Cell Review Worksheet Answer Key
Are you struggling to find the answers to your cell review worksheet? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the answer key for your cell review worksheet. Whether you are a student studying biology or a teacher looking to provide your students with additional resources, our answer key will help you gain a better understanding of the important concepts and components of cells. So, let's dive in and explore the fascinating world of cells together!
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Review Answer Key
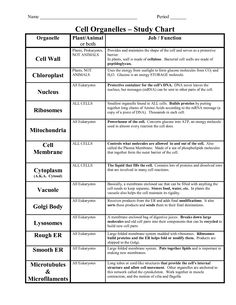
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Crossword Puzzle Worksheet Answers
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis Diagrams Worksheet Answer Key
- The Muscular System Worksheets Answer Key Chapter 6
- Properties of Water Worksheet Answers
- Science Review Answers Chapter 4
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheets
- Animal Cell Questions and Answers
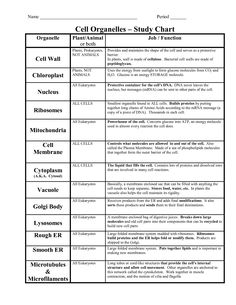
- Cell Organelles and Their Functions Chart
- Cell Organelles and Their Functions Chart
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms?
The basic unit of structure and function in living organisms is the cell. Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of life, capable of carrying out all necessary functions to sustain life. Each cell contains organelles that perform specific functions and work together to maintain the overall health and functioning of the organism.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell, allowing for the passage of essential nutrients and molecules while maintaining the internal environment of the cell. It also provides structural support and protection to the cell, as well as helps in cell recognition and communication with other cells.
How does the cell membrane maintain homeostasis?
The cell membrane maintains homeostasis by regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable, allowing only certain molecules to enter and exit based on the needs of the cell. This helps maintain the proper balance of ions, nutrients, and waste products inside the cell. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a role in communication with other cells and signaling pathways to coordinate responses to changes in the cell's environment, further contributing to homeostasis.
What are the two types of cells found in living organisms?
The two types of cells found in living organisms are prokaryotic cells, lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and eukaryotic cells, possessing a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the primary function of the nucleus?
The primary function of the nucleus is to store and protect the genetic material (DNA) of the cell and to regulate gene expression to control cellular activities and functions.
What are the organelles responsible for protein synthesis?
The organelles responsible for protein synthesis are ribosomes, which can be found either freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes are responsible for translating the instructions in messenger RNA into protein molecules through a process called translation.
How do cells obtain energy to carry out their functions?
Cells obtain energy to carry out their functions through a process called cellular respiration. This process involves breaking down glucose molecules from food to generate ATP, the energy currency of cells. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria, where glucose is oxidized to produce ATP through a series of enzymatic reactions involving glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
What is the purpose of the mitochondria in a cell?
The purpose of mitochondria in a cell is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration. This organelle converts nutrients from glucose into ATP, which is essential for powering various cellular activities and functions. Essentially, mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, providing the energy necessary for all cellular processes to occur.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in protein production?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is responsible for protein synthesis and processing within the cell. It acts as a site for the synthesis of proteins and also facilitates the folding, modification, and transport of these proteins. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes attached to the ER, and then they undergo various modifications such as glycosylation and disulfide bond formation as they move through the ER. The ER plays a crucial role in ensuring that proteins are properly folded and ready for their specific functions within the cell or for export outside the cell.
How do plant cells differ from animal cells in terms of structure and function?
Plant cells differ from animal cells in several ways. Structurally, plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose outside the cell membrane, which provides structural support and protection. They also contain organelles called chloroplasts, where photosynthesis occurs to produce food for the plant. Functionally, plant cells are specialized for photosynthesis, so they have a higher number of chloroplasts compared to animal cells. Additionally, plant cells store energy in the form of starch, whereas animal cells store energy in the form of glycogen.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments