Covalent Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
Are you searching for a reliable resource to help reinforce your understanding of covalent compounds? Look no further! This covalent compounds worksheet answer key is specifically designed to provide a comprehensive review of the topic. Geared towards students studying chemistry or those interested in expanding their knowledge of chemical bonding, this worksheet will allow you to test your comprehension and solidify your understanding of covalent compounds.
Table of Images 👆
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Ionic and Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Department of Chemistry University of Texas at Austin Ionic
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Organic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet
- Mixed Ionic Covalent Compound Naming Answers
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Naming Ionic and Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Compounds Covalent Bonds Worksheet Answers
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
- Lewis Dot Structure Covalent Bond Worksheet
- Naming Chemical Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Naming Compounds Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds are chemical compounds in which atoms are bonded together by the sharing of electrons. These compounds typically consist of nonmetal elements and form when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. In covalent compounds, the atoms are held together by strong covalent bonds, resulting in molecules with unique properties.
How are covalent compounds formed?
Covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms. When two atoms with similar electronegativities come together, they can share electrons in order to fill their outer electron shells and achieve a more stable configuration. This sharing of electrons creates a strong bond between the atoms and results in the formation of a covalent compound.
What are some examples of covalent compounds?
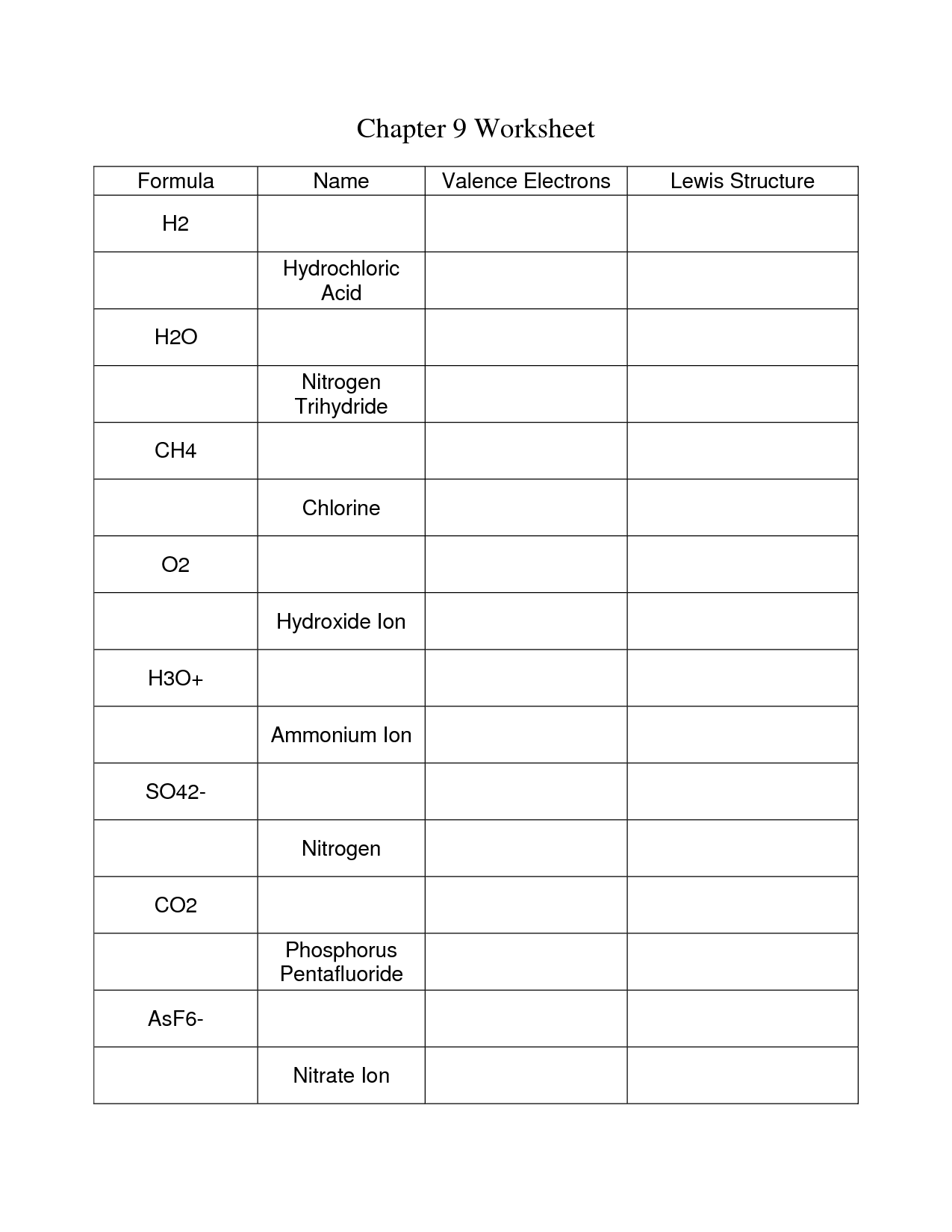
Some examples of covalent compounds include water (H2O), methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), ammonia (NH3), and hydrogen chloride (HCl). These compounds are formed by sharing electrons between atoms to create stable bonds.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds?
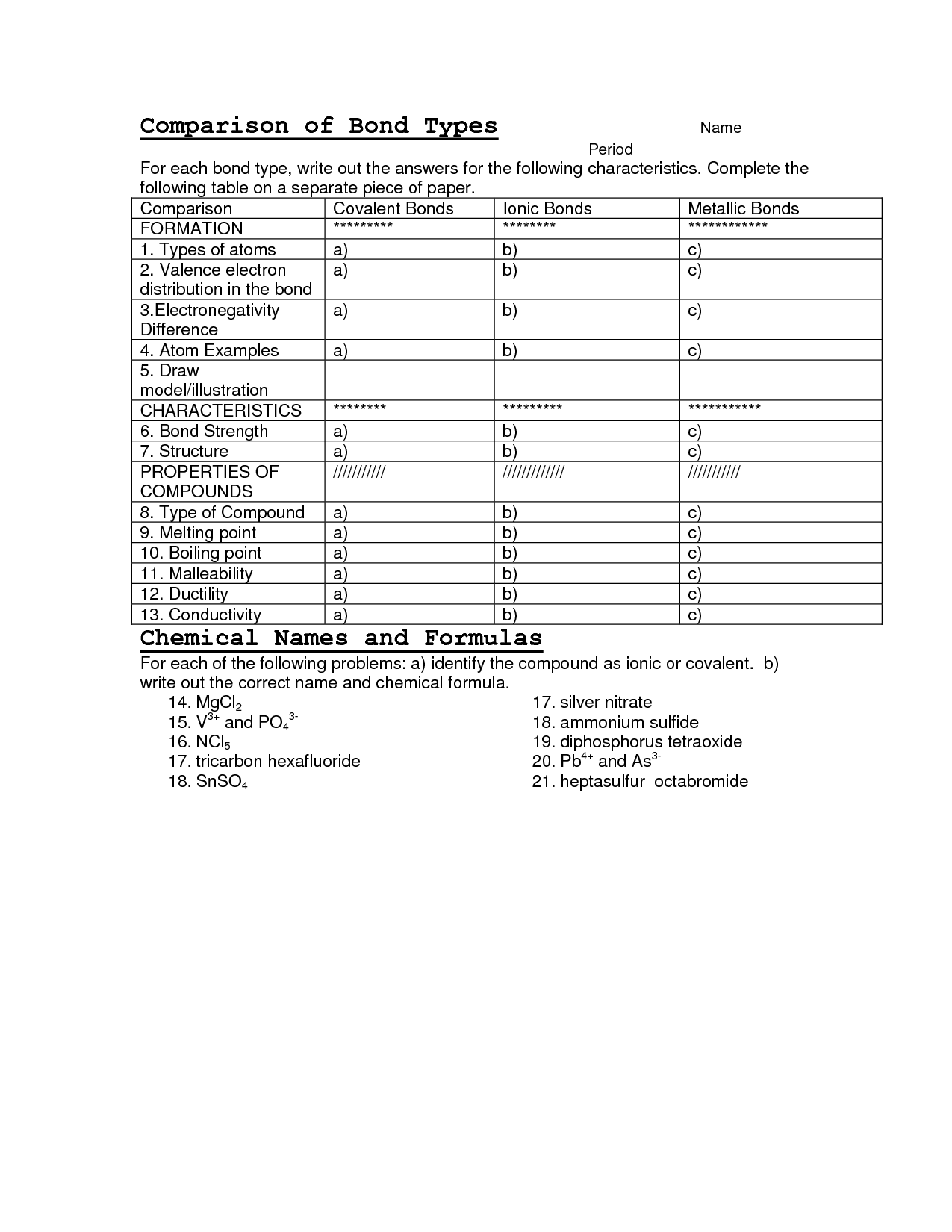
Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons between a metal and a non-metal, resulting in the formation of ions held together by electrostatic forces. In contrast, covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons between two non-metals, leading to the formation of molecules held together by strong covalent bonds. Ionic compounds tend to have higher melting and boiling points, conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water, and have a crystalline structure, while covalent compounds generally have lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity, and typically exist as gases, liquids, or soft solids.
What are the properties of covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds have properties such as low melting and boiling points, poor electrical conductivity, and they are typically formed between nonmetals sharing electrons to achieve stability. They often exist as gases, liquids, or soft solids due to weak intermolecular forces holding their molecules together. Covalent compounds also exhibit a wide range of solubilities in different solvents and are often insoluble in water.
What are some common uses of covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds, also known as molecular compounds, are commonly used in various industries and applications such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, fragrances, polymers, and materials science. They are often used in organic chemistry for drug manufacturing, in the production of plastics and synthetic fibers, as well as in the formulation of adhesives, dyes, and pigments. Additionally, covalent compounds play a crucial role in the development of specialty chemicals, flavors, and fragrances for use in food, cosmetics, and perfume industries.
How do covalent compounds dissolve in water?
Covalent compounds dissolve in water by forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules. The partially positive hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to the partially negative regions of the covalent compound, allowing the compound to break apart and disperse throughout the water. This interaction disrupts the intermolecular forces within the covalent compound, allowing it to dissolve and form a homogeneous solution with water.
How do you determine the formula of a covalent compound?
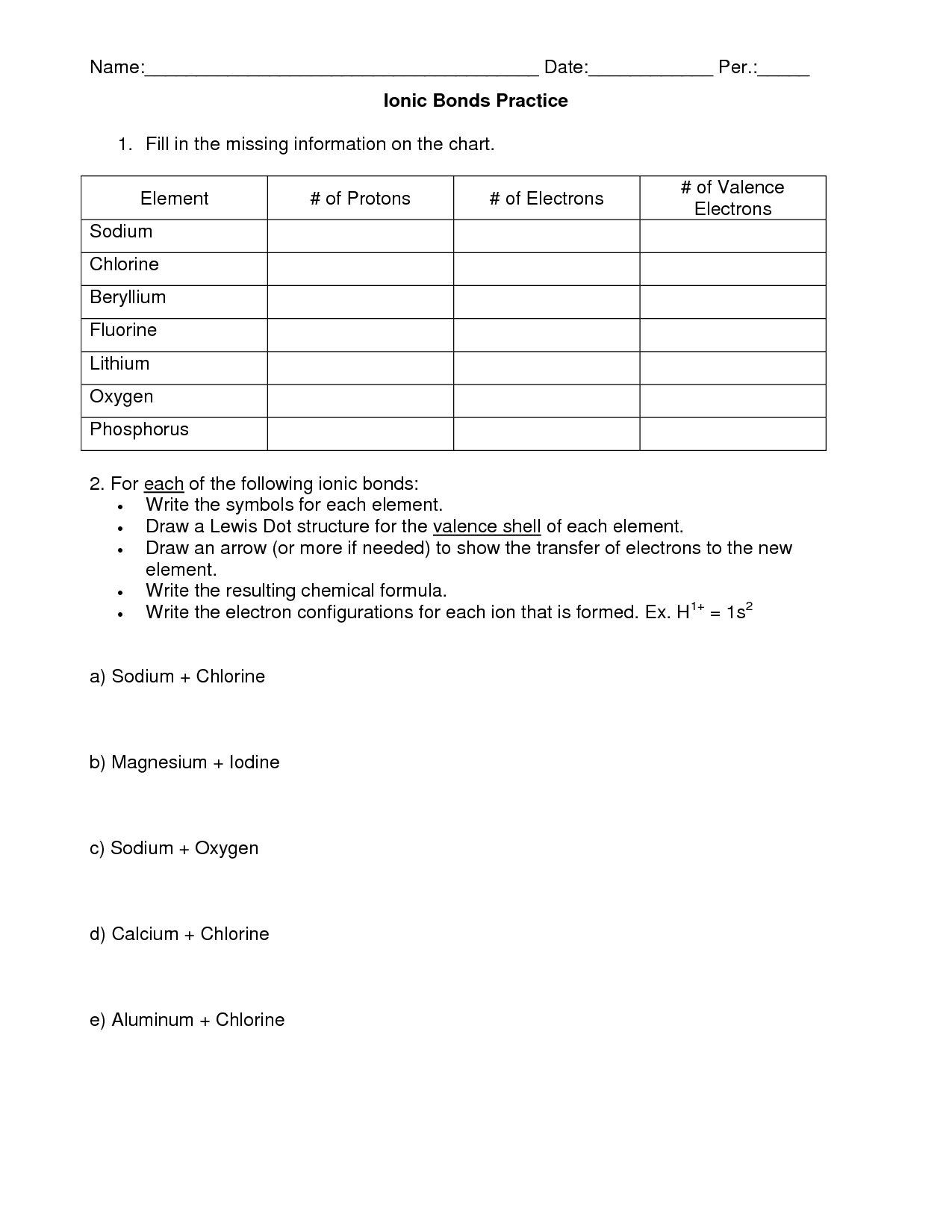
To determine the formula of a covalent compound, you need to consider the combining elements' valence electrons and use the criss-cross method or write their symbols with the correct subscript to balance the charges. Covalent compounds share electrons between atoms, rather than transferring them, so the subscript represents the number of atoms of each element in the compound to ensure neutral charge overall. Remember to simplify the subscripts to their lowest whole number ratios if necessary, and always follow the rules of valency and charge when writing the formula for a covalent compound.
Can covalent compounds conduct electricity?
Most covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because they consist of molecules that do not contain free-moving ions or electrons. However, there are some exceptions such as covalent compounds that are in the liquid state or are dissolved in water, as they can conduct electricity due to the presence of ions or the ability to dissociate into ions. Examples include acids, bases, and some organic solvents like dissolved salts or acids.
What are some important factors to consider when naming covalent compounds?
When naming covalent compounds, it is crucial to consider the prefixes used to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. These prefixes include mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, hepta-, octa-, nona-, and deca-. Additionally, it is important to pay attention to the order in which the elements are written in the compound's name, with the element that appears first in the compound formula being named first. Finally, it is necessary to modify the second element's name by adding the suffix "-ide.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments