of divergence of light rays passing through it. A greater curvature results in more divergence of light rays, leading to a greater dispersion of the light. This results in the diverging lens causing light rays to spread out, creating a virtual image that is upright and smaller than the object. The strength and characteristics of the divergence of the lens are directly related to the curvature of the lens surface.
What is the principal axis of a diverging lens?
The principal axis of a diverging lens is an imaginary line that passes through the center of the lens perpendicular to its surfaces. It is the axis along which the incident rays parallel to the principal axis appear to diverge after passing through the lens.
How are parallel rays of light affected when passing through a diverging lens?
Parallel rays of light passing through a diverging lens will diverge even further apart, as a diverging lens causes light rays passing through it to spread out rather than converge. This results in the formation of virtual images that appear smaller and upright compared to the original object.
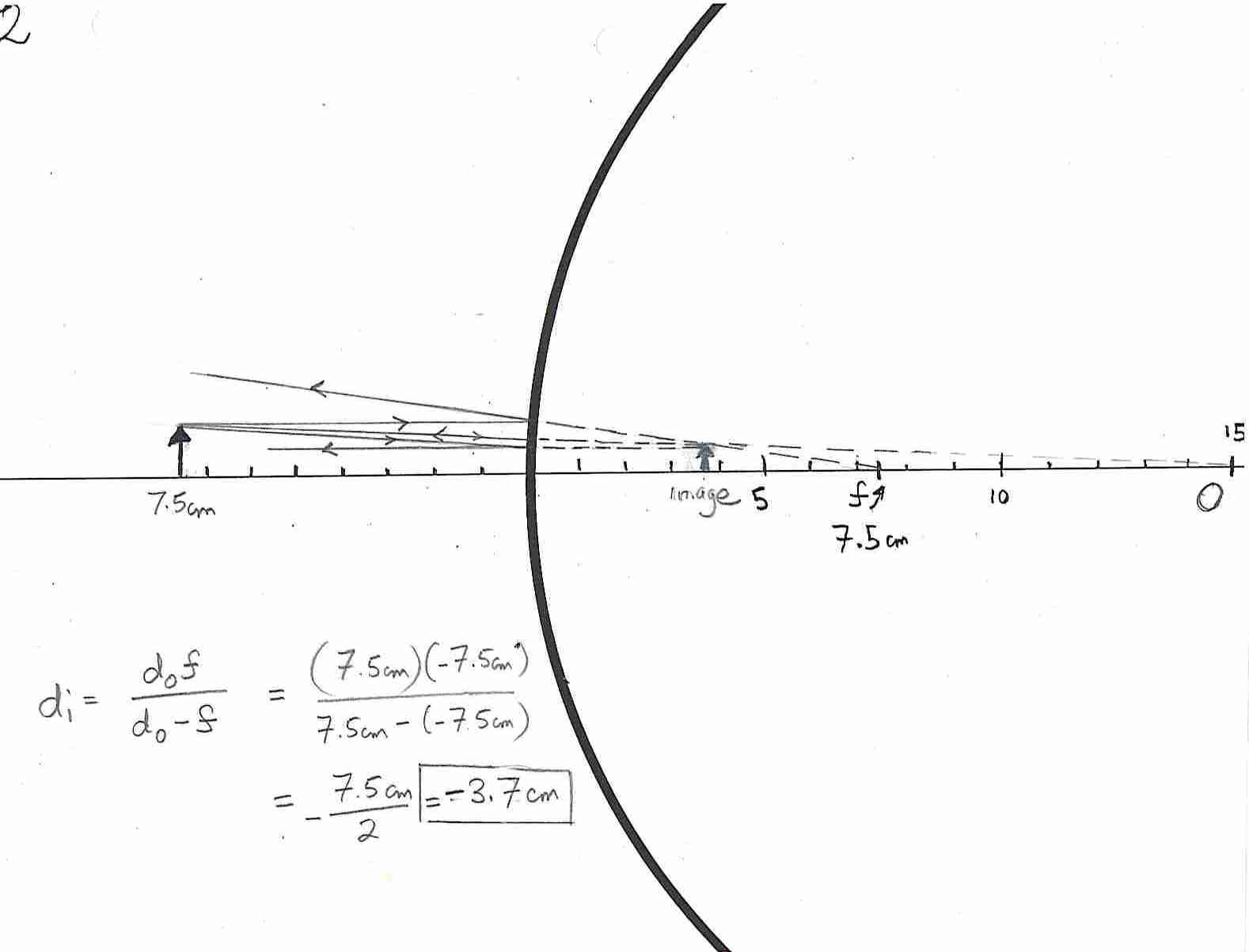
What is the virtual image formed by a diverging lens?
A diverging lens forms a virtual image that is upright, reduced in size, and located on the same side as the object. The virtual image is not real or physical, but appears as if it were located behind the lens when extended back from the direction of the diverging light rays.
How does the distance of an object from a diverging lens affect the size of the virtual image formed?
When an object is moved closer to a diverging lens, the virtual image formed also moves further away from the lens and becomes larger in size. Similarly, moving the object further away results in the virtual image moving closer to the lens and becoming smaller. This is due to the way diverging lenses spread out light rays, causing them to diverge rather than converge. As a result, the image formed by a diverging lens is always virtual, upright, and diminished compared to the object.
How does the distance of an object from a diverging lens affect the location of the virtual image formed?
The distance of an object from a diverging lens affects the location of the virtual image formed by influencing the position and size of the virtual image. When the object is moved closer to the diverging lens, the virtual image is formed farther away from the lens and is magnified. Conversely, when the object is moved farther from the lens, the virtual image is formed closer to the lens and is diminished in size. This is due to the diverging nature of the lens causing the light rays to diverge, resulting in the virtual image being formed on the same side as the object and appearing smaller or larger depending on the object distance.
How does the presence of a diverging lens affect the overall magnification of the image formed?
The presence of a diverging lens decreases the overall magnification of the image formed. Diverging lenses cause light rays to diverge or spread out, resulting in the virtual image formed being smaller and upright compared to the object. This decrease in magnification is a characteristic effect of diverging lenses in optical systems.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments