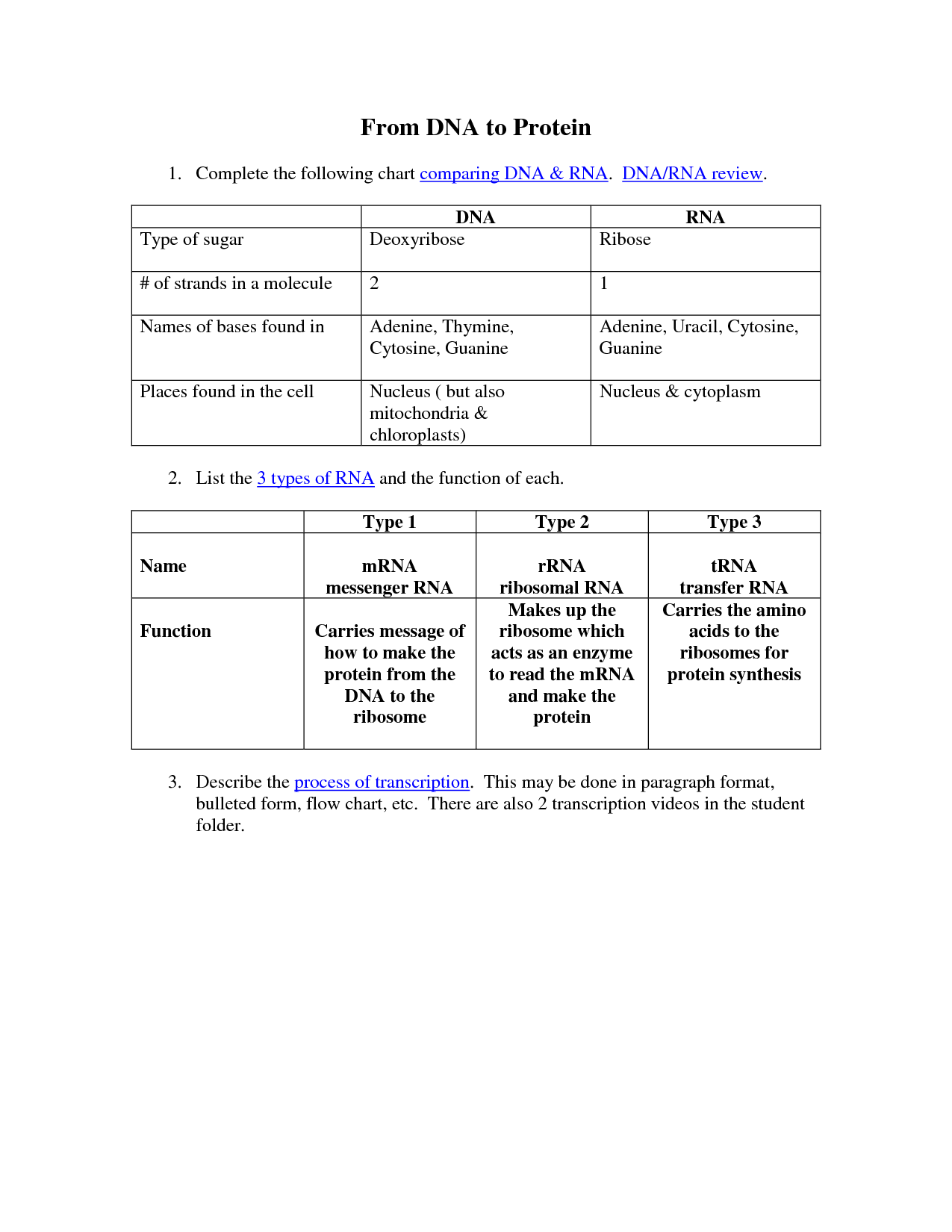
Comparing DNA and RNA Worksheet
Comparing DNA and RNA can be complex and challenging, especially when it comes to understanding the subtle differences between these two important molecules. To help simplify the learning process, we have created a comprehensive worksheet that focuses on the key aspects of DNA and RNA, making it easier for students and enthusiasts alike to grasp the entity and subject of these molecules. Whether you're a biology student studying for an exam or simply someone curious about the intricacies of genetics, our worksheet is designed to provide clarity and enhance your understanding.
Table of Images 👆
- Section 12 4 Mutations Answer Key
- Comparison DNA and RNA Worksheet
- Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
- DNA and RNA Molecules
- DNA vs RNA Venn Diagram
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Vocabulary Study Guide Template
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA and RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
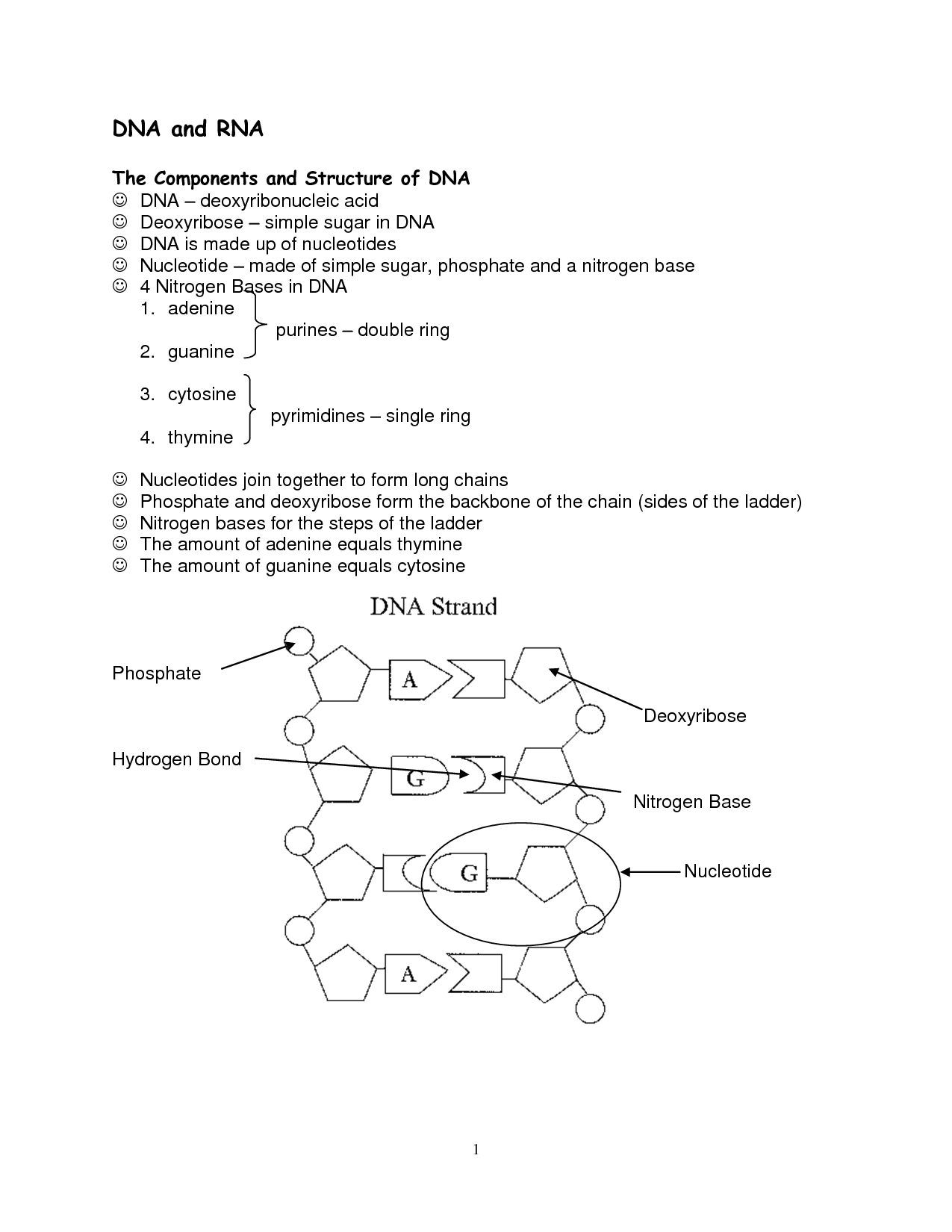
What are the nucleotides that make up DNA and RNA?
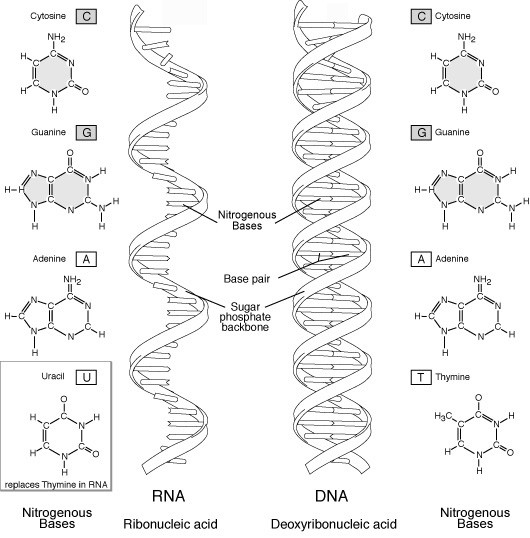
DNA is composed of four nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). RNA also contains adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), but uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) as the fourth nucleotide.
How many strands does DNA have? What about RNA?
DNA has two strands, while RNA has one strand.
What are the sugars present in DNA and RNA?
In DNA, the sugar present is deoxyribose, while in RNA, the sugar present is ribose. These sugars are important components of the nucleotides that make up the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules, respectively.
What are the bases present in DNA and RNA?
The bases present in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, the base thymine is replaced by uracil (U). So, RNA contains adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G) as its bases.
What are the complementary base pairings in DNA? And in RNA?
In DNA, the complementary base pairings are adenine (A) with thymine (T) and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). In RNA, adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U) instead of thymine (T), while guanine (G) still pairs with cytosine (C).
What is the function of DNA in living organisms? And what about RNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. It serves as the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins and regulates the expression of genes. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating the genetic information from DNA into proteins. It acts as a messenger that carries the instructions from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.Overall, both DNA and RNA are essential molecules that are central to the processes of life, responsible for transmitting and expressing genetic information in living organisms.
What is the full form of DNA? And what does RNA stand for?
The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid.
Where is DNA found within a eukaryotic cell? How about RNA?
In a eukaryotic cell, DNA is found primarily within the nucleus, where it is organized into structures called chromosomes. However, some DNA can also be found in organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. RNA, on the other hand, can be found in various locations throughout the cell, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, and organelles. RNA is involved in various cellular processes, including protein synthesis and gene regulation.
What is the shape of the DNA molecule? And what is the shape of RNA?
The DNA molecule has a double helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder. It is made up of two long strands of nucleotides that are intertwined around each other. RNA, on the other hand, can have different shapes depending on its type, but one common form is single-stranded with various folding patterns. This allows RNA to fold into secondary and tertiary structures that enable it to perform its diverse functions within cells.
How is DNA replicated? And how is RNA synthesized?
DNA replication occurs in three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the unwinding of the double helix structure by the enzyme helicase. This creates two template strands from which new DNA strands can be synthesized by DNA polymerase during the elongation phase. The new DNA strands are synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction. RNA synthesis, or transcription, is carried out by RNA polymerase and also involves three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region on the DNA strand. In elongation, RNA polymerase synthesizes an RNA molecule complementary to the DNA template strand. Finally, termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches a specific termination signal on the DNA strand, releasing the newly synthesized RNA molecule.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments