College Physical Science Worksheets
Are you a college student in need of extra practice and review in your physical science courses? Look no further than these college physical science worksheets! Designed specifically for students like you, these worksheets cover a wide range of topics from physics to chemistry, ensuring that you have ample opportunities to reinforce your understanding of key concepts. Whether you need additional help preparing for exams or simply want to deepen your knowledge, these worksheets provide a valuable resource for enhancing your learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
- Wellness Goal Setting Worksheet
- Printable Homeschool Report Card Template
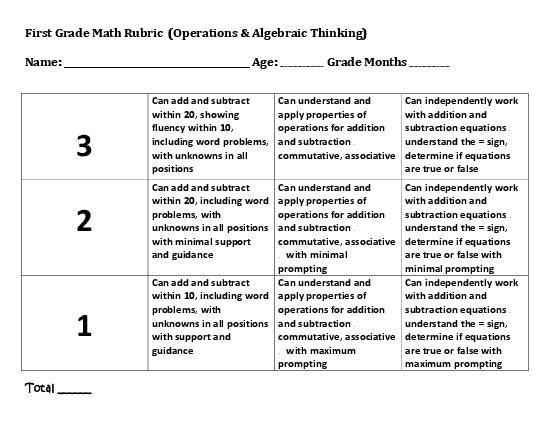
- First Grade Math Rubric
- Miley Cyrus
- 6th Grade Science Classification Worksheets
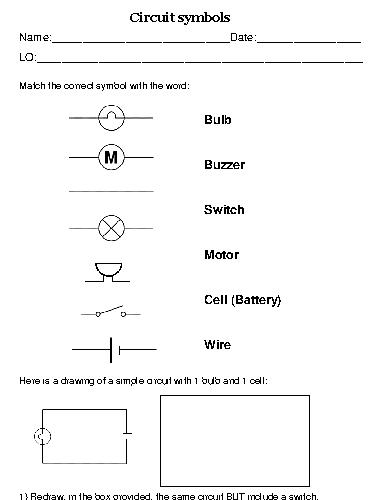
- Circuit Symbols Worksheet
- Christmas Activities in Australia
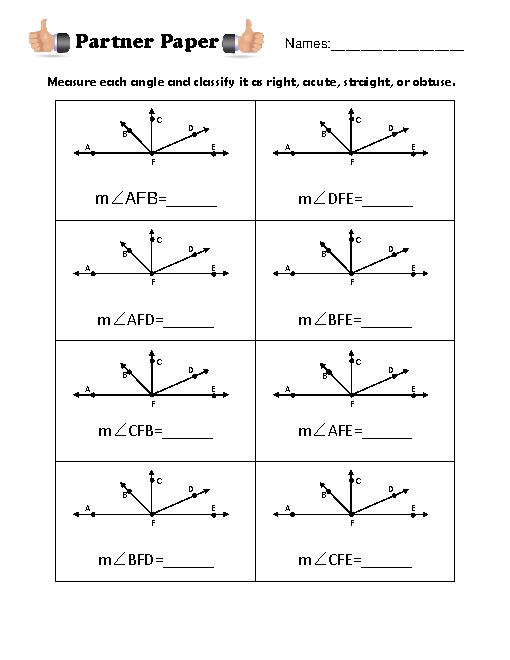
- Measure Angles with Protractor Worksheet
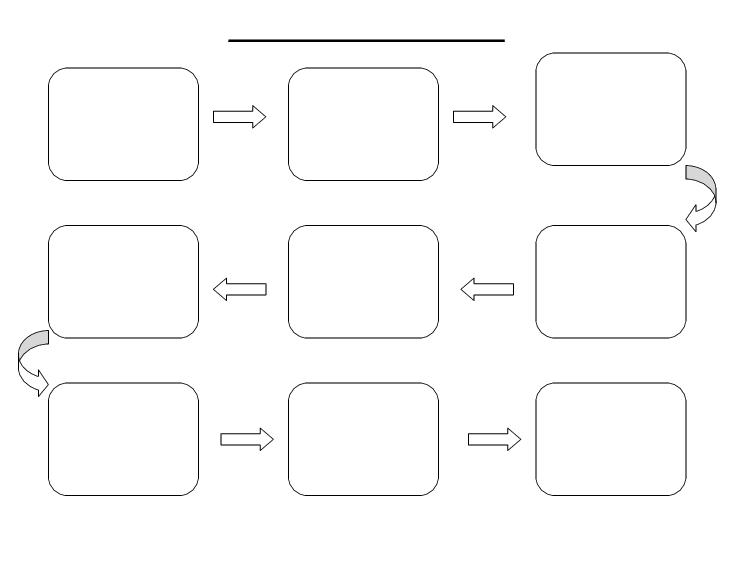
- Blank Process Flow Chart Template
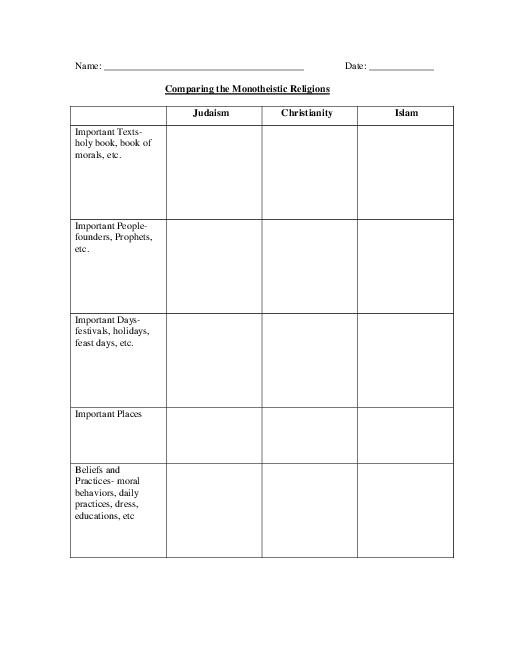
- Monotheistic Religions Graphic Organizer
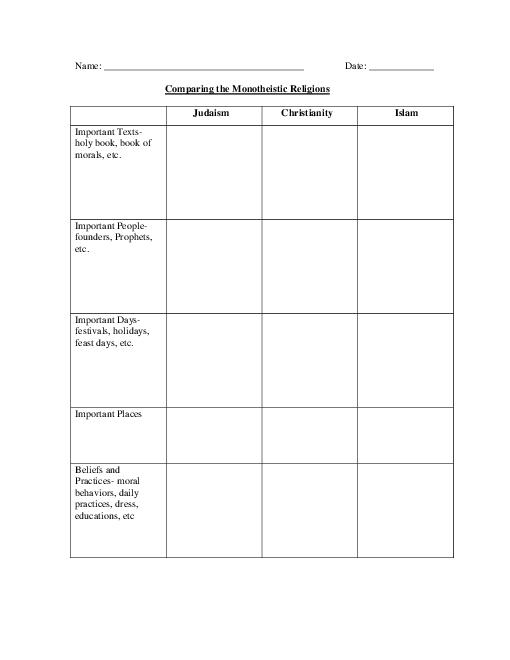
- Monotheistic Religions Graphic Organizer
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate natural phenomena, including making observations, forming hypotheses, conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. It is a structured and organized process that aims to ensure that research is conducted in a logical, objective, and reproducible manner in order to advance our understanding of the world around us.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
The key difference between speed and velocity is that speed is a scalar quantity that only measures the rate at which an object moves in a specific direction, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the speed of an object and its direction of motion. In other words, velocity not only tells you how fast an object is moving but also in which direction it is moving.
Describe the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is a complex biochemical process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll, a green pigment, to kickstart the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Through a series of enzymatic reactions known as the Calvin cycle, carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration occur to produce glucose, which serves as the primary source of energy for plant growth and metabolism, while releasing oxygen as a byproduct into the atmosphere.
What is Newton's first law of motion?
Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This means that an object will continue to stay in its current state of motion unless a force is applied to change that state.
Explain the concept of energy conservation.
Energy conservation is the practice of reducing the consumption of energy resources in order to preserve them for future generations. It involves using energy more efficiently and effectively through technologies, behaviours, and policies that minimize waste and promote sustainable practices. By conserving energy, individuals, businesses, and governments can reduce their environmental impact, lower energy costs, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy system for the long term.
How does a concave lens work?
A concave lens works by diverging or spreading out light rays that pass through it. It is thinner in the center than at the edges, causing incoming parallel rays to diverge as if they were coming from a virtual focus point behind the lens. This results in the formation of an upright and reduced virtual image on the same side as the object. Concave lenses are used to correct nearsightedness and to create a wider field of view in certain optical devices.
What is the composition of Earth's atmosphere?
Earth's atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases. Water vapor also plays a significant role in the atmosphere, varying in concentration depending on location and weather conditions.
Describe how sound travels through different mediums.
Sound travels through different mediums by creating vibrations that propagate through the molecules of the medium. In solids, such as steel or wood, sound travels fastest as molecules are closely packed, allowing for quick transmission of vibrations. In liquids, like water, sound travels by causing molecules to move in a wave-like motion. In gases, such as air, sound travels more slowly as molecules are more spread out, requiring more space for vibrations to propagate. Overall, sound travels most efficiently in solids, then liquids, and slowest in gases due to the density and arrangement of the molecules in each medium.
What are some characteristics of waves?
Waves can be described by several characteristics, including amplitude (height of wave), frequency (number of waves per unit time), wavelength (distance between identical points on consecutive waves), speed (how fast the wave moves through a medium), and direction of propagation (the path the wave follows). Waves can also be classified as transverse (oscillations perpendicular to wave direction) or longitudinal (oscillations parallel to wave direction). In addition, waves can exhibit properties like reflection (bouncing off a surface), refraction (bending when passing through different mediums), diffraction (bending around obstacles), and interference (combination of waves to produce complex patterns).
Explain the process of nuclear fusion in stars.
Nuclear fusion in stars occurs when the intense pressure and heat in the core of a star cause hydrogen atoms to combine and form helium atoms. This process releases a tremendous amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which is what makes stars shine brightly. The fusion reactions involve the conversion of mass into energy, following Einstein's famous equation E=mc^2. This continuous fusion of hydrogen into helium is what sustain a star's energy output throughout its lifetime.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments