Conduction Convection Radiation Worksheet
Worksheets play a vital role in reinforcing concepts and providing practical exercises for students to enhance their learning experience. When it comes to understanding the principles of conduction, convection, and radiation, a dedicated worksheet can be a valuable resource. Designed to engage learners and aid in the understanding of these topics, this conduction convection radiation worksheet offers students the opportunity to explore the intricate workings of heat transfer and its different modes. Whether you are a teacher looking for an effective teaching aid or a student seeking to deepen your knowledge in this area, this worksheet is tailored to suit your needs.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
Define conduction.
Conduction is the process by which heat or electricity is transferred through a material without any movement of the material itself. It occurs through direct contact between the particles of the material, where higher energy particles collide with lower energy particles, transferring their energy in the form of heat or electricity.
Give an example of conduction.
Placing a metal spoon in a hot cup of coffee and feeling the handle of the spoon quickly become warm is an example of conduction, as heat is transferred from the hot liquid to the cooler metal spoon through direct contact.
What is convection?
Convection is the process of heat transfer in fluids (liquids or gases) where warmer, less dense fluid rises while cooler, more dense fluid sinks. This creates a continuous cycle of fluid movement that helps distribute heat evenly throughout the fluid.
Provide an example of convection.
A common example of convection is the process of boiling water. As the water is heated at the bottom of a pot, it becomes less dense and rises to the top, while cooler water from the surface moves down to replace it. This continuous flow of hot water rising and cool water sinking creates a convection current, which evenly distributes heat throughout the water and eventually causes it to boil.
What is radiation?
Radiation is the emission of energy in the form of waves or particles, which can be categorized as ionizing or non-ionizing depending on their ability to ionize atoms in the matter they interact with. Ionizing radiation, such as gamma rays and X-rays, have enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, leading to the formation of ions. Non-ionizing radiation, such as visible light and radio waves, does not have enough energy to ionize atoms. Radiation is ubiquitous in our environment, coming from natural sources like the sun, as well as human-made sources such as medical devices and nuclear power plants.
Give an example of radiation.
An example of radiation is the emission of electromagnetic waves, such as visible light or ultraviolet rays, from the sun.
Explain how conduction transfers heat energy.
Conduction is the process by which heat energy is transferred through direct contact between particles or objects. When two objects at different temperatures are in contact, the particles with higher energy begin to collide with those of lower energy, transferring heat from the warmer object to the cooler one. This transfer of kinetic energy continues until thermal equilibrium is reached, with the objects reaching the same temperature. The rate of heat conduction is influenced by the materials' thermal conductivity, the temperature difference between the objects, and the distance over which the heat is being transferred.
Describe how convection transfers heat energy.
Convection transfers heat energy through the movement of fluids, such as air or liquid. As a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, carrying heat energy with it. The cooler, denser fluid then moves in to replace the rising fluid, creating a continuous flow that transfers heat from one location to another. This process of fluid movement enables convection to efficiently distribute heat energy throughout a space.
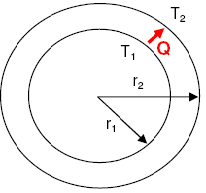
How does radiation transfer heat energy?
Radiation transfers heat energy through electromagnetic waves that carry thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler one. This transfer occurs without any physical medium, such as air or water, as the waves can travel through a vacuum. The hotter object emits energy in the form of infrared radiation, which is absorbed by the cooler object, causing its temperature to increase. This process is known as thermal radiation and plays a crucial role in heating and cooling processes in various systems and phenomena, from sunlight warming the Earth's surface to infrared heating in industrial processes.
Compare and contrast conduction, convection, and radiation in terms of how heat energy is transferred.
Conduction involves the transfer of heat through direct contact between materials, where heat flows from hotter to cooler objects. In convection, heat is transferred through the movement of fluids or gases, as the warmer substance rises and the cooler substance sinks. Radiation, on the other hand, transfers heat through electromagnetic waves that can travel through a vacuum, such as sunlight warming the Earth. While both conduction and convection require a material medium, radiation does not. Additionally, conduction and convection involve the movement of particles, while radiation does not require a medium and can occur through empty space.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments