Cell Division Worksheet
Cell division is an essential biological process that occurs in all living organisms, allowing them to grow, repair, and reproduce. If you are a student or teacher looking for a comprehensive and engaging resource to help you understand and practice cell division concepts, you have come to the right place. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of worksheets in learning about cell division and highlight key topics that these worksheets cover, providing a valuable tool for students of biology and educators alike.
Table of Images 👆
- Mitosis Notes Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Chromosomes and Cell Division Worksheet
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Diagram Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Printable Cell Word Search Puzzle
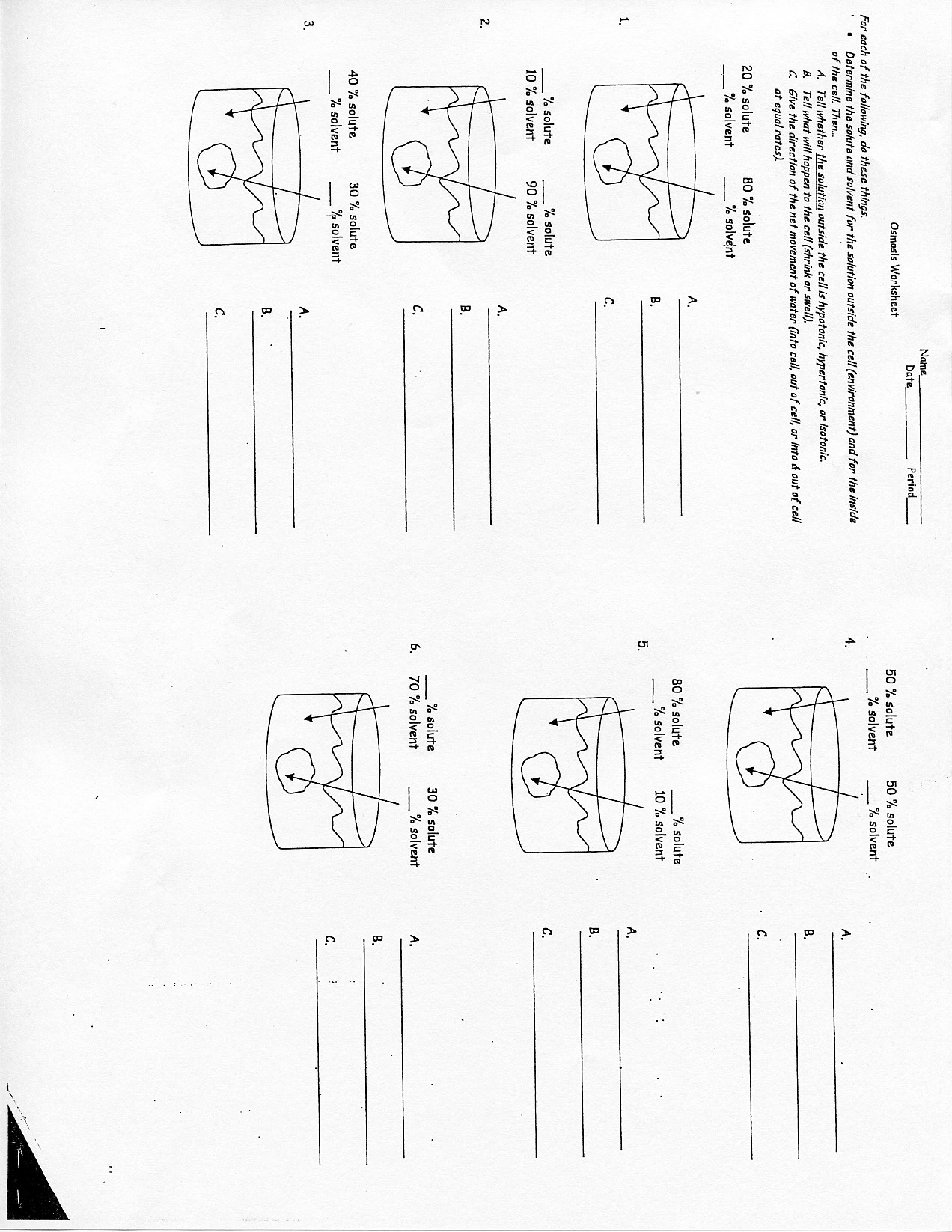
- Cell Transport Diffusion Osmosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Processes Worksheet
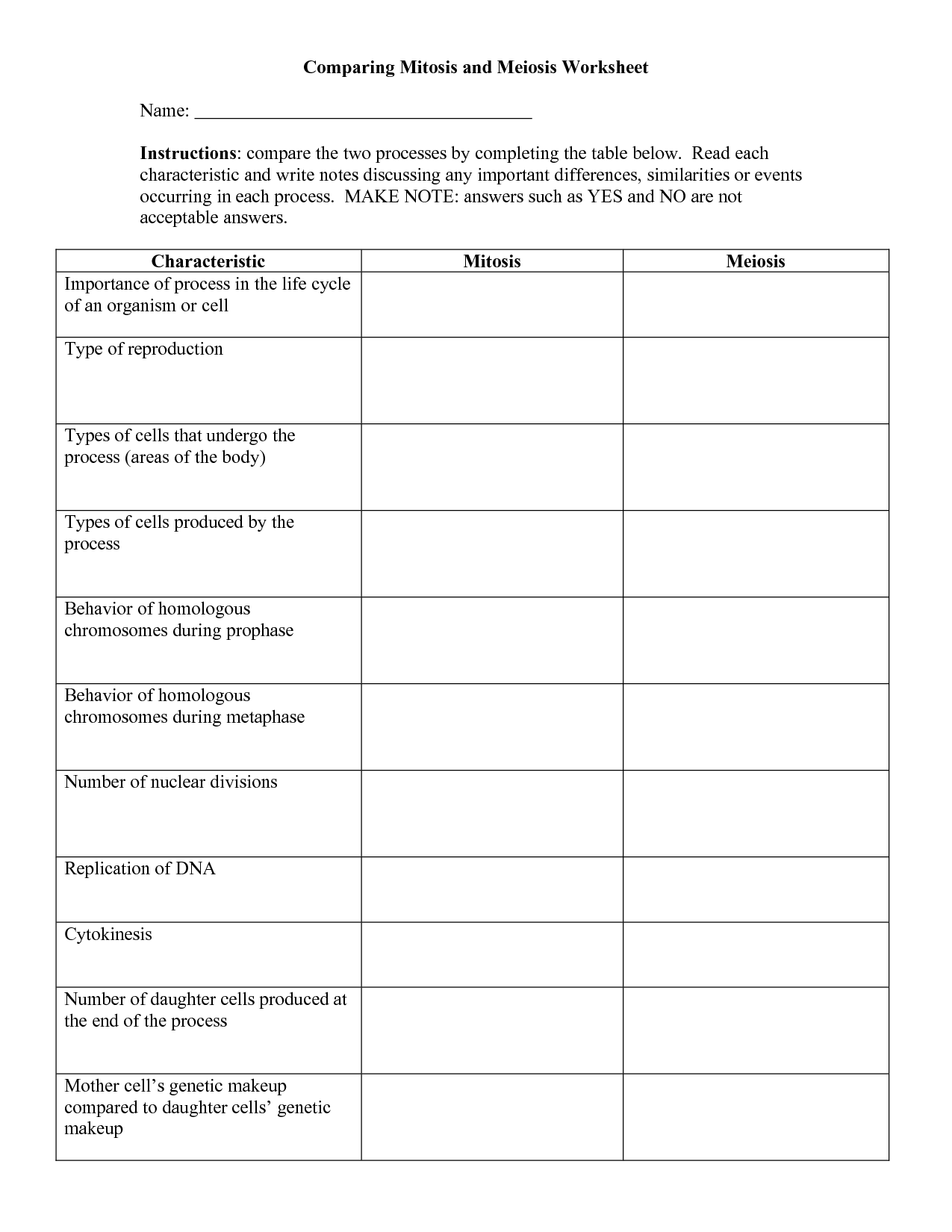
- Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet
- One Point Perspective Hand Out
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Prentice Hall Biology Workbook Answer Key Chapter 13
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is cell division?
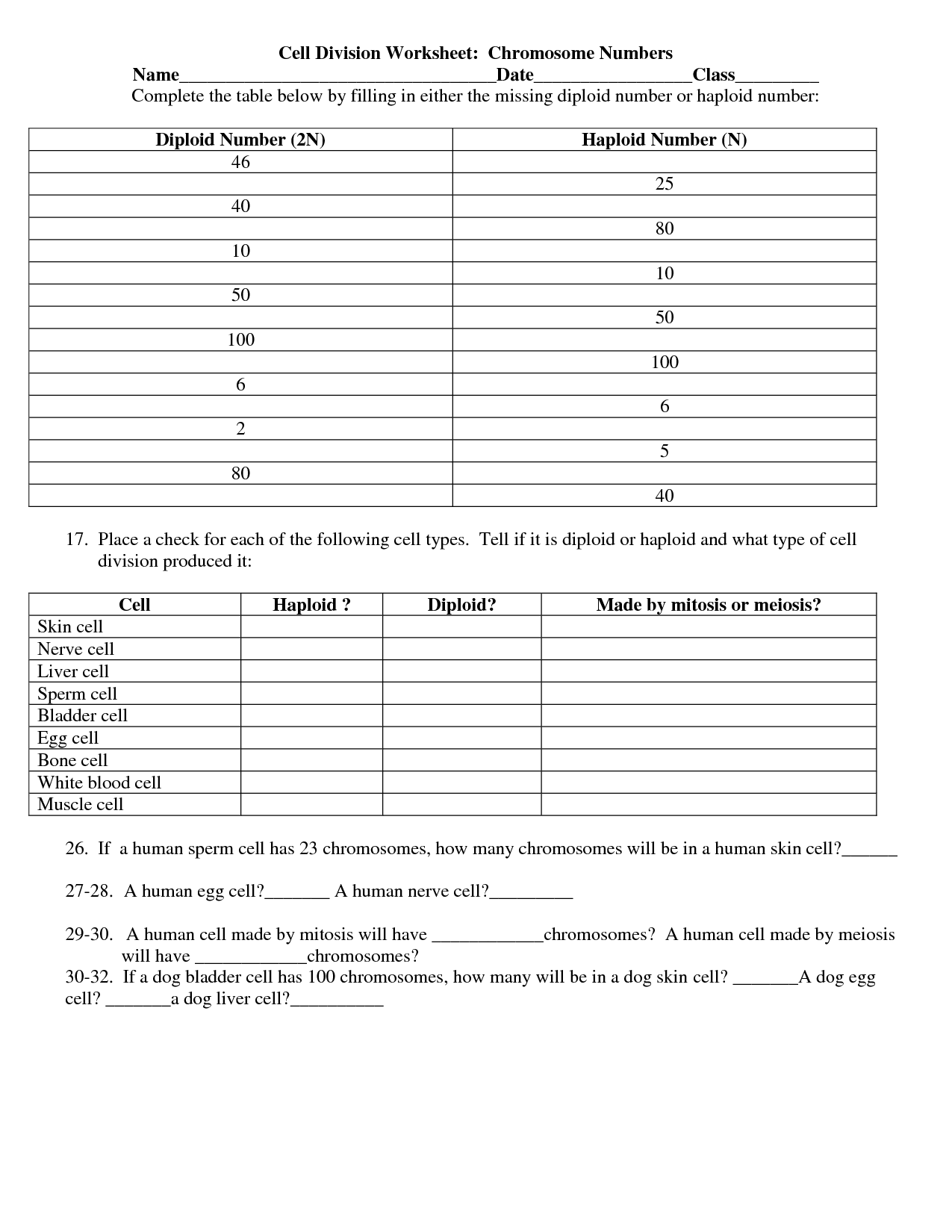
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells, each containing a complete set of chromosomes. It is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms, enabling the production of new cells to replace old or damaged ones. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis, which results in two genetically identical cells, and meiosis, which produces cells with half the number of chromosomes for sexual reproduction.
What happens to the DNA during cell division?
During cell division, the DNA replicates so that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material. The DNA is first tightly coiled into chromosomes, which are then separated and distributed equally into the two new daughter cells. This process ensures that each cell has the correct amount of genetic information needed for proper functioning.
What are the two main types of cell division?
The two main types of cell division are mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells and is involved in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a type of cell division that produces four genetically unique daughter cells and is involved in the formation of gametes for sexual reproduction.
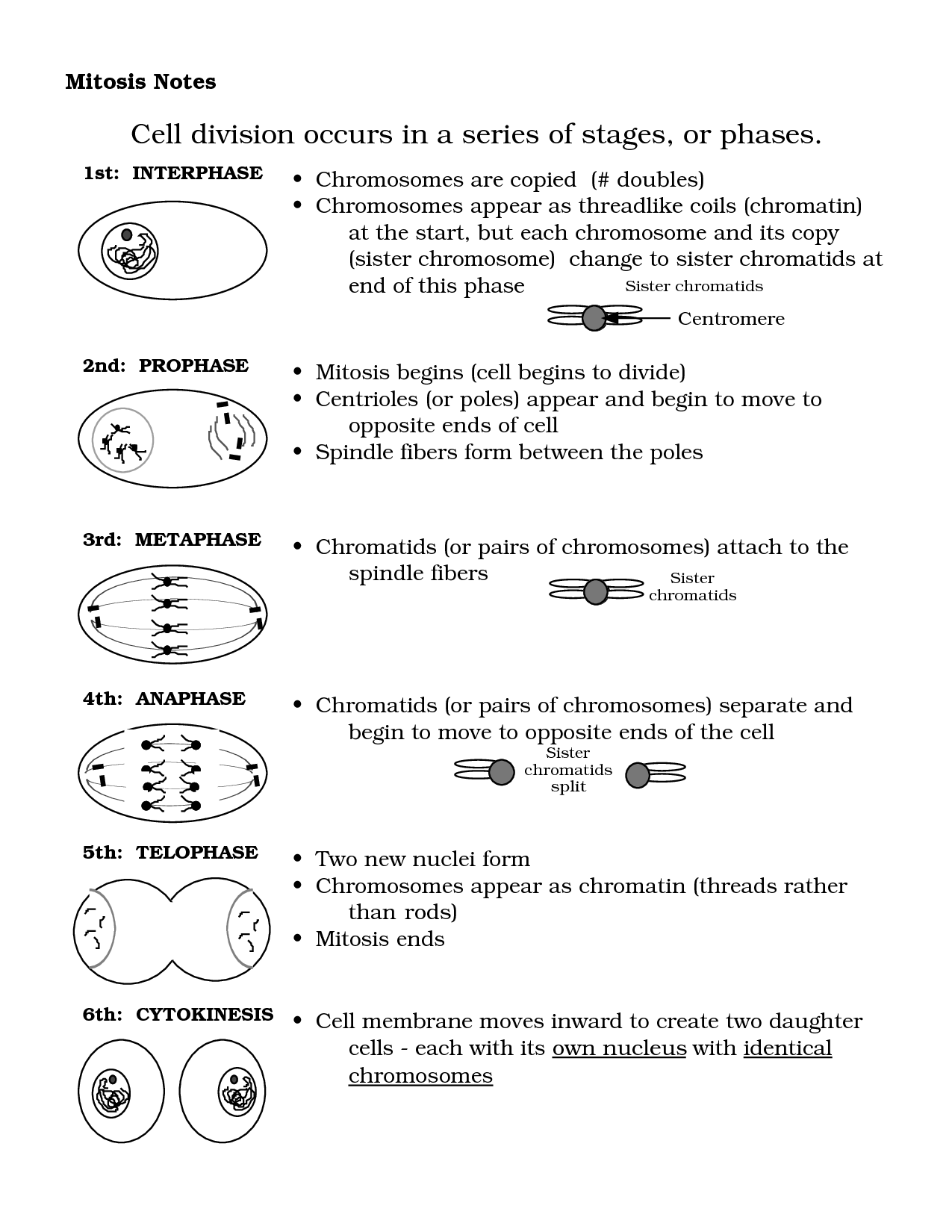
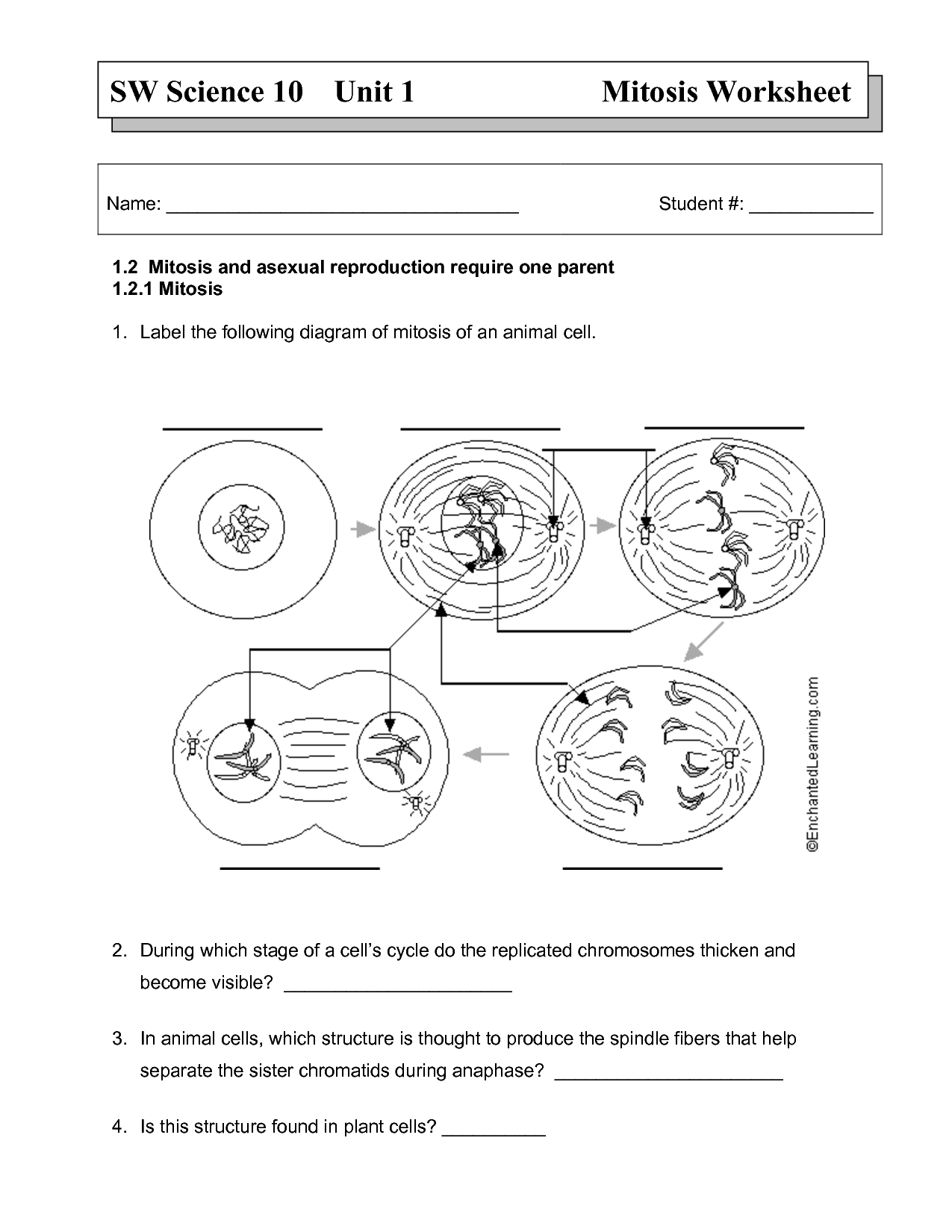
Describe the process of mitosis.
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The process consists of several stages, including prophase (chromosomes condense), metaphase (chromosomes align at the center), anaphase (chromatids separate and move to opposite poles), telophase (chromosomes decondense), and cytokinesis (cell membrane pinches off to form two separate daughter cells). Mitosis plays a critical role in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms.
What are the main stages of mitosis?
The main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase involves the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes, breakdown of the nuclear envelope, and formation of the mitotic spindle. Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes in the middle of the cell. Anaphase sees the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. Telophase involves the decondensation of chromosomes, reformation of the nuclear envelope, and cytokinesis, leading to the division of the cell into two daughter cells.
How does meiosis differ from mitosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces sex cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, resulting in genetic diversity, while mitosis is a cell division process that produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell for growth and repair in somatic cells. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in four haploid cells, while mitosis involves only one round of division, resulting in two diploid cells.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to produce genetically diverse offspring by reducing the chromosome number by half and shuffling genetic material through homologous recombination, resulting in the production of haploid sex cells (gametes) in organisms that reproduce sexually. This process ensures genetic variation and allows for the possibility of evolution through natural selection.
What is the significance of cell division in growth and development?
Cell division is vital for growth and development as it allows an organism to increase in size by producing new cells and replacing old or damaged ones. It plays a key role in embryonic development, tissue repair, and maintenance of physiological functions. The precise control of cell division ensures that an organism grows and develops properly, maintains its structure and functions, and has the ability to regenerate tissues when needed. Overall, cell division is crucial for the growth, development, and overall well-being of an organism.
How does cell division contribute to tissue repair?
Cell division plays a critical role in tissue repair by allowing damaged tissues to be replaced and regenerated. When tissues are injured, signals are sent to nearby cells to divide and multiply rapidly to form new cells. This process helps to fill in the damaged area and restore the structural integrity of the tissue. By continuously dividing and differentiating, cells in the tissue can effectively replace lost or damaged cells, promoting healing and repair.
What can go wrong during cell division and lead to genetic disorders?
Several things can go wrong during cell division that can lead to genetic disorders, such as errors in chromosome segregation during mitosis or meiosis, leading to aneuploidy, where cells end up with an abnormal number of chromosomes. Mutations in genes involved in cell division or DNA repair can also cause genetic disorders, as these errors can result in changes to the genetic code that can lead to diseases such as cancer or developmental disorders. Additionally, environmental factors like radiation or chemicals can damage DNA, causing disruptions in cell division and potentially leading to genetic disorders.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments