Create a Food Web Worksheet
A food web worksheet is a helpful resource that allows students to easily visualize and comprehend the complex relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem. By clearly presenting the interconnections between producers, consumers, and decomposers, this worksheet provides a thorough understanding of how energy and nutrients flow through the natural world. Whether you are a teacher seeking a resource for your science curriculum or a student looking to reinforce your knowledge on this topic, a food web worksheet can be a valuable tool to enhance your learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
- How to Draw Food Web
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Web Worksheets High School
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Blank Food Web Worksheets
- Food Chains and Webs Worksheets
- Food Chain Worksheets Free
- Food Chain Worksheet 3rd Grade
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Web Worksheet Middle School
- Terrestrial Food Web
- Printable Food Web Worksheets
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
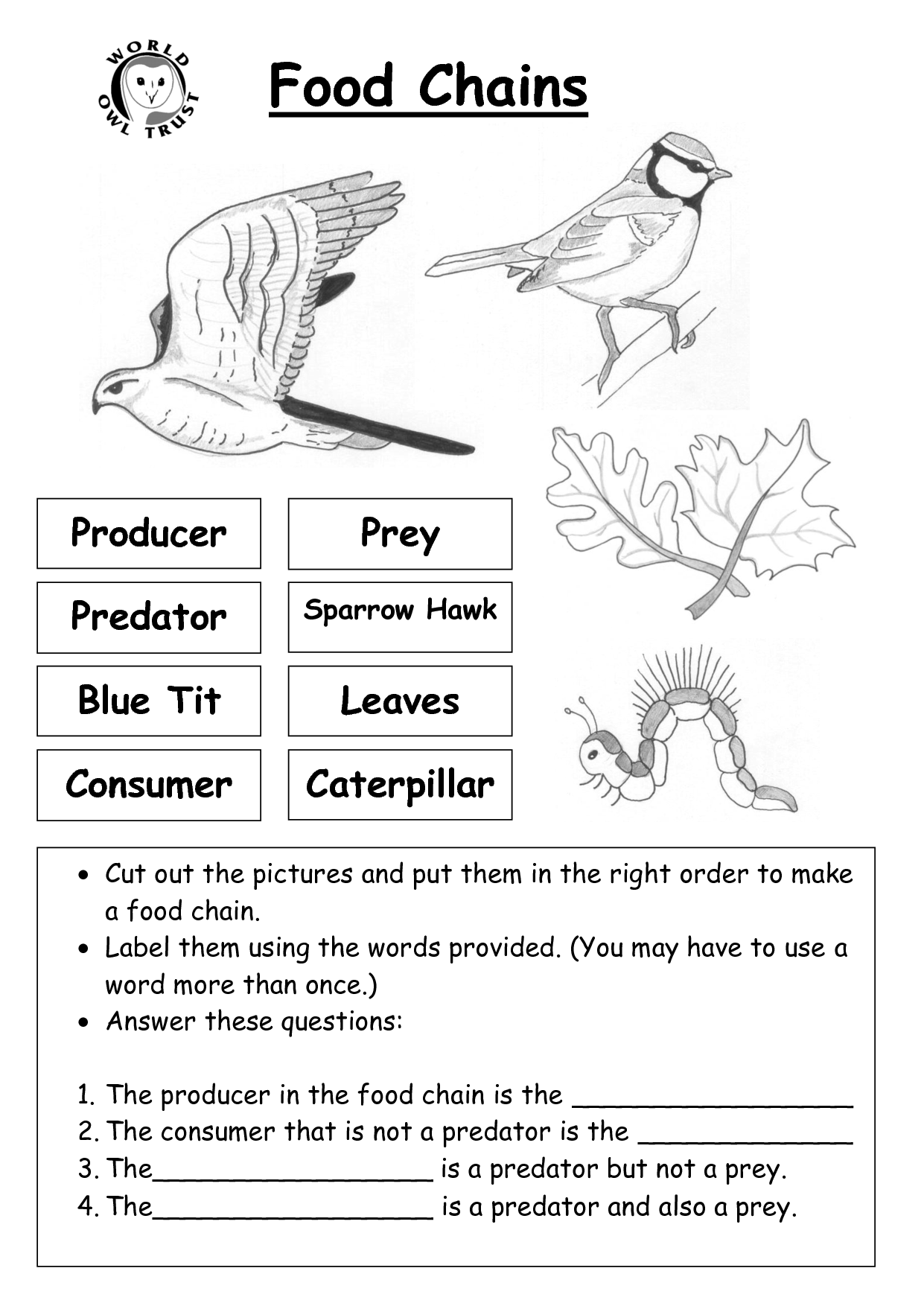
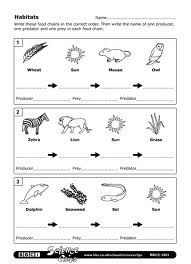
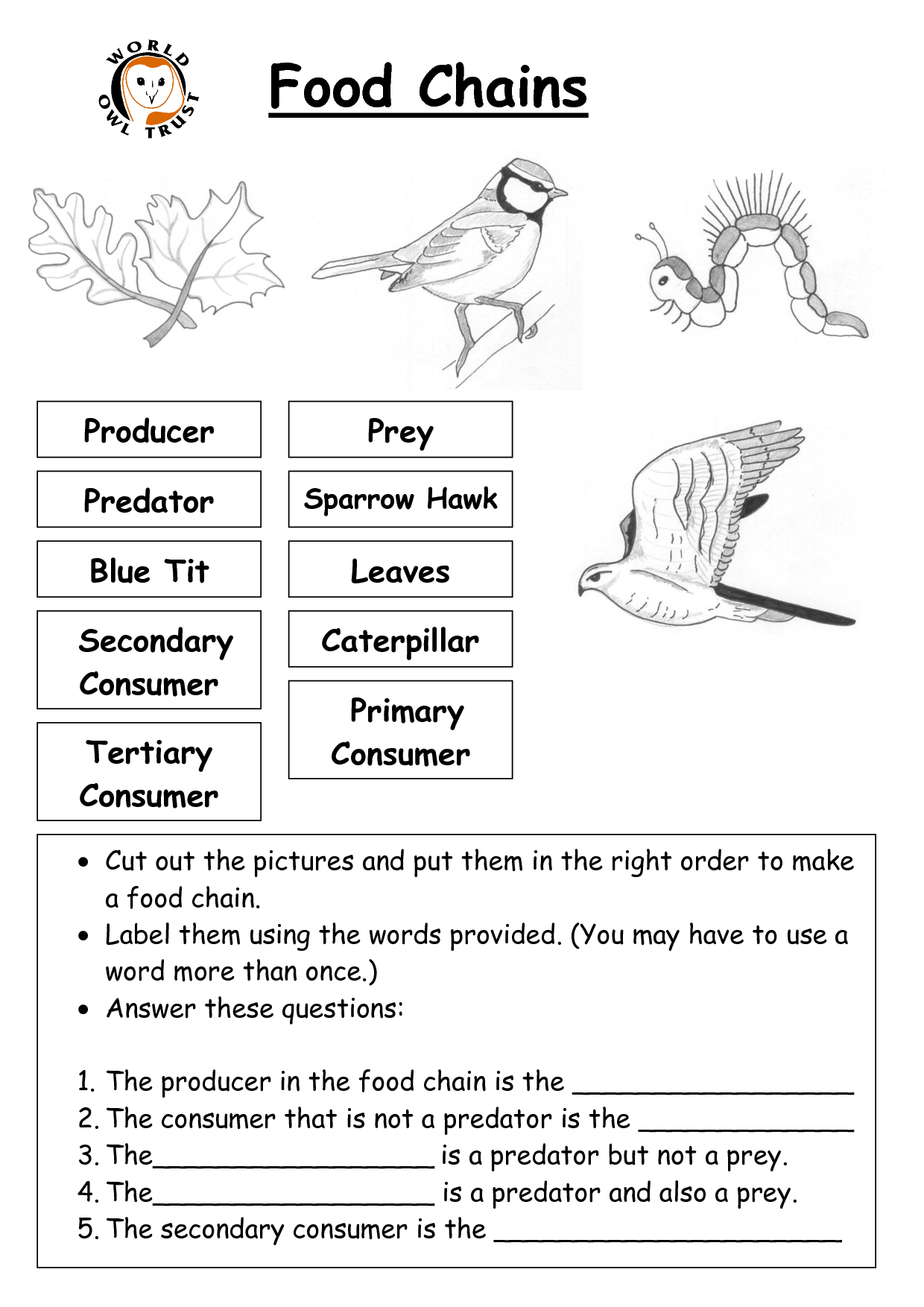
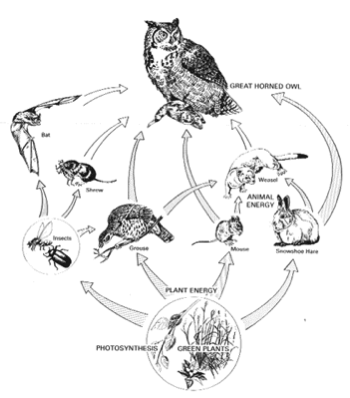
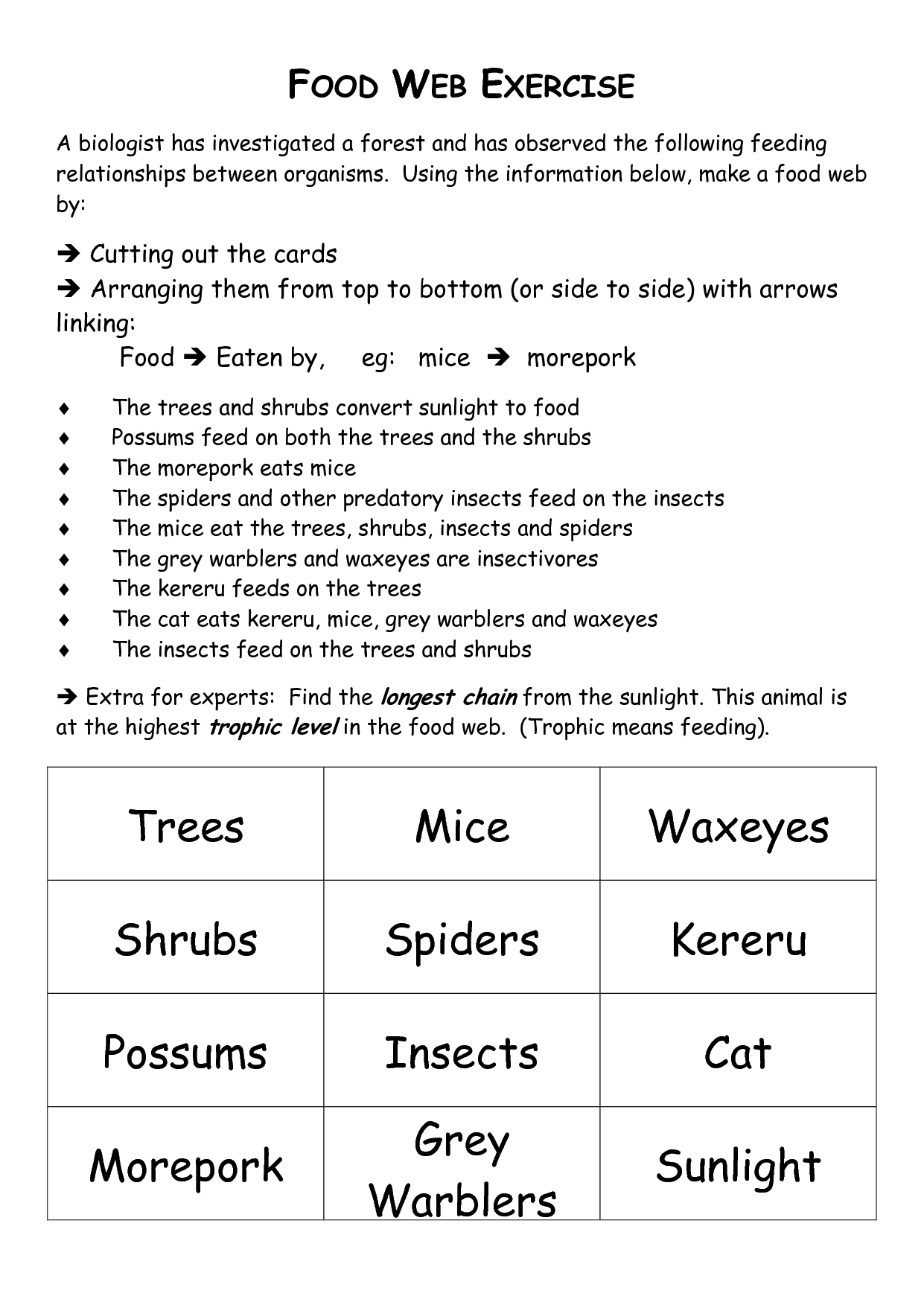
What is a food web?
A food web is a diagram or model that shows the interconnected relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem, illustrating how energy and nutrients are transferred through a series of predator-prey interactions. It provides a visual representation of the flow of energy from one organism to another, demonstrating the complex and dynamic nature of ecosystems and the interactions between different species.
How does energy flow in a food web?
Energy flows in a food web in a unidirectional manner, starting with the sun as the primary source. Producers such as plants capture solar energy through photosynthesis and convert it into chemical energy. Herbivores then consume the producers, transferring some of this energy. Next, carnivores feed on the herbivores, continuing the energy transfer. At each trophic level, some energy is lost as heat through metabolic processes, with only a portion being passed on to the next level. This process continues throughout the food web, creating a complex network of energy flow that sustains the ecosystem's functioning.
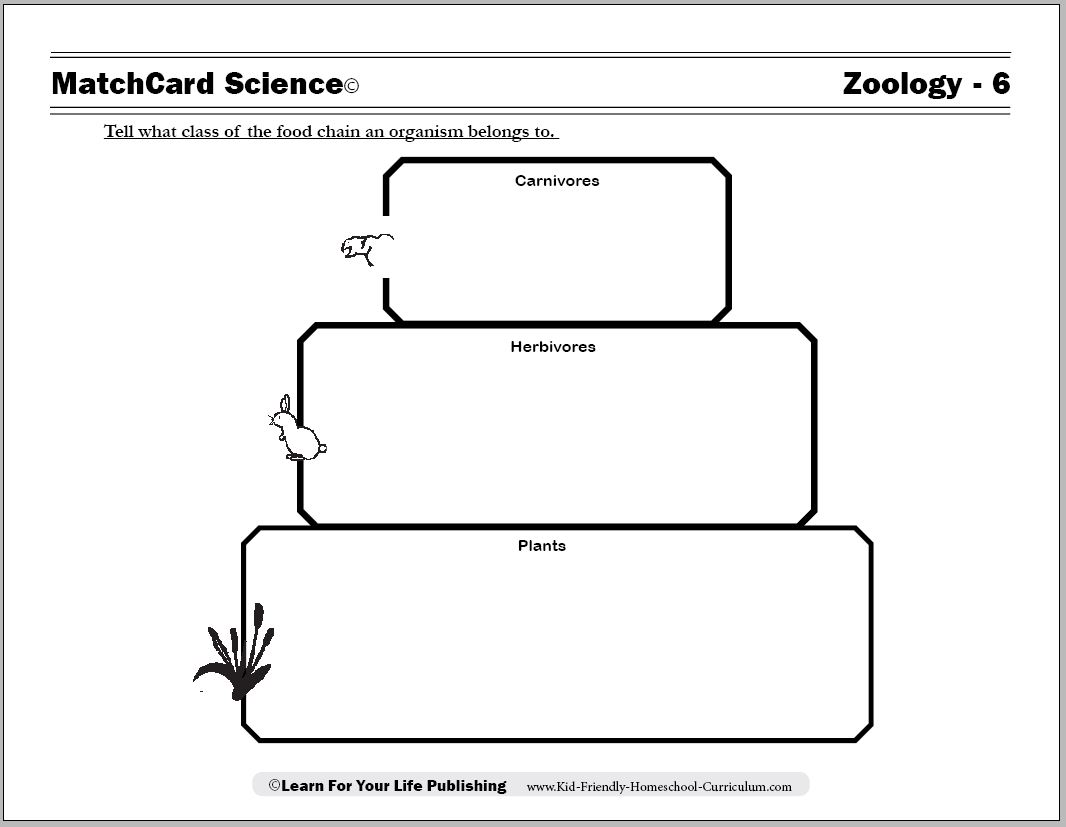
What are producers in a food web?
Producers in a food web are organisms, such as plants, that are capable of creating their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. They are the foundation of the food web, converting energy from the sun or chemicals into organic compounds that can be used by other organisms higher up in the food chain.
Give an example of a consumer in a food web.
An example of a consumer in a food web is a rabbit. Rabbits are primary consumers that feed on plants such as grass, flowers, and vegetables. They play a critical role in transferring energy from producers (plants) to higher trophic levels in the food web by being preyed upon by secondary consumers like foxes or hawks.
What is a decomposer in a food web?
A decomposer in a food web is an organism that breaks down dead plants and animals into simpler substances and releases nutrients back into the ecosystem. Decomposers play a crucial role in recycling organic matter and maintaining the balance of nutrients in the environment by breaking down complex compounds into simpler forms that can be used by other organisms.
How do primary consumers differ from secondary consumers?
Primary consumers feed directly on producers (plants) and are considered herbivores, while secondary consumers feed on primary consumers and are typically carnivores or omnivores. Primary consumers occupy the second trophic level in the food chain, while secondary consumers are at a higher trophic level. Primary consumers are essential for transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels, including secondary consumers, in an ecosystem.
Explain the concept of trophic levels in a food web.
Trophic levels are hierarchical levels in a food chain or food web that represent the feeding position of different organisms. At the base of the trophic levels are primary producers, such as plants, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores that consume plants occupy the next trophic level, followed by primary carnivores that feed on herbivores. Higher trophic levels include secondary and tertiary carnivores that feed on lower-level consumers. The transfer of energy through trophic levels determines the flow of nutrients and energy within an ecosystem, illustrating the interconnectedness of different organisms in a food web.
What is the importance of apex predators in a food web?
Apex predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystem by controlling the population of other species. They help regulate prey populations, which in turn affects the entire food web, preventing overgrazing or overpopulation of certain species. Additionally, apex predators can also influence the behavior and distribution of their prey, leading to a more diverse and healthy ecosystem.
How does the removal of one species impact the rest of the food web?
The removal of one species can have far-reaching impacts on the rest of the food web, disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems. This can lead to a cascade effect where the loss of a single species can affect multiple other species that depend on it for food, shelter, or other interactions. It can result in population decline or extinction of other species, changes in species composition, and alterations in ecosystem functions. Overall, the removal of one species can have profound consequences on the stability and biodiversity of the entire food web.
Describe the interconnectedness of species in a food web.
A food web illustrates the interconnectedness of species by showing how different organisms depend on one another for energy and nutrients. Each species in the web relies on other species for food, creating a complex network of relationships. For example, plants are eaten by herbivores, which are then consumed by predators. If one species is affected by factors such as disease or environmental changes, it can have ripple effects throughout the web, impacting multiple other species. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of biodiversity and the balance of ecosystems in maintaining the health and stability of the natural world.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments