Communities and Ecosystems Worksheets
If you're searching for educational resources to engage your students in meaningful learning about communities and ecosystems, worksheets can be a valuable tool. These worksheets provide a wealth of informative content and concise activities aimed at teaching students about the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment. By immersing students in thought-provoking tasks, these worksheets allow them to explore and understand the dynamics of communities and ecosystems in a structured manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Ecosystem Worksheet Answer Key
- Population Community Ecosystem Worksheet
- Population Community Ecosystem Worksheet
- Species Interactions Worksheet Answers
- Ecosystem Population Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answers
- Ecosystem Interactions Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Boy Scouts Environmental Science Timeline Worksheet
- Parts of an Ecosystem Worksheet
- Science Study Guide Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is a community in ecology?
In ecology, a community is a group of interacting living organisms that coexist in a specific habitat or area. These organisms can be diverse in terms of species, size, and function, and their interactions within the community can be competition, predation, mutualism, or commensalism. The structure and dynamics of a community are influenced by factors such as environmental conditions, resource availability, and disturbances, shaping the relationships among its members and the overall ecosystem.
What are examples of biotic factors in an ecosystem?
Examples of biotic factors in an ecosystem include plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. Plants serve as producers in the food chain, while animals act as consumers, predators, or prey. Fungi and bacteria play important roles in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in the ecosystem. Each of these biotic factors interacts with one another and with the abiotic factors in the environment to create a balanced and functioning ecosystem.
Describe the relationship between mutualism and commensalism.
Mutualism is a type of symbiotic relationship where both species involved benefit from the interaction, whereas commensalism is a relationship in which one species benefits while the other is unaffected. In mutualism, both species rely on each other for survival and both receive advantages from the relationship. In commensalism, one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor helped. While both relationships involve interactions between different species, mutualism is a more interdependent and mutually beneficial relationship compared to commensalism.
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each organism consumes the one below it and is consumed by the one above it, showing a single pathway of energy flow in an ecosystem. On the other hand, a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains that shows multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem, depicting a more realistic and intricate picture of the flow of energy and nutrients among different organisms.
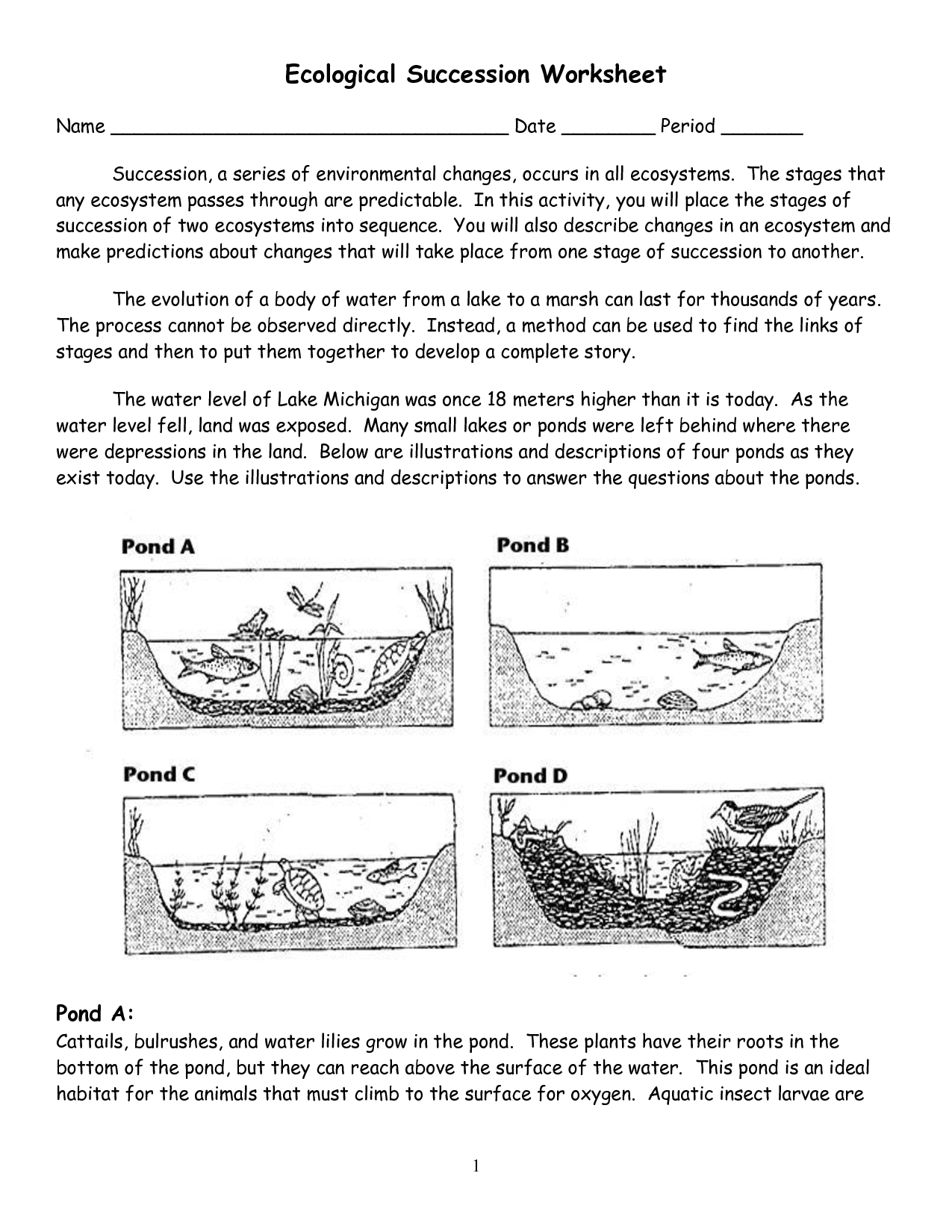
Explain the concept of ecological succession.
Ecological succession is the gradual process by which ecosystems undergo a series of changes over time. It typically starts with the colonization of pioneer species in a barren, disturbed area, which creates conditions for more complex communities to establish. Over time, these communities change in structure and species composition, leading to a more stable and diverse ecosystem. Succession can be primary, on newly formed land, or secondary, following a disturbance like a fire or logging. It is essential for ecosystem resilience and biodiversity, as different species thrive and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
How do biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem?
Biotic and abiotic factors interact in an ecosystem through complex relationships where living organisms depend on non-living factors for survival and vice versa. Biotic factors like plants and animals rely on abiotic factors such as sunlight, water, soil nutrients, and temperature for growth and reproduction. In turn, biotic factors influence abiotic factors through processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and decomposition. This mutual relationship forms the basis of ecosystem dynamics and ultimately impacts the balance and sustainability of the ecosystem as a whole.
Describe the role of decomposers in nutrient cycling.
Decomposers play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter like dead plants and animals into simpler compounds, releasing essential nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process, known as decomposition, helps to recycle nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, making them available for plants to use for growth and reproduction. By breaking down organic material, decomposers contribute to the overall health and productivity of ecosystems.
Discuss the importance of keystone species in an ecosystem.
Keystone species play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and stability of an ecosystem. These species have a disproportionately large impact on their environment relative to their abundance. By controlling the population size of other species or influencing important ecological processes, keystone species help to regulate the structure and functioning of the ecosystem. Their presence boosts biodiversity, enhances resilience to disturbances, and promotes overall ecosystem health. Therefore, the conservation and protection of keystone species are essential to safeguard the integrity and sustainability of ecosystems.
Explain how energy flows through trophic levels in a food chain.
Energy flows through trophic levels in a food chain in a unidirectional manner. Producers, such as plants and algae, harness sunlight to convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores then consume these producers, transferring the energy up the chain. Carnivores that eat herbivores obtain energy by consuming them, further transferring it along the trophic levels. At each transfer, energy is lost as heat through metabolic functions and through waste products, with only a portion being stored and available for the next trophic level. This process continues until the top predator, which receives the least amount of energy, is reached in the food chain.
Describe the process of primary succession in an ecosystem.
Primary succession is the process by which an ecosystem forms and develops in an area where no soil or organisms previously existed. It begins with pioneer species such as lichens and mosses that can grow on bare rock or soil, breaking it down and creating a layer of organic material. Over time, more complex plants like grasses and shrubs start to colonize the area, further enriching the soil and creating suitable conditions for larger plants and eventually trees to grow. As plant communities become established, they attract a variety of animals and insects, leading to a more diverse ecosystem. Primary succession can take hundreds to thousands of years to reach a stable climax community.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments