Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
Worksheets are an invaluable tool for both teachers and students when it comes to reinforcing learning and testing knowledge on specific subjects. They provide a structured and organized way to practice and assess understanding. For students who need extra practice or review in the area of cell transport, having access to a reliable answer key can be highly beneficial.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell and Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
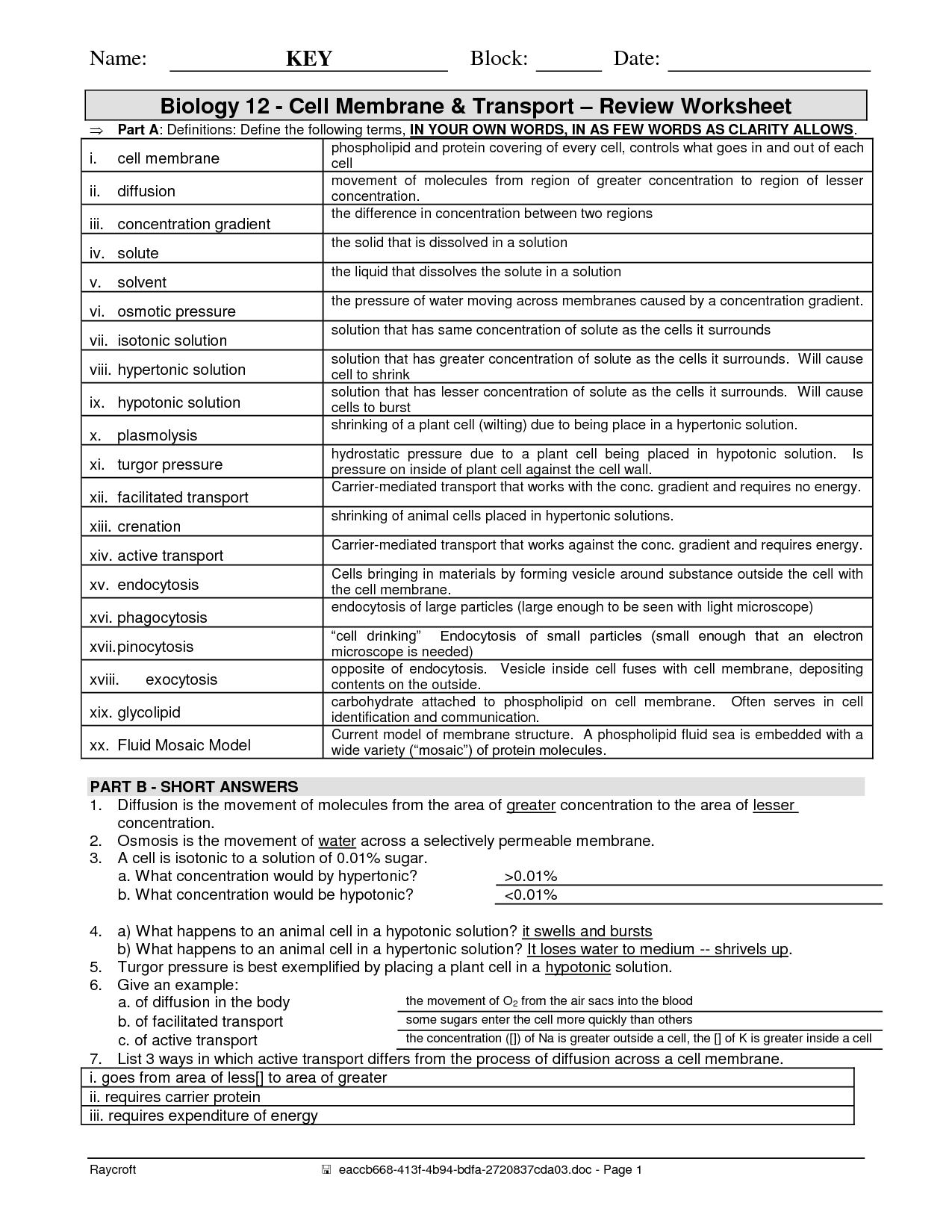
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Cell Transport Worksheet
- Cell Membrane Worksheet Answer Key
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
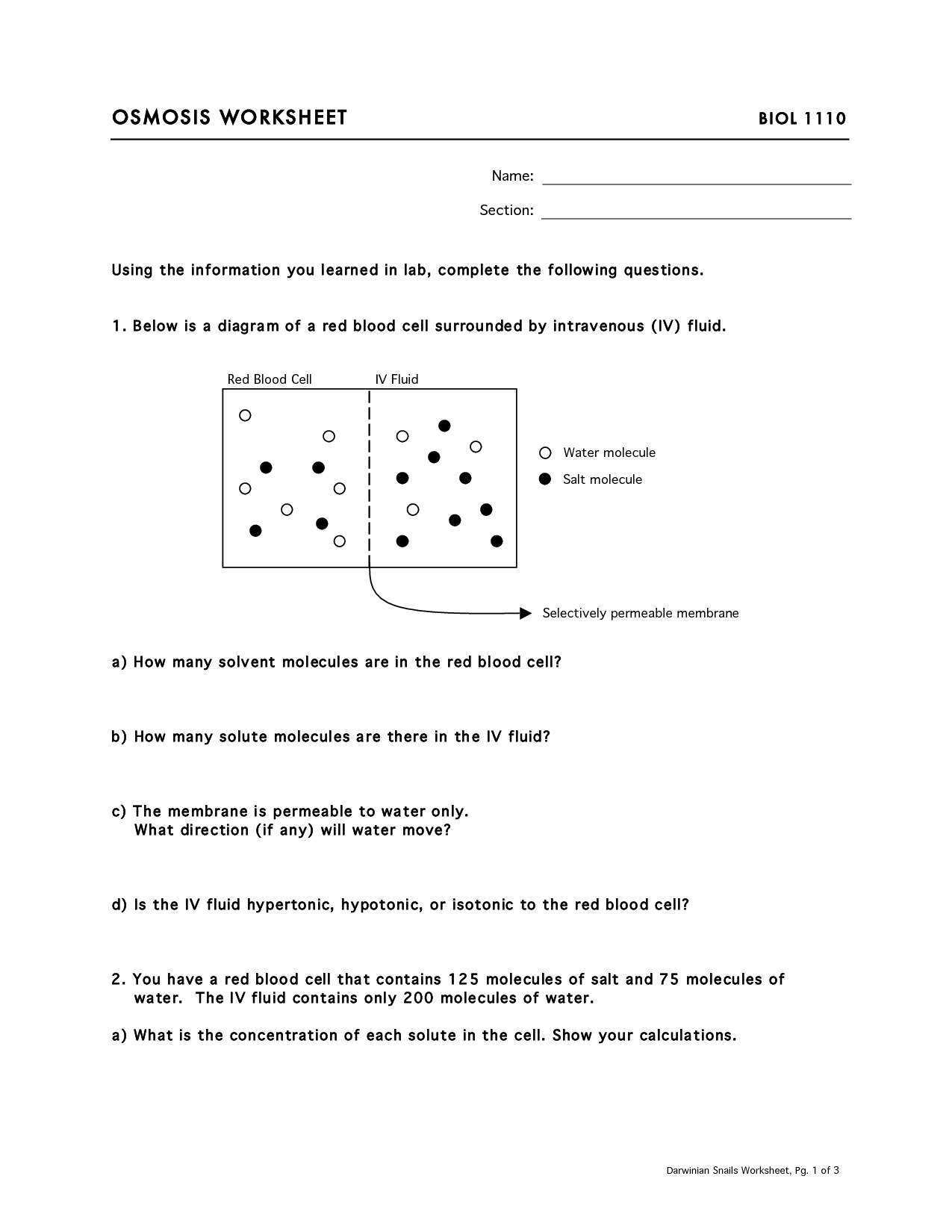
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Cell Processes Worksheet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Review Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is cell transport?
Cell transport is the process of moving materials into and out of a cell. This can be done through various mechanisms such as diffusion, osmosis, active transport, and vesicle transport. These processes are essential for maintaining the proper balance of nutrients, ions, and waste products within a cell, allowing it to function properly and stay healthy.
What are the two main types of cell transport?
The two main types of cell transport are passive transport, which does not require energy and includes diffusion and osmosis, and active transport, which requires energy and includes processes like protein pumps and endocytosis/exocytosis.
Describe passive transport.
Passive transport is a process in which molecules move across a cell membrane without the use of additional energy. This movement occurs down the concentration gradient, from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Passive transport includes processes such as simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, all of which allow substances to pass through the cell membrane to maintain cellular homeostasis.
Explain the process of diffusion.
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This occurs spontaneously, driven by the natural tendency of particles to spread out and reach equilibrium. In this process, molecules move randomly and collide with each other, leading to a net movement from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration until a dynamic equilibrium is reached. Diffusion is vital for processes such as gas exchange in the lungs, nutrient uptake in cells, and the dispersal of molecules across cell membranes.
What is osmosis and how does it occur?
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration, in order to equalize the concentration of solute on both sides of the membrane. This process occurs until equilibrium is reached and is driven by the natural tendency of water to move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration in an effort to balance the solute concentrations on either side of the membrane.
Describe facilitated diffusion.
Facilitated diffusion is a passive transport process where large or polar molecules move across the cell membrane with the help of specific protein channels or carriers. These proteins create a pathway for molecules to pass through the membrane down their concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to low concentration, without the need for energy input. Facilitated diffusion enables the transport of essential molecules such as glucose and amino acids into cells, allowing for the maintenance of proper cellular function.
What is active transport?
Active transport is a process in which a cell expends energy, typically in the form of ATP, to move molecules or ions across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient. This mechanism enables cells to maintain specific internal concentrations of substances that differ from those in their external environment, allowing for key cellular functions such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction.
How do cells use ATP in active transport?
Cells use ATP in active transport as a source of energy to move molecules or ions against their concentration gradient across the cell membrane. ATP provides the necessary energy for the transport proteins embedded in the cell membrane to pump these substances across the membrane, allowing the cell to maintain proper concentration gradients and perform essential functions such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction.
Explain endocytosis and exocytosis.
Endocytosis is the process by which a cell takes in molecules by engulfing them within a vesicle formed from its plasma membrane. There are different types of endocytosis, including phagocytosis (cell eating) and pinocytosis (cell drinking). On the other hand, exocytosis is the process by which cells release molecules from vesicles within the cell into the extracellular space. This process is important for the secretion of hormones, enzymes, and neurotransmitters. Both endocytosis and exocytosis play crucial roles in maintaining the internal environment of the cell and communicating with the external environment.
What are the differences between phagocytosis and pinocytosis?
The main difference between phagocytosis and pinocytosis lies in the substances being engulfed by the cell. Phagocytosis involves the cell engulfing large particles such as bacteria or other cells, while pinocytosis involves the cell engulfing smaller particles or fluids from its surroundings. Phagocytosis is more targeted and selective in its process compared to pinocytosis, which is more generalized and involves the nonspecific ingestion of extracellular fluid and particles.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments