Cell Theory Worksheet
If you are a student studying biology and eager to dive into the fascinating world of cells, then this Cell Theory Worksheet is just what you need. This worksheet will help you solidify your understanding of the cell theory, a fundamental concept in biology, by providing a range of engaging and thought-provoking questions.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is cell theory?
Cell theory is a fundamental scientific theory that states all living organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms, and all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This theory forms the foundation of modern biology and our understanding of how living organisms are organized and function.
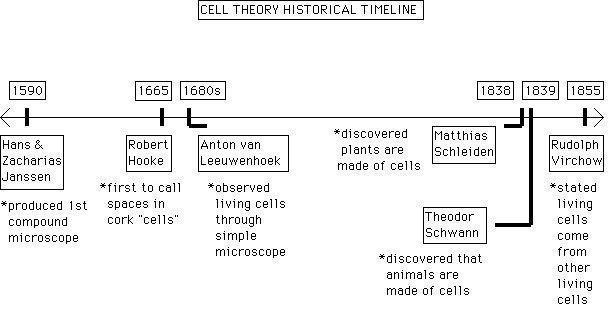
When was cell theory first proposed?
The cell theory was first proposed in the mid-17th century, with the works of scientists like Robert Hooke and Anton van Leeuwenhoek contributing to its development. However, it was not until the 19th century that the modern cell theory, emphasizing the cell as the fundamental unit of life and the idea that all living organisms are composed of cells, was fully established by scientists like Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.
Who are the scientists credited with formulating cell theory?
The scientists credited with formulating cell theory are Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. Schleiden and Schwann proposed the theory that all living organisms are composed of cells, while Virchow added the idea that all cells come from pre-existing cells. Together, their work laid the foundation for our understanding of the fundamental unit of life, the cell.
What are the three main principles of cell theory?
The three main principles of cell theory are: 1) all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, 2) the cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms, and 3) all cells come from pre-existing cells through the process of cell division.
Name and describe the components of a typical eukaryotic cell.
A typical eukaryotic cell consists of several key components. The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material and controls cellular activities. The cytoplasm includes various organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and mitochondria, each serving specific functions like protein synthesis, transportation, digestion, and energy production. The plasma membrane surrounds the cell, regulating the passage of substances in and out. Additionally, eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeleton, composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, which maintain cell shape and enable movement.
How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller in size and have a simpler structure compared to eukaryotic cells. Additionally, prokaryotic cells have a circular DNA molecule, whereas eukaryotic cells have linear DNA molecules. Eukaryotic cells are found in multicellular organisms, while prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms like bacteria.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a protective barrier, regulating the transport of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining cell shape and integrity, and allowing cells to communicate with each other by interacting with the external environment and other cells.
Name and describe the main organelles found in most animal cells.
The main organelles found in most animal cells are the nucleus, which houses the genetic material of the cell and controls its activities; the mitochondria, responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration; the endoplasmic reticulum, involved in protein and lipid synthesis; the Golgi apparatus, which modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport; lysosomes, which contain enzymes to break down cellular waste and pathogens; and the plasma membrane, which acts as a barrier, controlling the exchange of substances between the cell and its environment.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus is the control center of a cell, housing the cell's DNA and directing all cellular activities. It regulates gene expression, controls cell growth and division, and is responsible for transmitting genetic information to the next generation. The nucleus also acts as a barrier, protecting the DNA from potentially harmful substances in the cytoplasm.
Describe the process of cell division and its significance in cell theory.
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides to form two daughter cells. This is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in living organisms. In cell theory, cell division is significant because it underpins the idea that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, and new cells can only arise from pre-existing cells. This process allows cells to maintain a balance between growth and division, ensuring proper function and development in organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments