Cell Structure and Processes Worksheet
Are you a biology student looking for a comprehensive resource to help you understand cell structure and processes? Look no further! Our Cell Structure and Processes Worksheet is designed to provide you with an in-depth exploration of this fascinating subject. With this worksheet, you will gain a solid understanding of the various components and functions of cells, allowing you to excel in your studies and achieve academic success.
Table of Images 👆
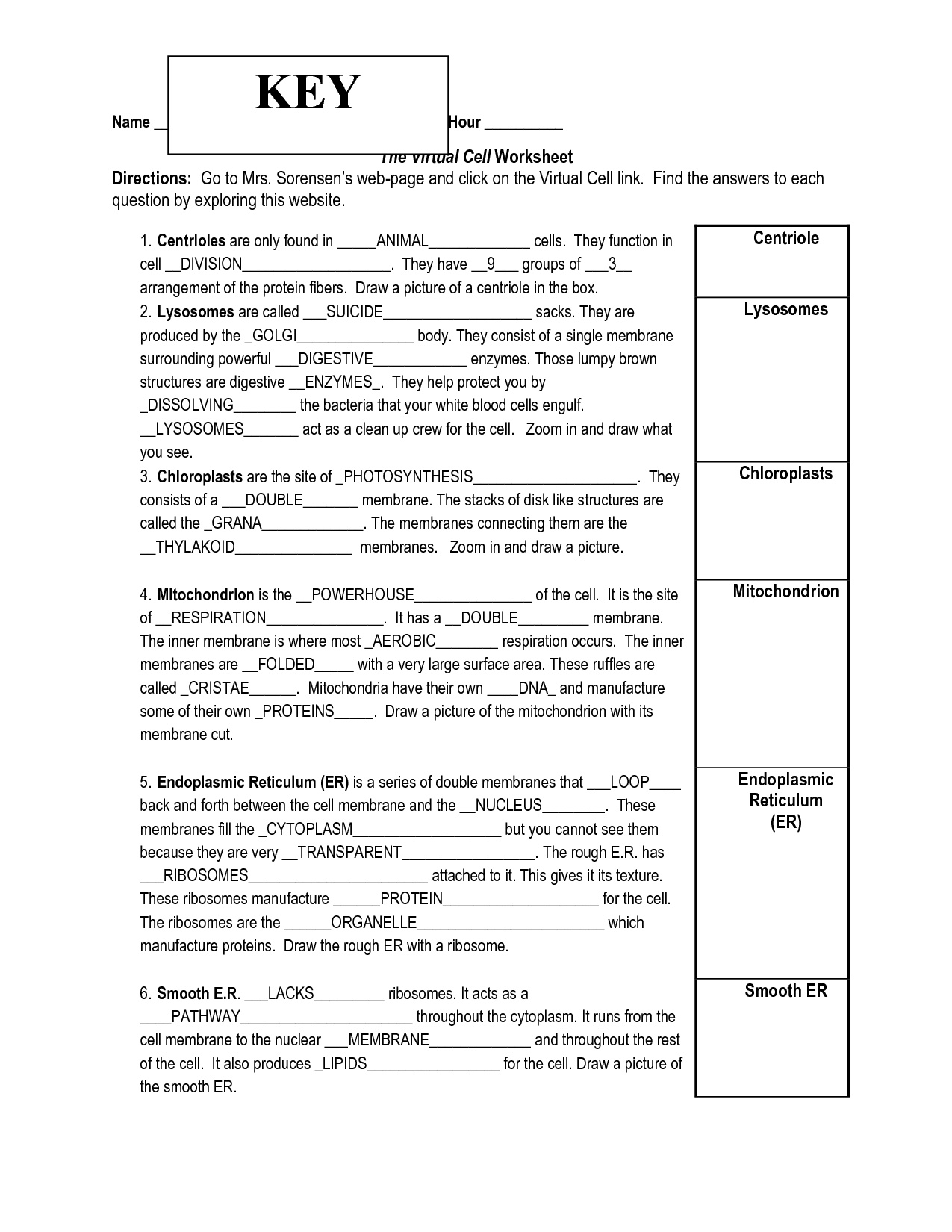
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Parts and Functions Worksheet Answers
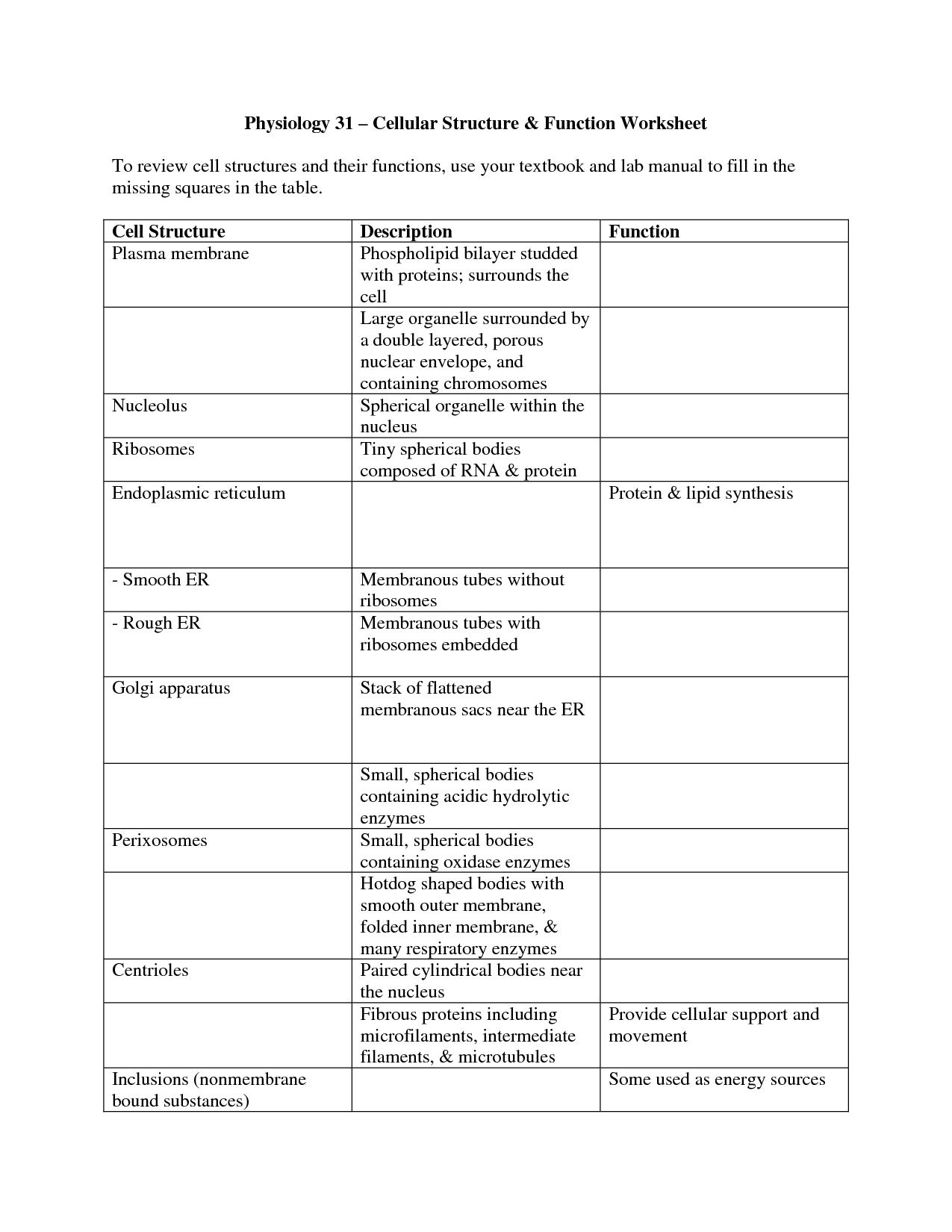
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
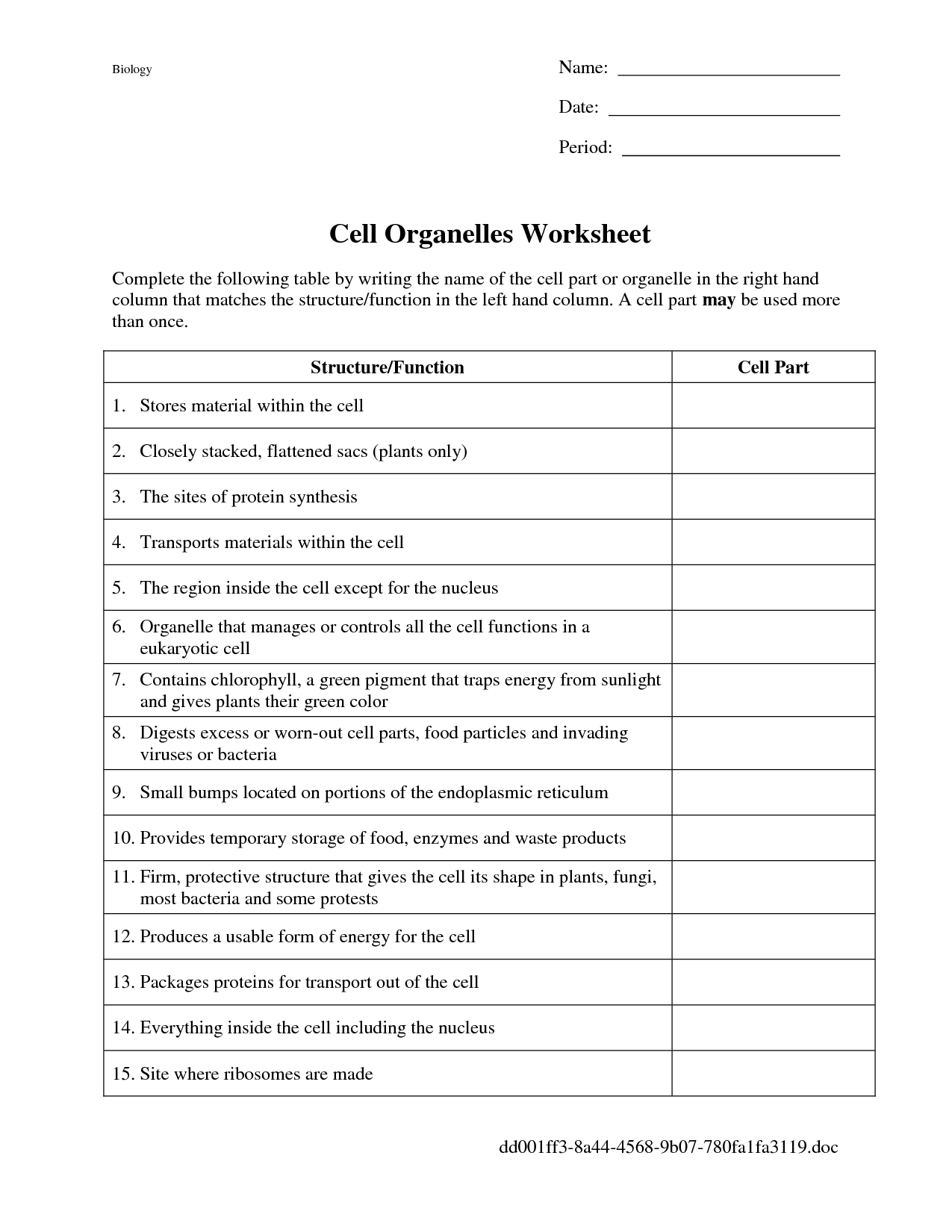
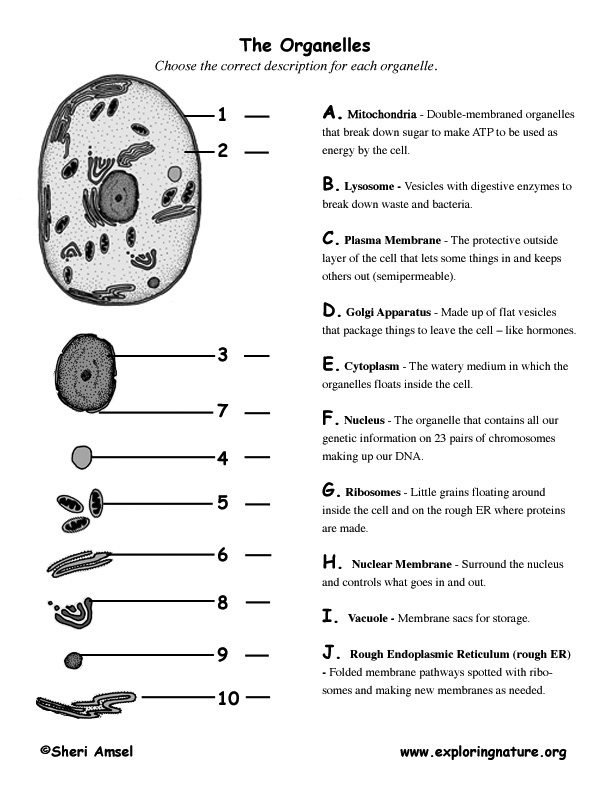
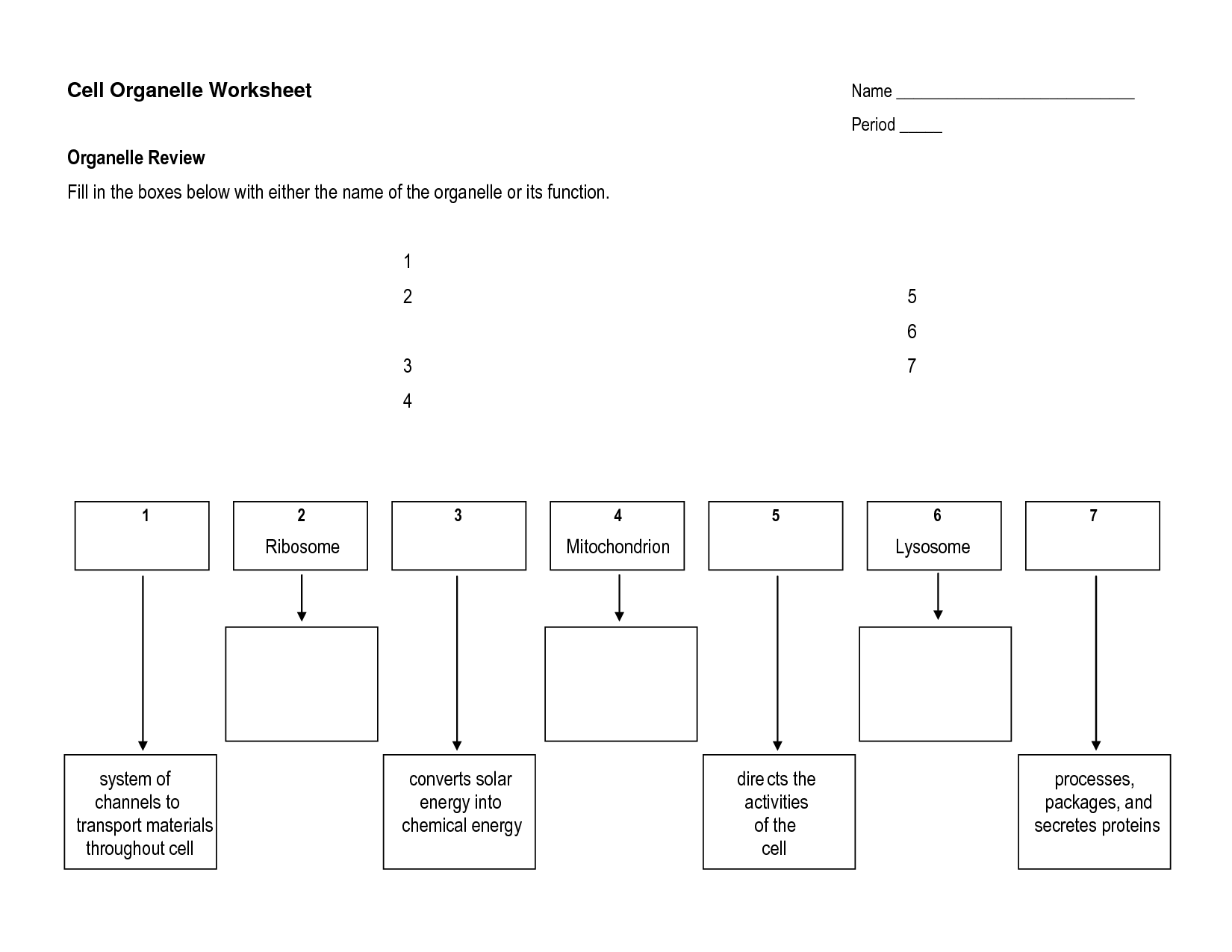
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheets
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle Answers
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheet
- Cell Crossword Puzzle Worksheet
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Function of the Cell: Welcome to Modern Biology
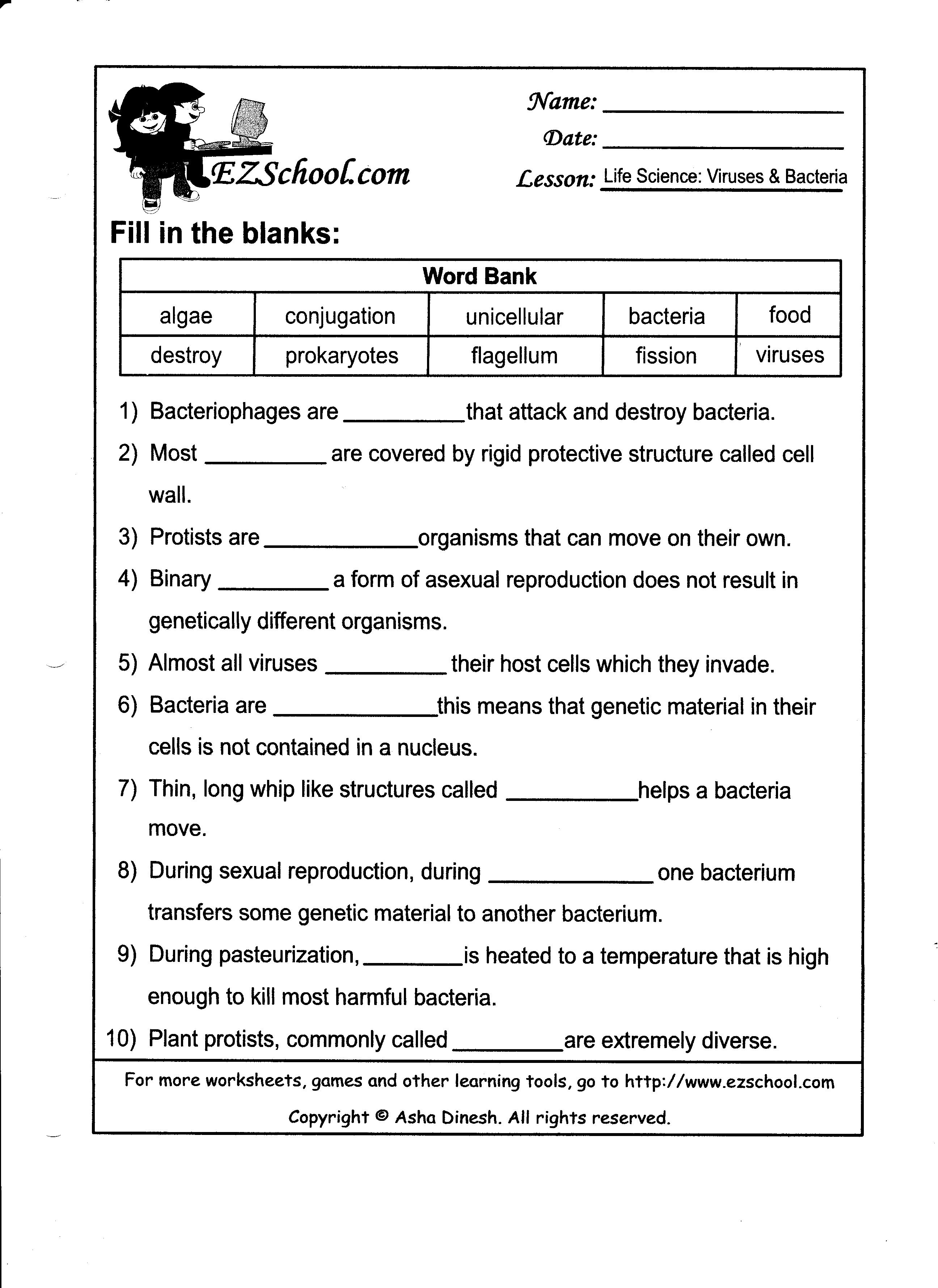
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
- Cell Organelles and Functions
- Cells and Organelles Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The main function of the cell membrane is to control what enters and exits the cell, maintaining the cell's internal environment and facilitating communication with surrounding cells. This barrier is selectively permeable, allowing nutrients and essential molecules to enter while preventing harmful substances from coming in. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a role in cell signaling, cell adhesion, and maintaining the cell's shape and structure.
What are the three main components of the cell theory?
The three main components of the cell theory are: 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, 2) The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms, and 3) Cells arise from pre-existing cells through cell division.
Describe the structure and function of the nucleus.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material in the form of chromosomes. Its main function is to regulate gene expression by controlling the transcription and replication of DNA. The nucleus also plays a vital role in storing and protecting the genetic information that determines cell function and structure. Additionally, it is involved in cell division processes such as mitosis and meiosis, ensuring accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
Explain the role of mitochondria in cell metabolism.
Mitochondria play a crucial role in cell metabolism by generating the majority of a cell's adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which serves as the primary energy source for cellular activities. They carry out aerobic respiration, a process that involves converting nutrients from food into usable energy through a series of biochemical reactions. This ATP production occurs in the mitochondrial inner membrane through the electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Additionally, mitochondria are involved in other metabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the regulation of cellular metabolism. Overall, mitochondria are essential organelles that are central to the energy production and metabolism of cells.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, processing, and transport within cells. It consists of two regions: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is responsible for lipid metabolism and detoxification. Additionally, the ER plays a role in calcium storage and signaling within cells.
Describe the differences between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes on its surface, giving it a rough appearance, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and appears smooth. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis and processing, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum plays a role in lipid and steroid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium ion storage. Additionally, the rough endoplasmic reticulum is more prevalent in cells that have a high protein synthesis demand, such as secretory cells, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is prominent in cells that require lipid metabolism, like liver cells.
What is the purpose of the Golgi apparatus in a cell?
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids that are synthesized in the cell. It acts as a processing center where proteins undergo post-translational modifications and are then packaged into vesicles for transportation to their final destinations within the cell or outside of the cell. In essence, the Golgi apparatus plays a critical role in the secretory pathway and intracellular transport of molecules.
Explain the role of lysosomes in intracellular digestion.
Lysosomes play a crucial role in intracellular digestion by containing enzymes that can break down various biological molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. These enzymes are highly acidic and work optimally at low pH levels, allowing the lysosome to digest and recycle cellular waste, unwanted materials, and even pathogens, helping to maintain a healthy cellular environment. In this way, lysosomes act as the "digestive system" of the cell, ensuring that necessary nutrients are recycled, waste is eliminated, and potentially harmful materials are destroyed.
Describe the structure and function of chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells responsible for photosynthesis, the process that converts sunlight into energy. They have a double membrane structure with an inner membrane enclosing a fluid-filled stroma where thylakoid membranes are stacked into grana. Within the thylakoid membranes, pigments like chlorophyll capture sunlight, initiating a series of chemical reactions that produce ATP and NADPH, which are used in the Calvin cycle to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. Chloroplasts also contain their own DNA and ribosomes, allowing them to partially self-replicate.
What is the purpose of vacuoles in plant cells?
The purpose of vacuoles in plant cells is to provide structural support, store nutrients and waste products, regulate turgor pressure to maintain cell rigidity, and aid in the degradation and recycling of cellular components. Additionally, vacuoles help maintain the pH balance and store pigments that give plants their color.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments