Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answers
If you're a student studying chemistry or physics and need practice with the combined gas law, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will provide you with the answers to a combined gas law worksheet, helping you review and solidify your understanding of this important topic. By having access to these answers, you can check your work and identify any areas that may require further study or clarification.
Table of Images 👆
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Gas Laws Worksheet
- Gas Laws Worksheet with Answers
- Chemistry Gas Laws Worksheet
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Combined Gas Law Practice Worksheet
- Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet Answers
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Combined Gas Law Worksheet
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Mixed Gas Laws Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
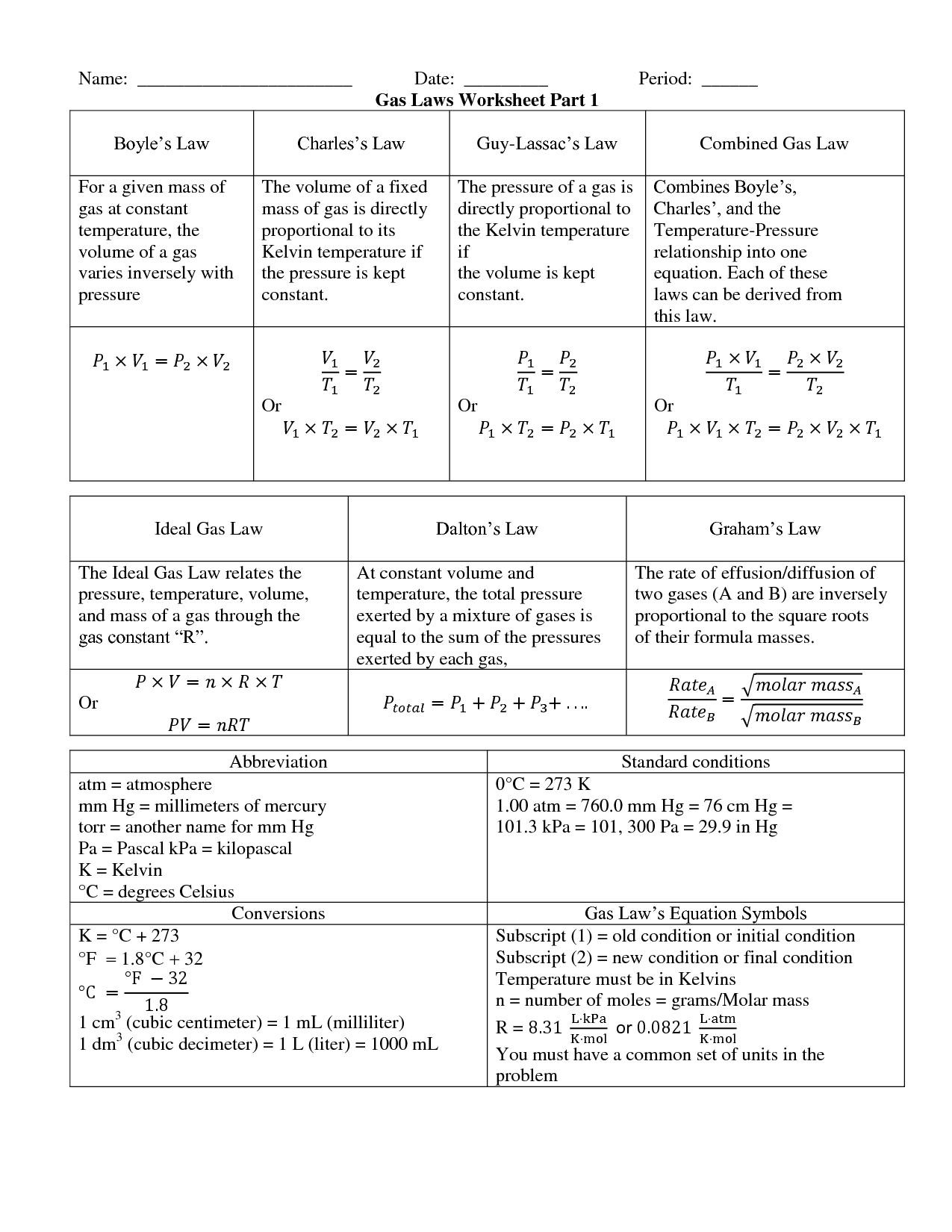
What is the Combined Gas Law equation?
The Combined Gas Law equation is expressed as (P1V1)/T1 = (P2V2)/T2, where P represents pressure, V represents volume, and T represents temperature. It combines Boyle's Law (P1V1 = P2V2), Charles's Law (V1/T1 = V2/T2), and Gay-Lussac's Law (P1/T1 = P2/T2) into a single equation that relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas when one or more of these variables change.
How is the Combined Gas Law different from other gas laws?
The Combined Gas Law differs from other gas laws, like Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, and Gay-Lussac's Law, because it combines the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature all in one equation. This means that the Combined Gas Law can be used to predict changes in any of these variables simultaneously, while the other gas laws focus on the relationship between only two of the variables at a time.
What are the units of pressure used in the Combined Gas Law equation?
The units of pressure used in the Combined Gas Law equation are typically in atmospheres (atm) or in Pascal (Pa).
What are the units of volume used in the Combined Gas Law equation?
The units of volume in the Combined Gas Law equation are typically measured in liters (L) for gases at standard conditions.
What are the units of temperature used in the Combined Gas Law equation?
The units of temperature used in the Combined Gas Law equation are always in Kelvin (K).
How is the pressure affected when the volume and temperature decrease?
When the volume and temperature decrease, the pressure increases. This is known as Boyle's Law, which states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume when the temperature is kept constant, and Charles's Law, which states that pressure is directly proportional to temperature when the volume is kept constant. As the volume decreases, the gas molecules are confined to a smaller space, resulting in more frequent collisions with the walls of the container, increasing the pressure. Similarly, as temperature decreases, the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules decreases, leading to a decrease in pressure.
How is the volume affected when the pressure and temperature increase?
When pressure and temperature increase, the volume of a gas decreases. This is described by Boyle's Law and Charles's Law, which state that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure and directly proportional to the temperature, respectively. As pressure and temperature increase, the gas particles move closer together, leading to a decrease in volume.
How is the temperature affected when the pressure and volume decrease?
When pressure and volume decrease, the temperature of a gas will also decrease. This is because as the volume decreases, the gas molecules are more closely packed together, leading to greater interactions between them. This results in a decrease in kinetic energy and therefore a decrease in temperature according to the ideal gas law equation PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature.
How can you rearrange the Combined Gas Law equation to solve for a specific variable?
To rearrange the Combined Gas Law equation to solve for a specific variable, you need to isolate that variable on one side of the equation. You can achieve this by performing algebraic operations such as multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction on both sides of the equation. By manipulating the equation in this way, you can ultimately solve for the desired variable as needed.
What are some real-world applications of the Combined Gas Law?
The Combined Gas Law is used in various real-world applications, such as in the design and operation of air conditioning and refrigeration systems, the fabrication of pressure vessels like scuba tanks, gas cylinders, and aerosol containers, as well as in the production of industrial gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. Additionally, it is useful in understanding the behavior of gases in weather forecasting and the analysis of combustion processes in engines.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments