Chemistry Worksheet Matter
Chemistry worksheets are an essential learning tool for students in the field of science. These worksheets provide a structured and organized way to explore the complexities of matter and its properties. By offering a clear entity to focus on, worksheets create a suitable learning environment for students aiming to enhance their understanding of the subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Matter Substances vs Mixtures Worksheet
- Chemistry Worksheet Matter 1 Answer Key
- Properties of Matter Worksheet Answers
- Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry Scavenger Hunt Worksheet Answers
- Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
- Elements Compounds Mixtures Worksheet Answers
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Matter Solid-Liquid Gas Worksheet
- Intensive Extensive Properties Worksheet
- 5th Grade Science Worksheets
More Chemistry Worksheets
Chemistry Lab Equipment WorksheetChemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
Chemistry Conversion Factors Worksheet
Fun Chemistry Worksheets
What is the definition of matter in chemistry?
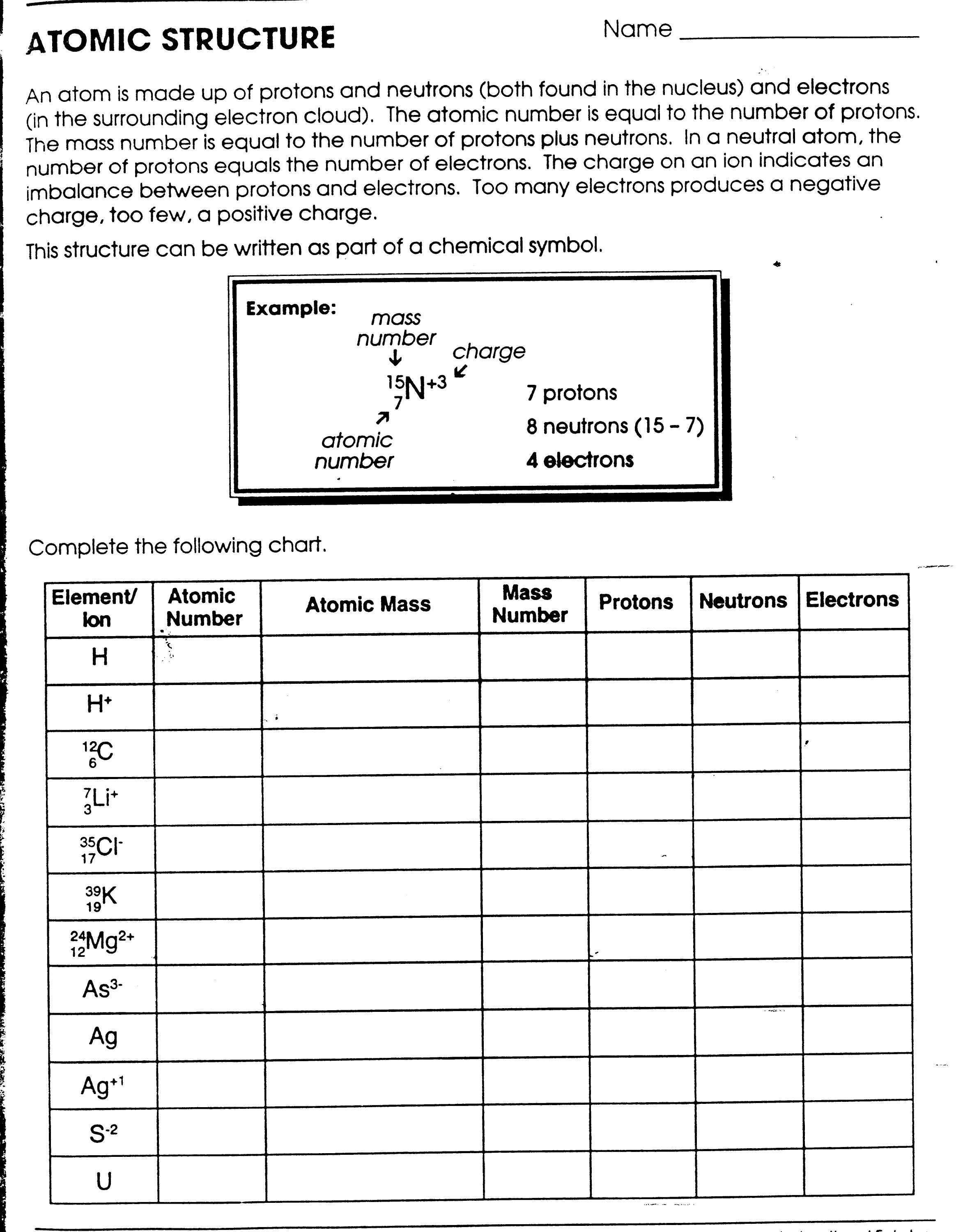
Matter in chemistry is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass, consisting of atoms and molecules. It is the substance of which all physical objects are composed, and it can exist in various states such as solid, liquid, or gas. Different types of matter can undergo changes through physical or chemical processes, leading to the formation of new substances.
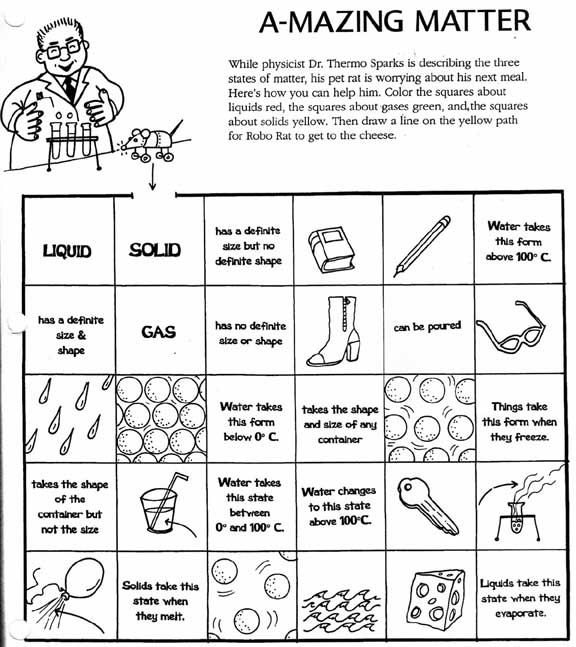
What are the three states of matter?
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
What is the difference between a physical and a chemical change?
A physical change alters the form or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical composition, such as melting ice into water. In contrast, a chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties from the original substances, like the rusting of iron or the combustion of wood.
Give an example of a physical change.
An example of a physical change is melting ice. When ice is exposed to heat, it changes state from a solid to a liquid without altering its chemical composition. This transformation is reversible, as the liquid water can be frozen back into ice by cooling it.
Give an example of a chemical change.
One example of a chemical change is the process of rusting, where iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of water to form iron oxide, a reddish-brown compound. This change is irreversible and involves the formation of new substances with different chemical properties than the original iron.
What are elements and how are they related to matter?
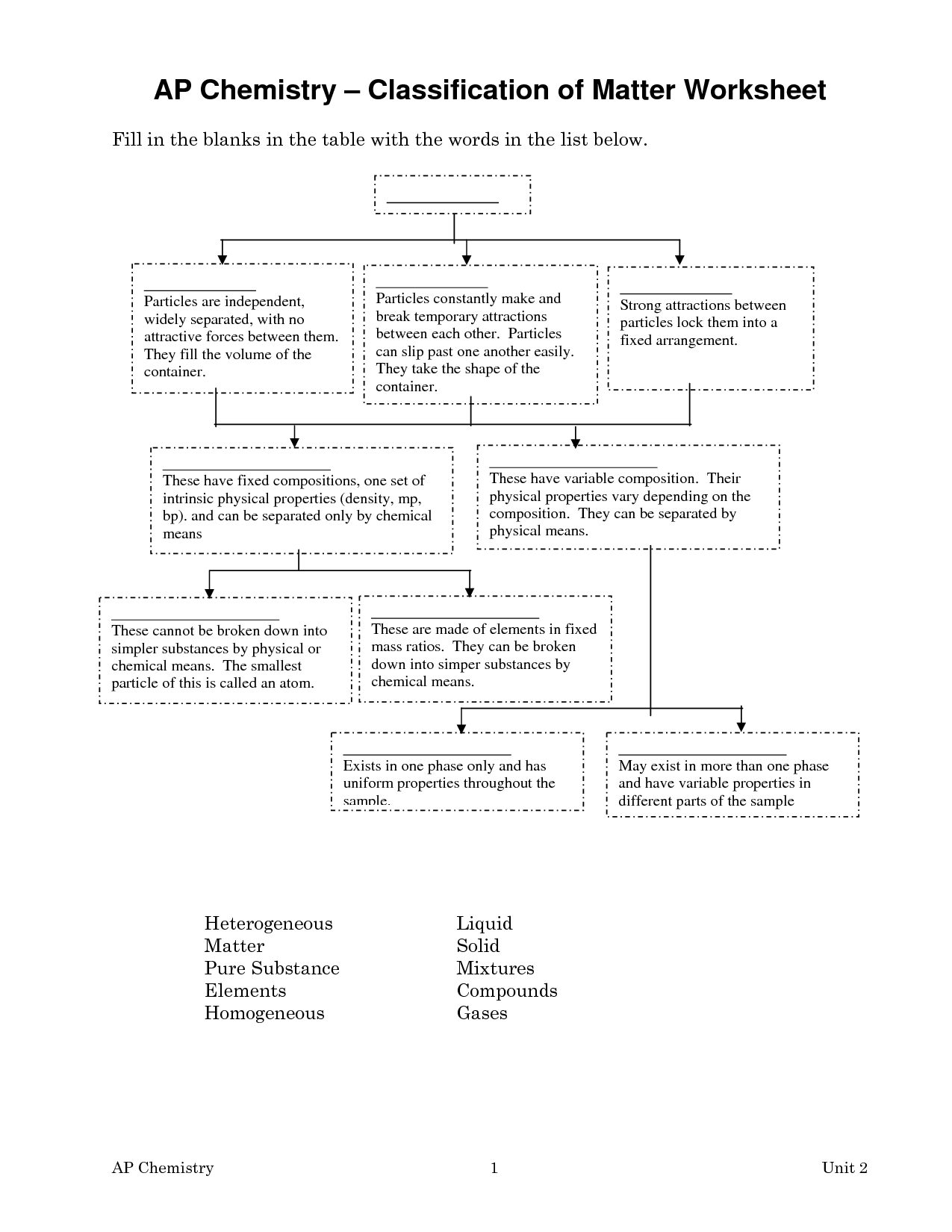
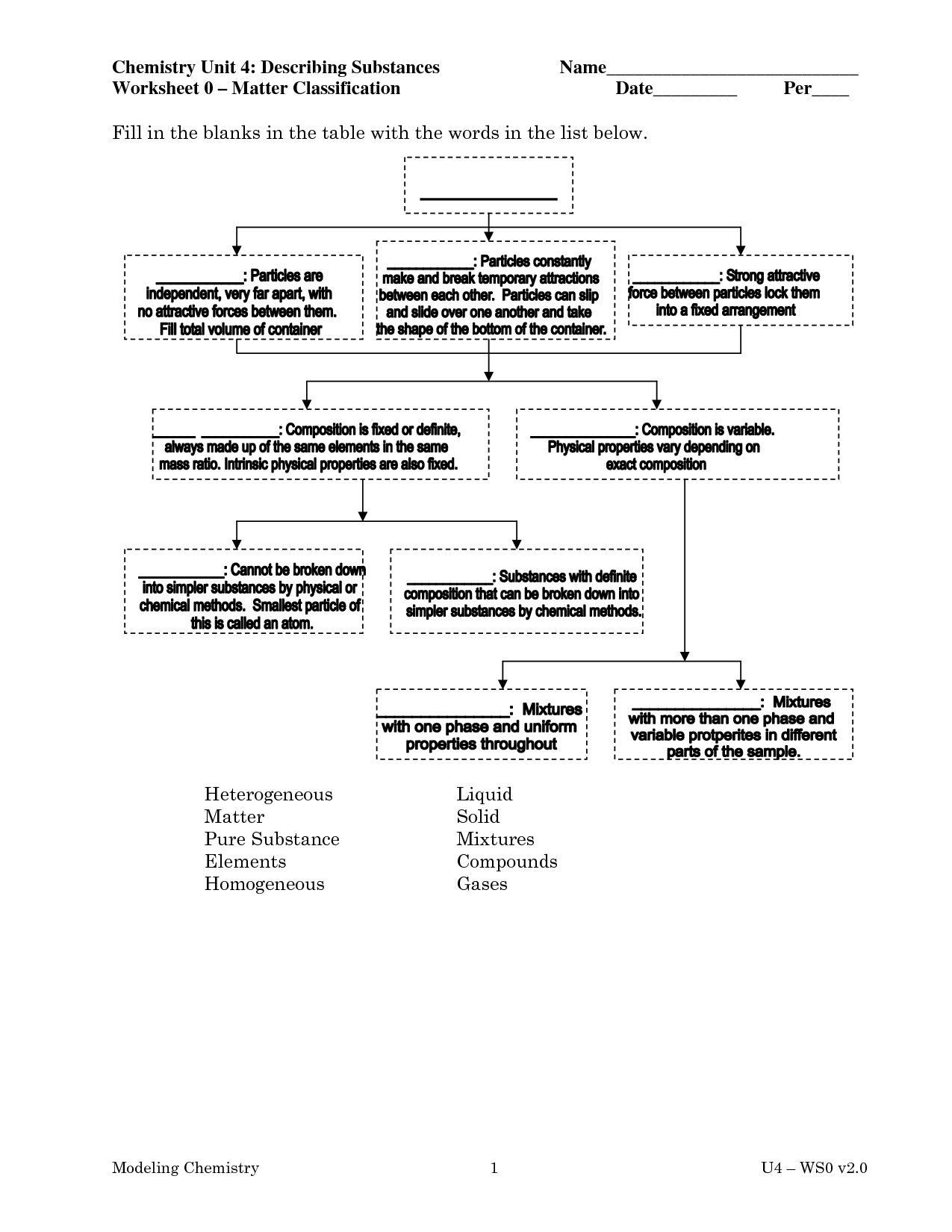
Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical means. They are the building blocks of matter and are composed of atoms with a specific number of protons in the nucleus. Each element has unique physical and chemical properties that determine how it interacts with other elements to form compounds. Matter is made up of elements and compounds that consist of various combinations of elements. The composition of matter determines its properties and behavior, making elements integral components of the material world around us.
What are compounds and how are they different from elements?
Compounds are substances composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together in specific ratios, resulting in unique properties. Elements, on the other hand, are pure substances made up of only one type of atom. In compounds, the elements chemically combine to form a new substance with characteristics different from those of the individual elements, while elements exist as standalone entities with distinct properties.
What is a mixture and give an example.
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically blended together, but not chemically bonded. An example of a mixture is saltwater, where salt (sodium chloride) is dissolved in water but can easily be separated by physical means such as evaporation.
What are the two types of mixtures and how do they differ?
The two types of mixtures are homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout, with the components being evenly distributed at a molecular level. Examples include saltwater and air. Heterogeneous mixtures contain visibly different substances that can be easily distinguished, with the components not evenly distributed. Examples include a mixture of oil and water or a salad.
Explain the concept of conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
The concept of conservation of mass in chemical reactions states that the total mass of the reactants involved in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products formed. In other words, mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, it simply changes form. This principle is a fundamental law of nature and is known as the law of conservation of mass, first proposed by Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century. By adhering to this principle, scientists can accurately predict and balance chemical equations to ensure that mass is conserved throughout the reaction.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments