Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are an essential tool for students studying biology, as they provide a structured format for practicing and reinforcing important concepts. Whether you are a high school student preparing for exams or a college student reviewing lectures, worksheets offer a valuable opportunity to engage with the material. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets for studying cells and tissues, focusing on how they can assist you in understanding and retaining the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Biology If8765 Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Worksheet
- Cell Membrane Worksheet Answer Key
- Muscular System Answer Key Chapter 6
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets
- The Muscular System Worksheets Answer Key Chapter 6
- The Muscular System Answer Key Chapter 6
- Connective Tissue Worksheet Answers
- Principles of Evolution Answer Key Chapter 10
- Anatomy Epithelial Tissues Worksheet Answers
- Tissue Worksheets Anatomy and Physiology Answers
- Cancer Cell Cycle Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Boundaries Worksheet Answers
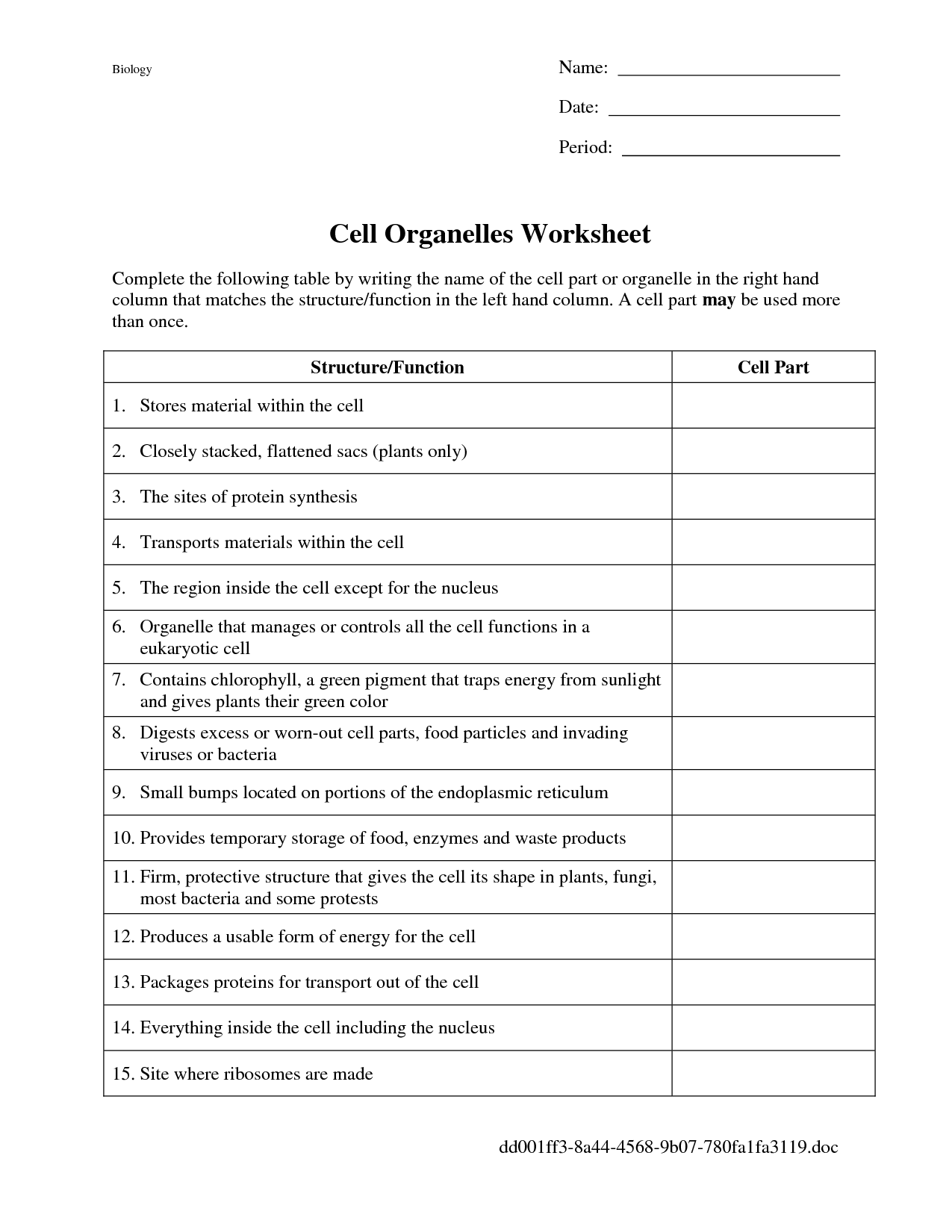
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are the basic building blocks of life?
The basic building blocks of life are known as biomolecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates provide energy, proteins are essential for cell structure and function, lipids are important for cell membranes and energy storage, and nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, carry genetic information and allow for cellular processes like protein synthesis. These biomolecules are crucial for the growth, development, and overall functioning of living organisms.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, functions as a protective barrier that separates the interior of a cell from its external environment. It regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell, allowing essential nutrients to enter and waste products to be removed. The plasma membrane also plays a crucial role in cell communication and signaling, enabling cells to interact with their surroundings and other cells. Additionally, it helps maintain cell shape and structure.
What are the three main components of the cytoplasm?
The three main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol, which is the gel-like fluid where organelles are suspended, the organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus that carry out specific functions within the cell, and the cytoskeleton, which provides structural support and assists in cell movement and division.
How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are more complex, including a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells typically have a single circular chromosome and are smaller in size, whereas eukaryotic cells have multiple linear chromosomes and can be larger in size. Additionally, prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually via binary fission, while eukaryotic cells can undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction.
What is the role of DNA in the cell?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that contains instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms. In the cell, DNA serves as the blueprint for proteins and enzymes, which are essential for carrying out various cellular functions. It also carries the genetic information passed from parents to offspring, determining an individual's physical traits and characteristics. Ultimately, DNA plays a crucial role in storing and transmitting genetic information that is vital for the survival and functioning of cells and organisms.
What are the main types of tissues in the human body?
The main types of tissues in the human body are epithelial tissue (covering and lining), connective tissue (support, connection, and protection), muscle tissue (movement), and nervous tissue (communication and control).
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue functions as a protective barrier that covers the surfaces of the body and lines organs, cavities, and passageways. It serves to regulate the exchange of ions and nutrients, provide sensation, facilitate secretion and absorption, as well as protect against pathogens and mechanical damage. Additionally, epithelial tissue plays a role in controlling the passage of substances in and out of the body.
What is the structure and function of muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue is composed of muscle fibers that contain specialized proteins called actin and myosin, which enable the muscles to contract and generate force. This tissue is responsible for movement, as well as supporting vital body functions such as the beating of the heart and digestion. Muscle tissue can be divided into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each with its own structure and functions. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are under voluntary control, allowing for conscious movement. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and contracts rhythmically to pump blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle is found in organs and blood vessels, regulating involuntary processes like digestion and blood flow.
How does nervous tissue transmit electrical signals?
Nervous tissue transmits electrical signals by utilizing specialized cells called neurons. Neurons have an electrically excitable membrane that allows them to generate and propagate electrochemical impulses known as action potentials. When a neuron receives a stimulus, it causes a change in the membrane potential, initiating an action potential that travels down the length of the neuron. This electrical signal is transmitted through the neuron via ion channels and neurotransmitters, allowing for communication between neurons and ultimately leading to a coordinated response throughout the nervous system.
What is the role of connective tissue in the body?
Connective tissue in the body plays a crucial role in providing structural support, connecting and anchoring different tissues and organs, and aiding in the transport of nutrients and waste products. It also helps in maintaining the shape and integrity of organs, as well as in the repair and healing processes of the body. Additionally, connective tissue also plays a role in the immune response and inflammation within the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments