Covalent Nomenclature Worksheet
If you are a chemistry student looking to practice covalent nomenclature, you've come to the right place. This blog post will introduce you to a helpful worksheet that will enhance your understanding of naming covalent compounds. With clear and concise instructions, the worksheet focuses on identifying the entity and subject of each compound, allowing you to master this essential concept in no time.
Table of Images 👆
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Writing Ionic Compound Formula Worksheet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Chemistry Naming Alkanes Worksheet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet
- Covalent Bonding Worksheet
- Binary Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Salt Chemical Formula
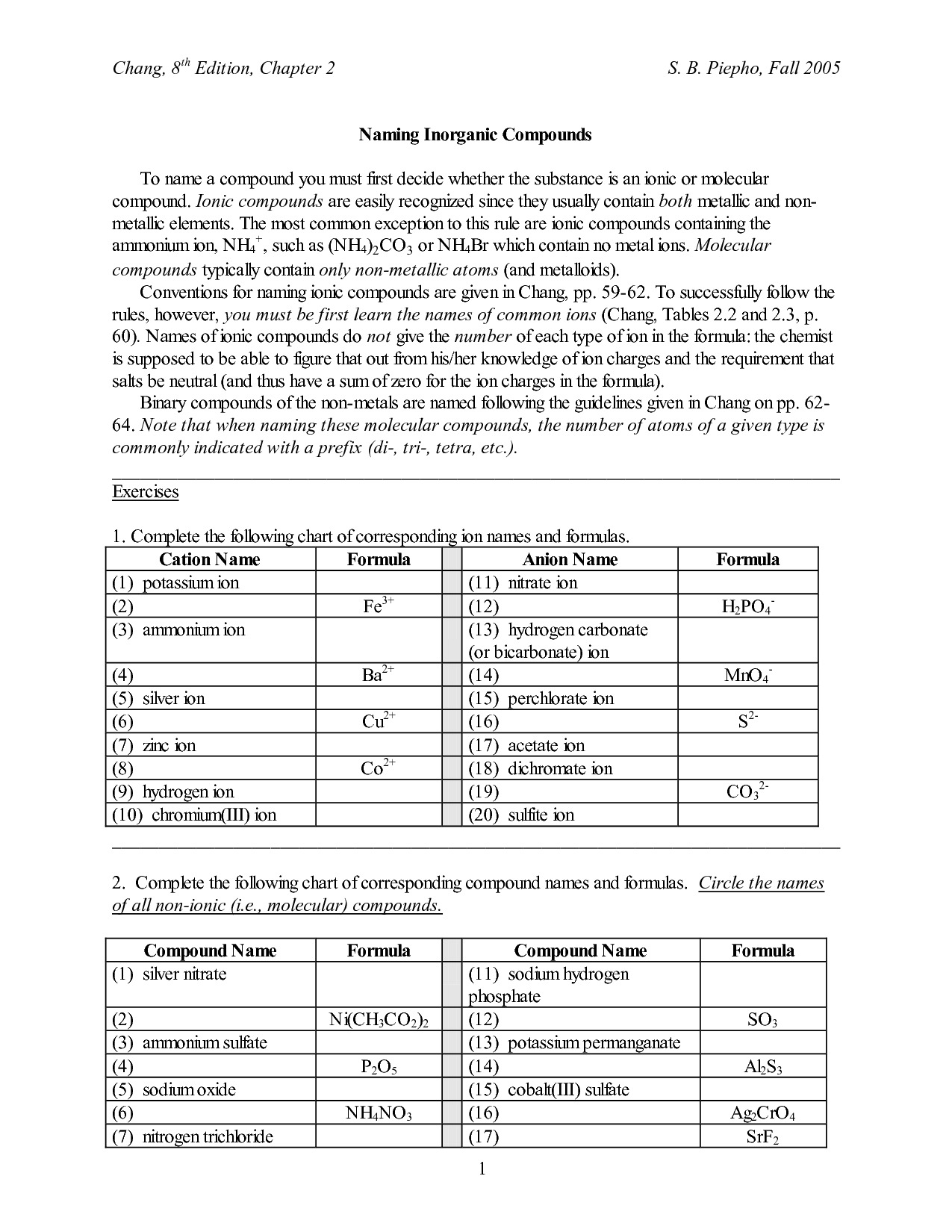
- Naming Chemical Compounds Worksheet Answers
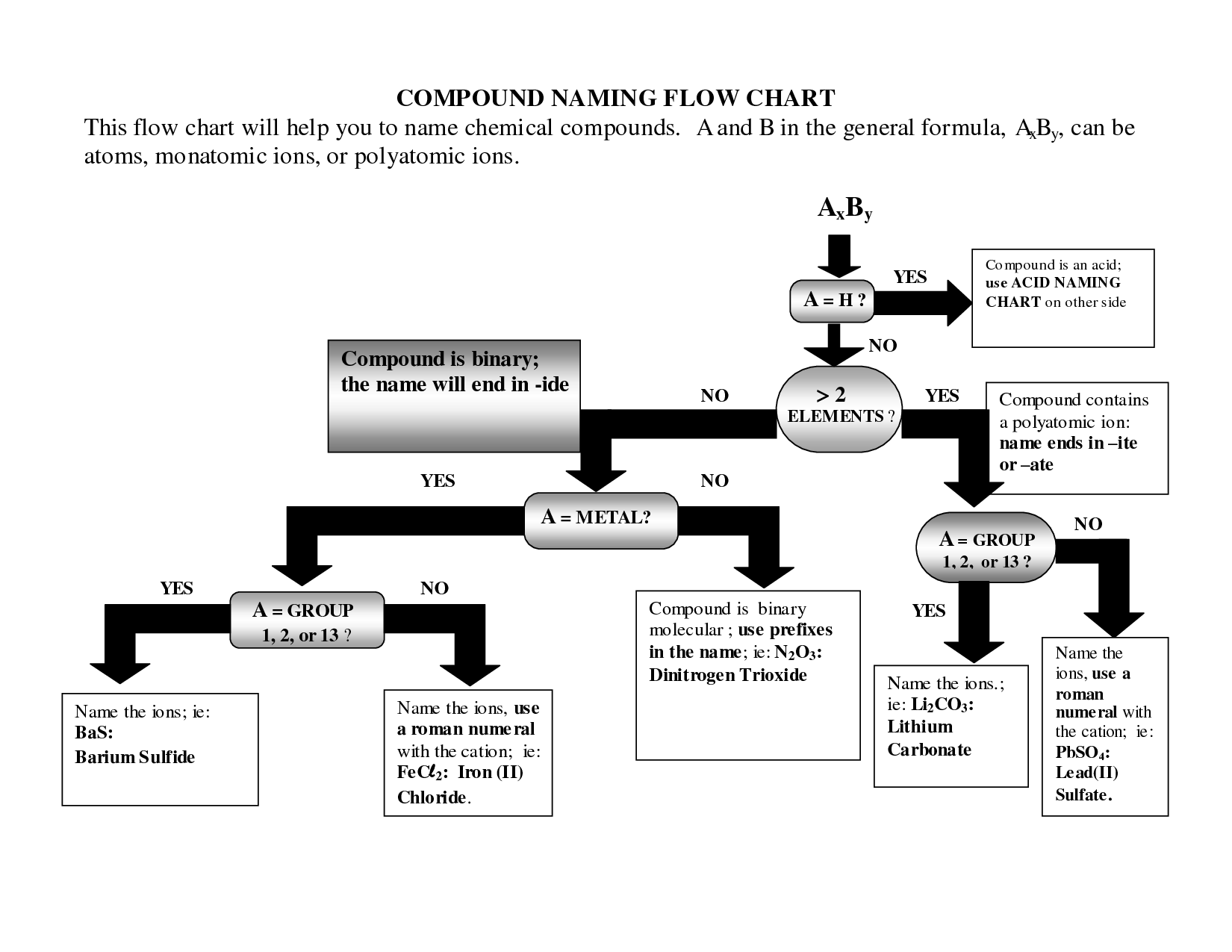
- Naming Chemical Compounds Flow Chart
- IUPAC Nomenclature Organic Chemistry
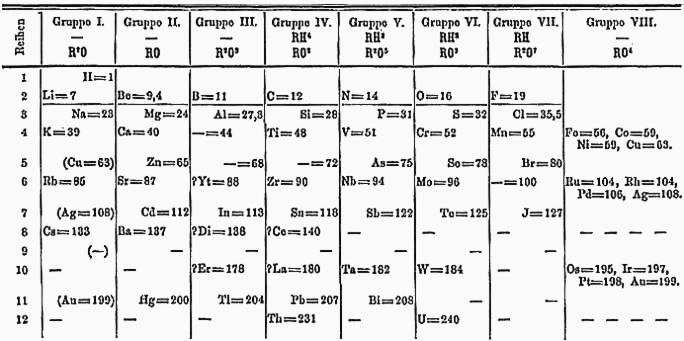
- Dmitri Mendeleev Periodic Table
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer
- Chemistry Mole Conversion Chart
- Molarity Problems Worksheet Answer Key
- Molarity Problems Worksheet Answer Key
- Molarity Problems Worksheet Answer Key
- Molarity Problems Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the purpose of covalent nomenclature?
The purpose of covalent nomenclature is to systematically name compounds composed of covalently bonded elements according to a set of rules, allowing scientists to effectively communicate and differentiate between different molecules and their structures. This naming system helps in identifying the types and numbers of atoms present in each compound, facilitating clear and consistent communication within the scientific community.
Define a covalent bond.
A covalent bond is a type of chemical bond formed between two atoms when they share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing of electrons allows the atoms to achieve a more stable configuration by filling their outer electron shells. As a result, covalent bonds are typically found in molecules where atoms are held together by the sharing of electrons.
What are the different types of covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds can be classified into different types based on the number of atoms involved in the bonding. These include diatomic molecules (such as O2 and N2) composed of two atoms, triatomic molecules (such as O3 and H2O) composed of three atoms, and polyatomic molecules (such as CH4 and CO2) comprising more than three atoms bonded covalently. Additionally, covalent compounds can also be categorized as polar or nonpolar based on the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved in the bond.
How do you name covalent compounds using the stock system?
In the stock system for naming covalent compounds, the cation (usually a metal) is named first followed by the anion (usually a nonmetal) with a modified ending. The name of the metal is simply the name of the element, while the nonmetal's ending is adjusted to "-ide." The name of the nonmetal may also include a Greek prefix to indicate the number of atoms present.
How do you name covalent compounds using the traditional naming system?
In traditional covalent compound naming, you use prefixes to indicate the number of each element present. The prefix "mono-" is used for the first element only if more than one of the second element is present. The prefixes are as follows: mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, hepta-, octa-, nona-, and deca-. The second element has the suffix "-ide" added to its name. For example, CO₂ is carbon dioxide because there is one carbon atom (mono-) and two oxygen atoms (di-).
What are prefixes in covalent compound names used for?
Prefixes in covalent compound names are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule. They specify the quantity of each element participating in the compound, helping to distinguish between different molecules with the same elements but in different proportions. Prefixes such as mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, etc., are used to denote the number of atoms of each element in the compound name.
How do you determine the number of each element in a covalent compound formula?
To determine the number of each element in a covalent compound formula, you look at the subscript numbers following each element symbol in the formula. These subscript numbers represent the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. Counting the number of atoms of each element based on the subscript numbers will give you the correct ratio of elements in the compound.
What are the rules for writing formulas of covalent compounds?
When writing formulas for covalent compounds, the prefixes indicating the number of atoms in each element must be included before each element. The prefix “mono” is often omitted for the first element in a compound. Additionally, elements with multiple atoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, or carbon usually have their second element name end in “-ide.” It is crucial to balance the subscripts so that the overall charge of the compound is neutral.
How do you differentiate between an ionic compound and a covalent compound?
Ionic compounds are formed between a metal and a nonmetal where electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions that are held together by electrostatic forces. On the other hand, covalent compounds are formed between two nonmetals where electrons are shared between atoms, creating a strong bond due to the sharing of electrons. The main difference lies in the type of bonding - ionic compounds have ionic bonds, while covalent compounds have covalent bonds.
Provide an example of a covalent compound and explain how to name it.
An example of a covalent compound is carbon dioxide (CO2). To name covalent compounds, you use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. In the case of carbon dioxide, the prefix "di-" is used to indicate two oxygen atoms, and the prefix "mono-" is not used for the first element, carbon. Therefore, the compound is named as carbon dioxide.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments