Diffusion Worksheet Key
Worksheets provide a valuable learning tool for students of all ages and levels. They offer a structured format for practicing and reinforcing concepts in various subject areas. Whether you are a teacher searching for additional resources to engage your students or a parent looking to support your child's learning at home, worksheets can serve as an effective entity for enhancing understanding and retention.
Table of Images 👆
- Osmosis and Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell and Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Gizmos Answer Key Cell Structure Worksheet
- Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Free Patriotic Page Borders Clip Art
- Osmosis Jones Worksheet Answer Key
- Sponge Anatomy Diagram Answer Key
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet
- Diversity Worksheet for Teens
- Stoichiometry Worksheet Answers
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
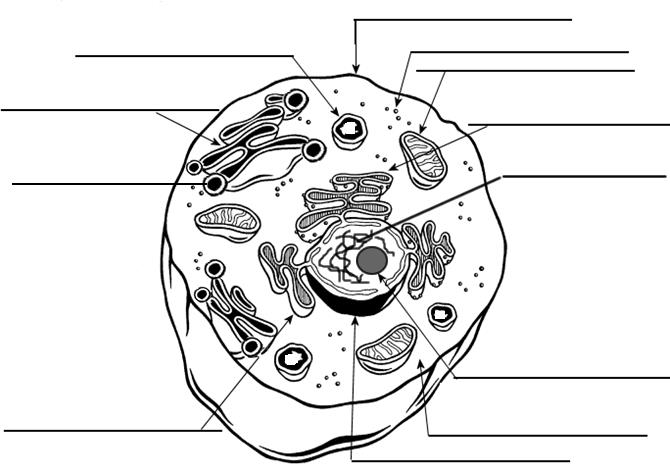
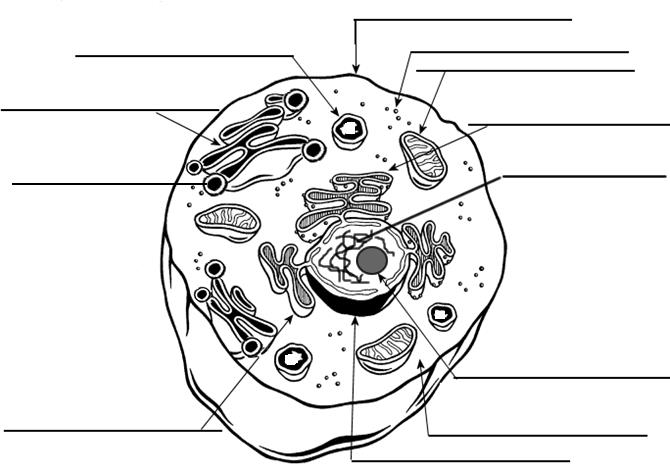
- Cell Organelle Labeling Worksheet
- Cell Organelle Labeling Worksheet
- Cell Organelle Labeling Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is a process in which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, in order to distribute themselves evenly. This is a passive process that does not require any additional energy input, and it occurs in various systems such as gases, liquids, and solids.
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
Temperature directly affects the rate of diffusion by increasing the kinetic energy of the particles involved in the process. As temperature rises, the particles move faster and collide more frequently, leading to an increase in diffusion rate. This is because the higher kinetic energy allows molecules to overcome barriers and travel a greater distance in a shorter amount of time, resulting in faster diffusion. Conversely, lower temperatures decrease the rate of diffusion as particles move more slowly and collisions are less frequent.
What is the role of concentration gradient in diffusion?
The concentration gradient plays a crucial role in diffusion by driving the movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This gradient represents the difference in concentration between two regions and acts as the driving force for diffusion to occur. The steeper the concentration gradient, the faster diffusion will occur, as particles naturally move down their concentration gradient in an attempt to reach equilibrium.
Define osmosis.
Osmosis is the process by which solvent molecules, typically water, move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane, such as a cell membrane. This movement occurs in order to equalize the concentration of solute molecules on both sides of the membrane.
Differentiate between diffusion and active transport.
Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the natural tendency of particles to spread out and equalize their concentration. In contrast, active transport is the process of moving particles across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy input in the form of ATP to pump particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Essentially, diffusion does not require energy input, while active transport does.
How does the size of particles affect the rate of diffusion?
The size of particles directly affects the rate of diffusion, with smaller particles diffusing more quickly than larger ones. This is because smaller particles have a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, allowing them to make more contact with the surrounding medium and therefore diffuse faster. In contrast, larger particles have a lower surface area-to-volume ratio, resulting in a slower rate of diffusion due to less contact with the medium.
Describe the process of facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport where specific proteins embedded in the cell membrane help move specific molecules across the membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. These proteins create channels or carriers that allow the molecules to pass through the membrane without the need for energy input from the cell. This process is selective and only works for molecules that can bind to the proteins in the membrane.
Explain the concept of equilibrium in relation to diffusion.
In the context of diffusion, equilibrium refers to the state when there is an equal distribution of particles or molecules across a specific area. This means that the rate of movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration is balanced, resulting in a uniform distribution of the particles. At equilibrium, there is no overall change in the concentration gradient, as the movement of particles in one direction is matched by an equal movement in the opposite direction. Therefore, equilibrium in diffusion signifies a stable state where there is no net movement of particles.
What is the significance of diffusion in biological systems?
Diffusion plays a crucial role in biological systems by enabling the movement of molecules such as oxygen, nutrients, and waste products across cell membranes. This process is vital for maintaining cellular function, as it allows for the distribution of essential substances that cells need to survive and function properly. Additionally, diffusion helps to establish gradients within cells and tissues, which are important for processes such as signaling and nerve conduction. In summary, diffusion is essential for the transportation of molecules in and out of cells, contributing to the overall homeostasis and functioning of biological systems.
How does diffusion play a role in gas exchange in the respiratory system?
Diffusion plays a key role in gas exchange in the respiratory system by allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to move across the respiratory membrane. In the lungs, oxygen from inhaled air diffuses from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillaries, where it binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells for transport to tissues. Conversely, carbon dioxide produced by cellular metabolism diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli to be exhaled. The process of diffusion ensures that the respiratory system efficiently exchanges gases to meet the body's oxygen demands and remove carbon dioxide waste.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments