Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
The Cell Cycle Review Worksheet provides a comprehensive review of the different phases of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. This worksheet is designed for students who are studying biology or any related fields and need a concise and engaging way to review the key concepts and processes involved in the cell cycle.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
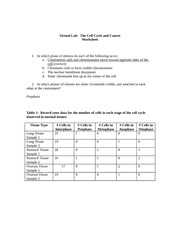
- Cancer and Cell Cycle Worksheet
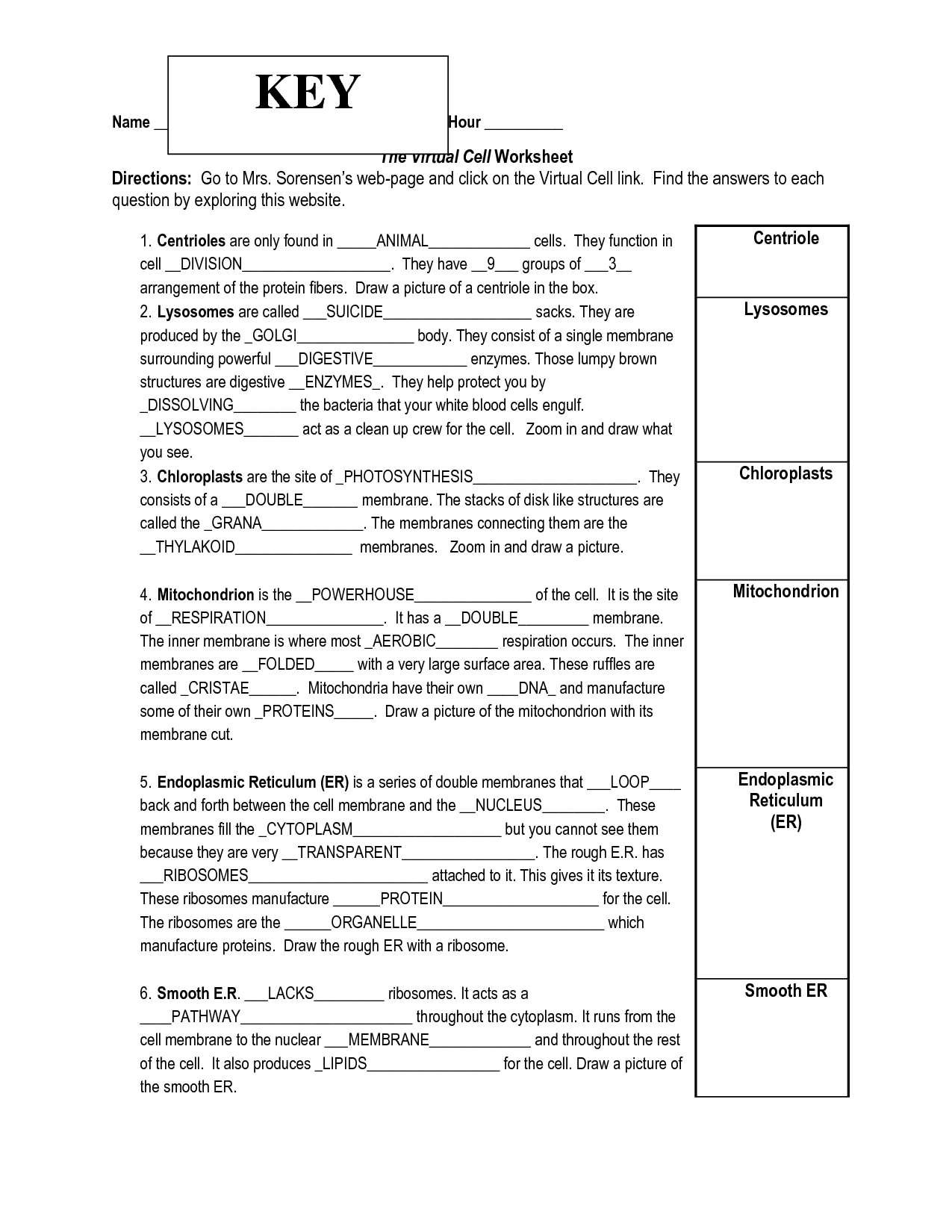
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Worksheet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Circulatory System Worksheet Answer Key
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Biology If8765 Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure that cells can grow, replicate their DNA, and divide to form new cells. It allows cells to maintain proper function, growth, repair damaged tissues, and replace old or dying cells. The cell cycle is a tightly regulated process that encompasses different phases to accurately produce daughter cells with identical genetic information.
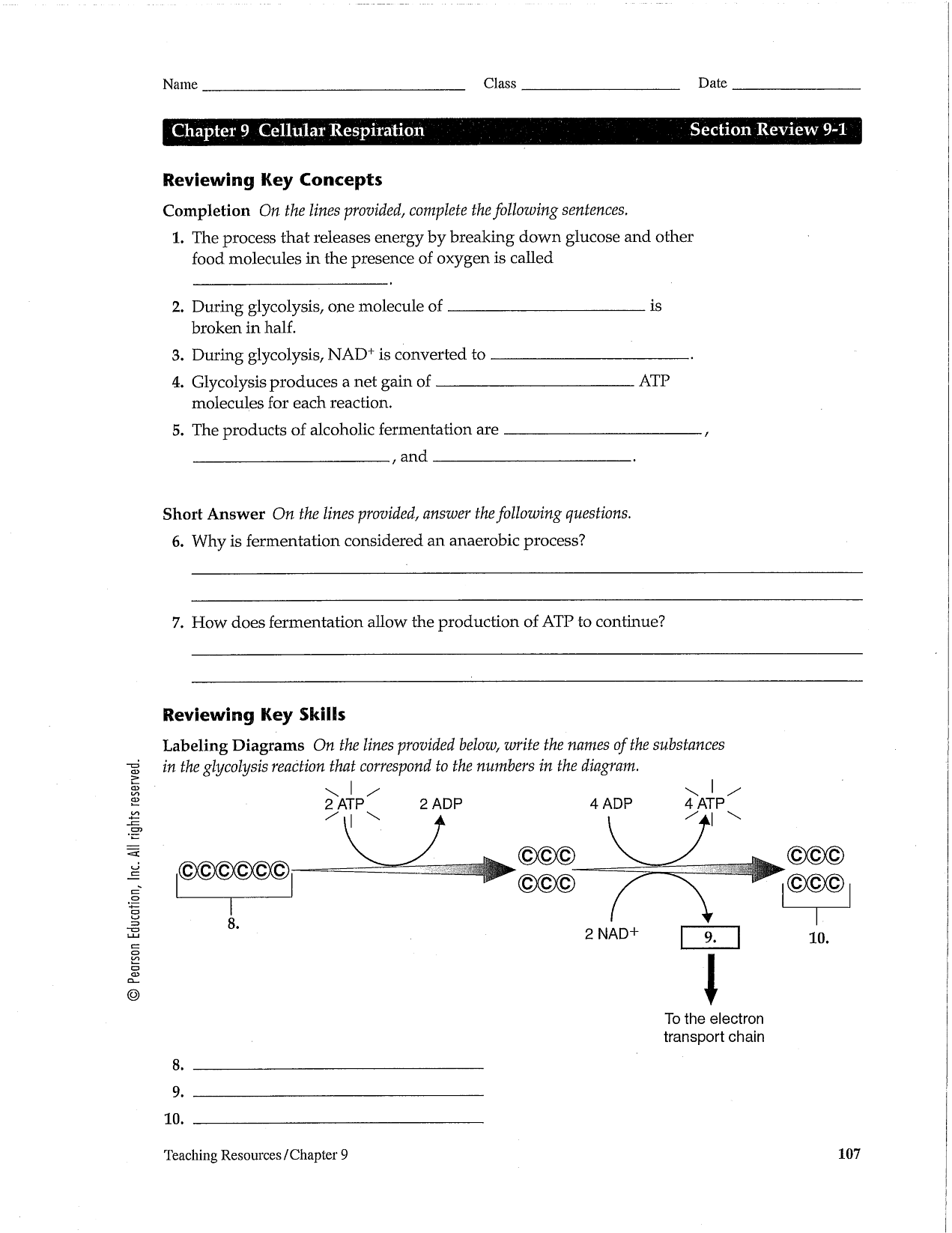
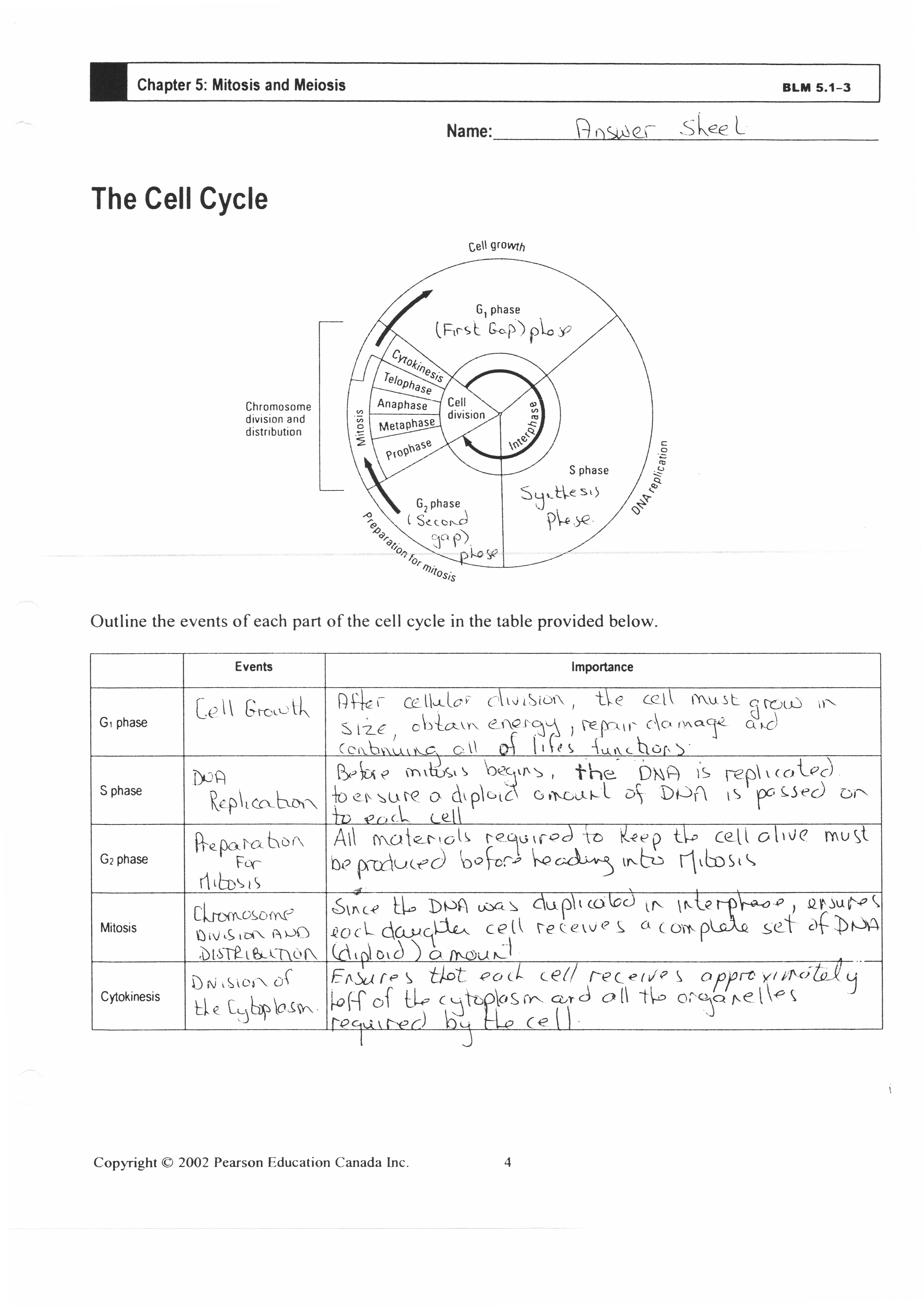
What are the main phases of the cell cycle?
The main phases of the cell cycle are interphase, which consists of three stages: G1 (cell growth), S (DNA synthesis), and G2 (preparation for cell division); and mitotic phase, which includes mitosis (dividing the genetic material) and cytokinesis (dividing the cytoplasm) resulting in two daughter cells.
How does the cell cycle ensure proper growth and repair of tissues?
The cell cycle ensures proper growth and repair of tissues by regulating the orderly process of cell division and duplication. This cycle allows cells to grow and eventually divide to produce new cells that can replace damaged or old cells. By tightly controlling each phase of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, the body can maintain the optimal balance of cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation to support tissue growth and repair. Proper coordination of the cell cycle is crucial for ensuring tissues have the correct number and type of cells to function effectively.
What is the role of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
Checkpoints in the cell cycle act as control mechanisms that monitor the progression of the cell through various stages of the cycle. These checkpoints ensure that the cell has properly completed certain processes before advancing to the next stage, such as DNA replication, chromosome segregation, and cell division. If any abnormalities or errors are detected at these checkpoints, the cell cycle can be halted to allow for repair mechanisms to fix the issues before proceeding, thus helping to maintain genomic stability and prevent the propagation of damaged or mutated cells.
What is the importance of DNA replication during the cell cycle?
DNA replication is crucial during the cell cycle as it ensures that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic information stored in the parent cell. This process is essential for growth, development, and the repair of damaged tissues in multicellular organisms. By accurately replicating the DNA, cells can pass on the correct genetic instructions to their offspring, maintaining genetic stability and allowing for proper functioning of cells and ultimately the organism as a whole.
How does the cell ensure accurate chromosome segregation during cell division?
The cell ensures accurate chromosome segregation during cell division through a series of tightly regulated processes. One key mechanism is the attachment of chromosomes to spindle fibers, which helps to align them correctly during metaphase. Additionally, the cell checks for proper chromosome attachment through the spindle assembly checkpoint before allowing the cell to progress to anaphase. Once all chromosomes are correctly aligned and attached, the cell then proceeds to segregate them evenly to daughter cells during anaphase, ensuring each new cell receives the correct number of chromosomes.
What is the significance of mitosis in the cell cycle?
Mitosis is a crucial process in the cell cycle as it is responsible for cell division and replication. It ensures the accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells, allowing for growth, development, and repair of tissues. Through mitosis, a single cell can produce two genetically identical daughter cells, playing a vital role in maintaining the organism's overall health and function.
How does cytokinesis differ between animal and plant cells?
Cytokinesis is the process in which a cell divides to form two daughter cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell in two, separating the cytoplasm and organelles. In contrast, plant cells have a rigid cell wall that prevents the formation of a cleavage furrow. Instead, plant cells form a cell plate in the middle of the cell, which develops into a new cell wall between the two daughter cells during cytokinesis. This distinction in cytokinesis reflects the structural differences between animal and plant cells.
What are the consequences of uncontrolled cell division?
The consequences of uncontrolled cell division, known as cancer, can include the formation of tumors that can invade nearby tissues, spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system (metastasis), disrupt normal organ function, and potentially lead to death if left untreated. Additionally, cancer can cause symptoms such as pain, fatigue, weight loss, and other complications depending on the site of the tumor and its effects on the body. It is essential to diagnose and treat cancer early to improve the chances of successful outcomes and prevent further progression of the disease.
How do cancer cells bypass the normal cell cycle regulations?
Cancer cells can bypass normal cell cycle regulations through various mechanisms, such as mutations in genes that control the cell cycle, altered signaling pathways, dysfunction in cell cycle checkpoints, and dysregulation of cell cycle proteins. These alterations can lead to uncontrolled cell division, unchecked growth, and evasion of programmed cell death, allowing cancer cells to continue dividing and spreading uncontrollably.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments