Carbon Cycle Worksheet High School
The carbon cycle is a fundamental process that all high school students studying biology need to understand. To help reinforce this important topic, we have developed a comprehensive carbon cycle worksheet specifically designed for high school students. This worksheet is tailored to engage students with clear explanations of key concepts and interactive activities to reinforce learning. Whether you are a teacher looking to enhance your curriculum or a student seeking additional practice, our carbon cycle worksheet is the perfect resource to support your learning journey.
Table of Images 👆
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Middle School
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Middle School
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbon Cycle Game Worksheet
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Middle School
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Answers High School
- Carbon Cycle Game Worksheet
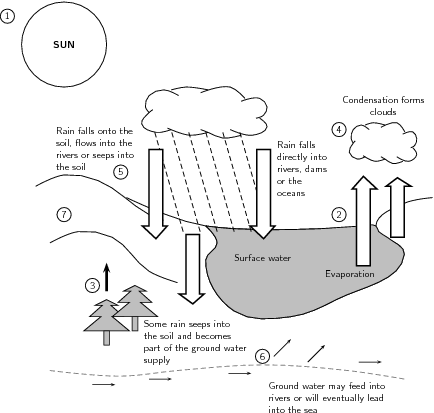
- Water Cycle Diagram Worksheet
- Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet High School
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biogeochemical Cycles Worksheet Answers
- The New Testament
- Water Cycle Worksheet High School
- Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheets High School
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle is a natural process that involves the movement of carbon in different forms between the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. It consists of various processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and decomposition that cycle carbon between the air, plants, animals, and the Earth's crust. This cycle plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, maintaining the Earth's climate, and supporting life on our planet.
What are the main sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
The main sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are fossil fuel combustion, such as from vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes, deforestation and land-use changes releasing carbon stored in vegetation and soils, and agricultural practices like rice cultivation and livestock farming that produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas that can ultimately contribute to CO2 levels in the atmosphere.
How do plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through tiny openings in their leaves called stomata. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through the stomata and is then used in the process of photosynthesis, where it is converted into carbohydrates and oxygen with the help of sunlight and water. This process helps plants grow and thrive while also reducing the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its role in the carbon cycle.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize nutrients from carbon dioxide and water. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water from the soil to produce glucose and oxygen using sunlight as an energy source. This glucose is used as a source of energy for the plant, while the oxygen is released back into the atmosphere as a byproduct. In the carbon cycle, photosynthesis plays a crucial role as it helps in removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converting it into organic compounds, which are then used by plants and eventually passed on through the food chain to other organisms. This process helps to regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and is essential for maintaining the balance of gases necessary for life on Earth.
How does carbon dioxide enter the oceans and why is it important?
Carbon dioxide enters the oceans primarily through the process of diffusion from the atmosphere. This transfer is crucial for regulating the Earth's climate as oceans act as a carbon sink, absorbing a significant portion of the CO2 emitted by human activities. However, the increased levels of carbon dioxide in the oceans can lead to ocean acidification, which poses a threat to marine ecosystems and biodiversity. Monitoring and understanding this process is essential for addressing climate change and preserving the health of our oceans.
What happens to carbon dioxide in the oceans?
Carbon dioxide in the oceans undergoes a process called ocean acidification, where the CO2 dissolves in seawater, forming carbonic acid. This process lowers the pH levels of the ocean, leading to detrimental effects on marine life and ecosystems. Excessive ocean acidification can disrupt the ability of marine organisms such as corals, shellfish, and plankton to build their calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, ultimately impacting the entire marine food chain.
Explain the process of respiration and its role in the carbon cycle.
Respiration is the process through which organisms extract energy from food molecules by converting them into ATP. During respiration, organisms take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide as a byproduct. In the carbon cycle, respiration plays a crucial role as it releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, which is then used by plants during photosynthesis to produce oxygen and sugars. This exchange of gases between organisms maintains a balance of carbon and oxygen in the atmosphere, supporting life on Earth.
Describe the role of decomposers in the carbon cycle.
Decomposers play a crucial role in the carbon cycle by breaking down dead organisms and organic matter, such as leaves and wood, into simpler compounds through the process of decomposition. During this breakdown, carbon is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. This cycling of carbon by decomposers helps to facilitate the transfer of carbon between living organisms and the environment, ultimately contributing to the balance of carbon in ecosystems and the global carbon cycle.
How does human activity contribute to the imbalance in the carbon cycle?
Human activity contributes to the imbalance in the carbon cycle primarily through the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. When fossil fuels are burned for energy, they release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which increases the concentration of greenhouse gases. Deforestation also plays a significant role as trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and when they are cut down, this stored carbon is released back into the air. These activities disrupt the natural equilibrium of the carbon cycle, leading to an accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and contributing to climate change.
Explain the term "carbon sequestration" and its importance in mitigating climate change.
Carbon sequestration refers to the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to prevent it from contributing to climate change. It involves techniques such as afforestation, reforestation, soil carbon sequestration, and carbon capture and storage. Carbon sequestration is vital in mitigating climate change because it helps reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, thus slowing down global warming and its associated impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human societies. By enhancing natural carbon sinks and developing innovative technologies, we can offset carbon emissions and work towards achieving a more sustainable and resilient future for our planet.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


































Comments