Carbon Carbohydrate Structure Worksheet
Are you a science student or researcher seeking a comprehensive resource to enhance your understanding of the intricate world of carbon carbohydrate structures? Look no further, as this worksheet is specifically designed to provide you with a clear and detailed overview of these essential entities and subjects.
Table of Images 👆
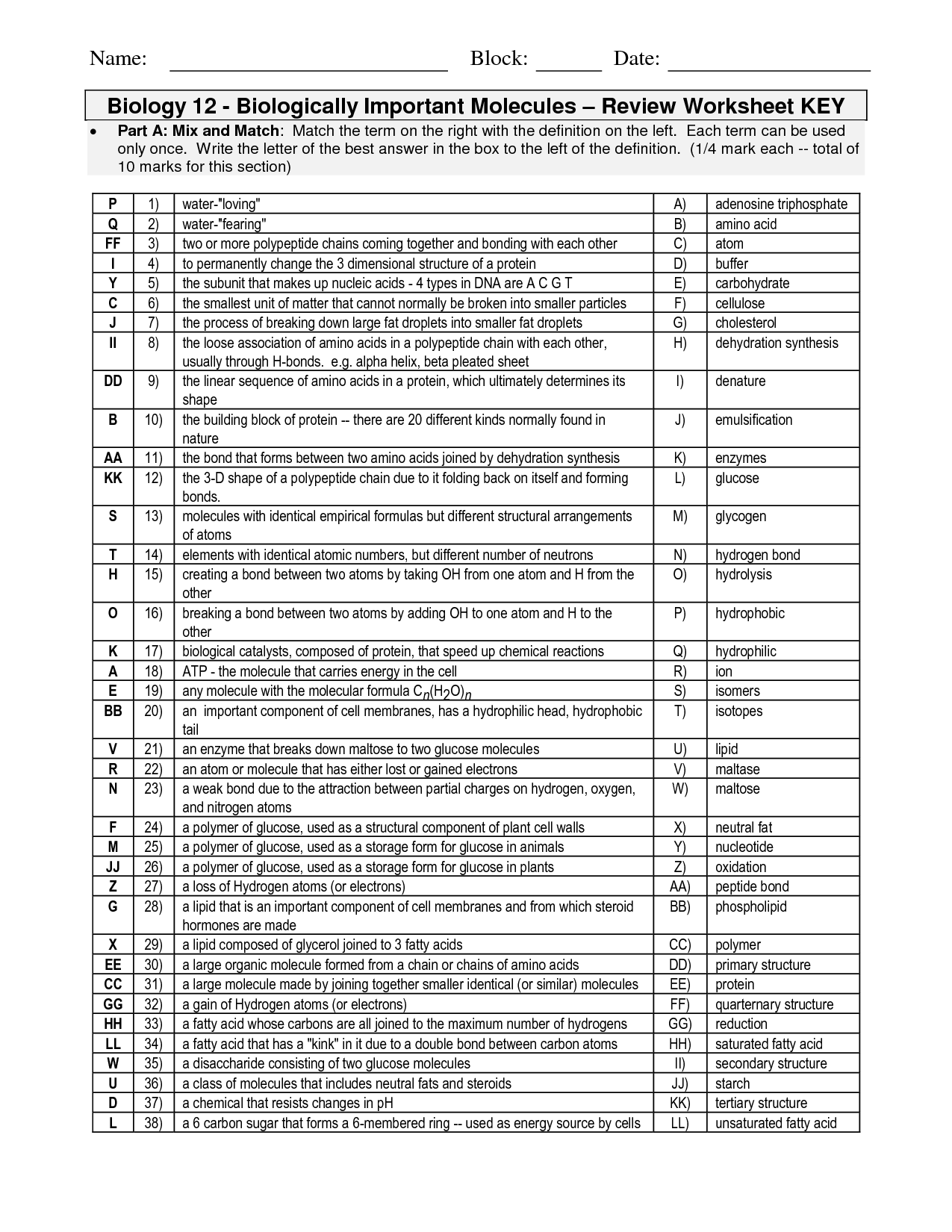
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Chemical Reaction Types Worksheet
- What Elements Make Up Carbohydrates and Lipids Symbols
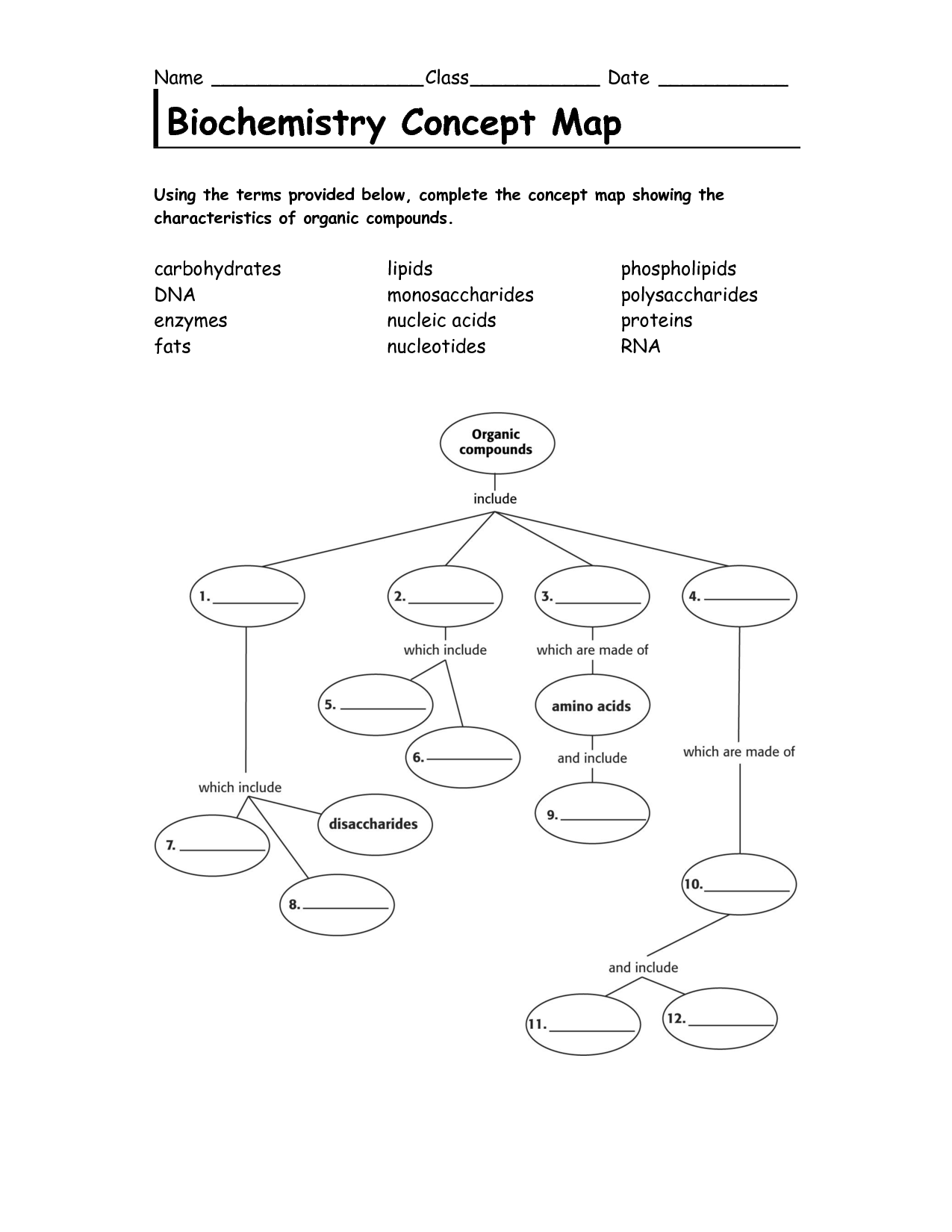
- Biochemistry Concept Map Organic Compounds Answers
- Protein Synthesis Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
- Physical vs Chemical Change Worksheet
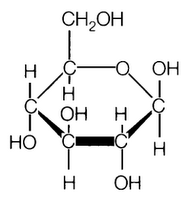
- Glucose Molecule Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Matter Science Graphic Organizers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the primary element present in carbohydrates?
The primary element present in carbohydrates is carbon.
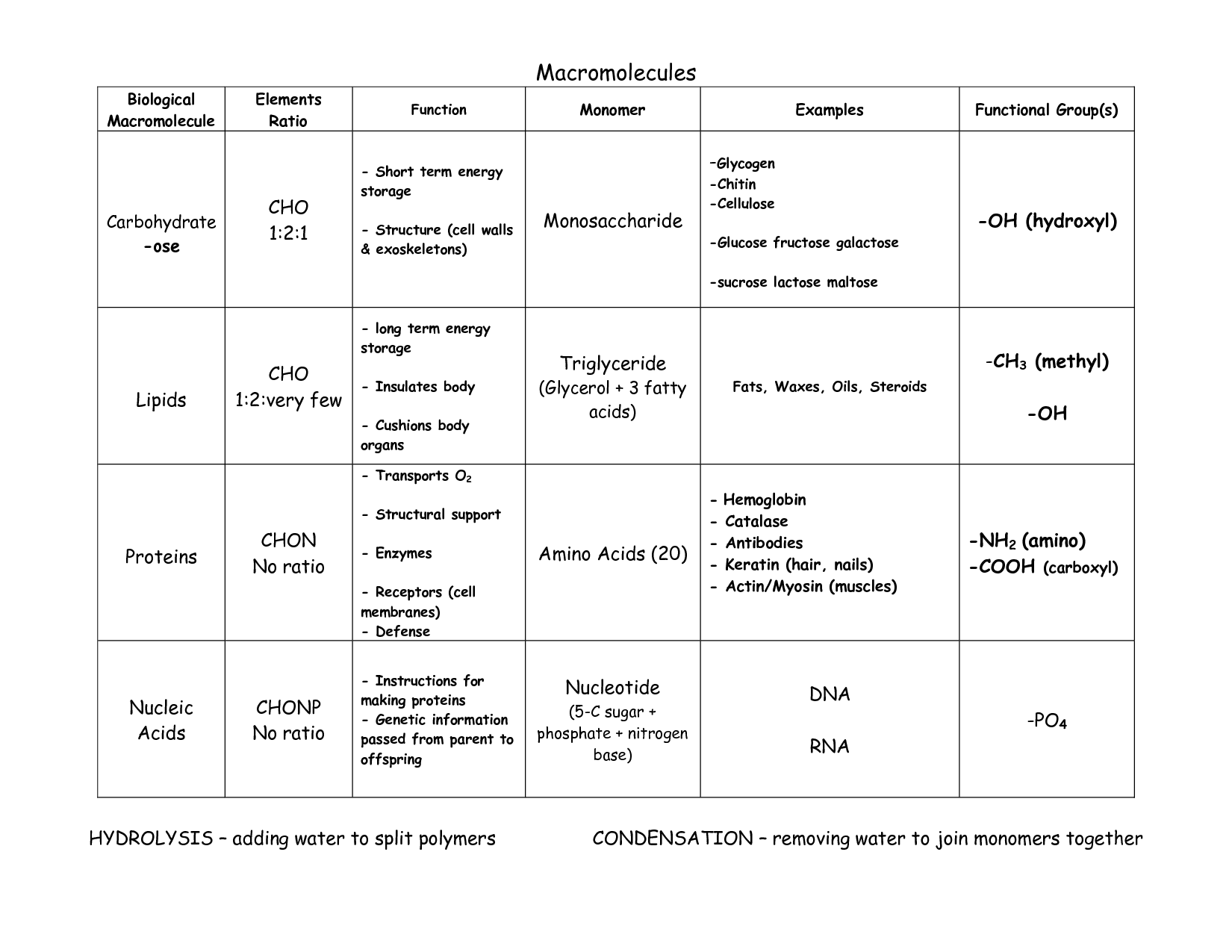
How are carbohydrates classified based on their molecular structure?
Carbohydrates are classified into three groups based on their molecular structure: monosaccharides (simple sugars), disaccharides (two monosaccharides linked together), and polysaccharides (long chains of monosaccharides). Monosaccharides include glucose and fructose, while sucrose and lactose are examples of disaccharides. Polysaccharides, such as starch and cellulose, are made up of many monosaccharide units linked together.
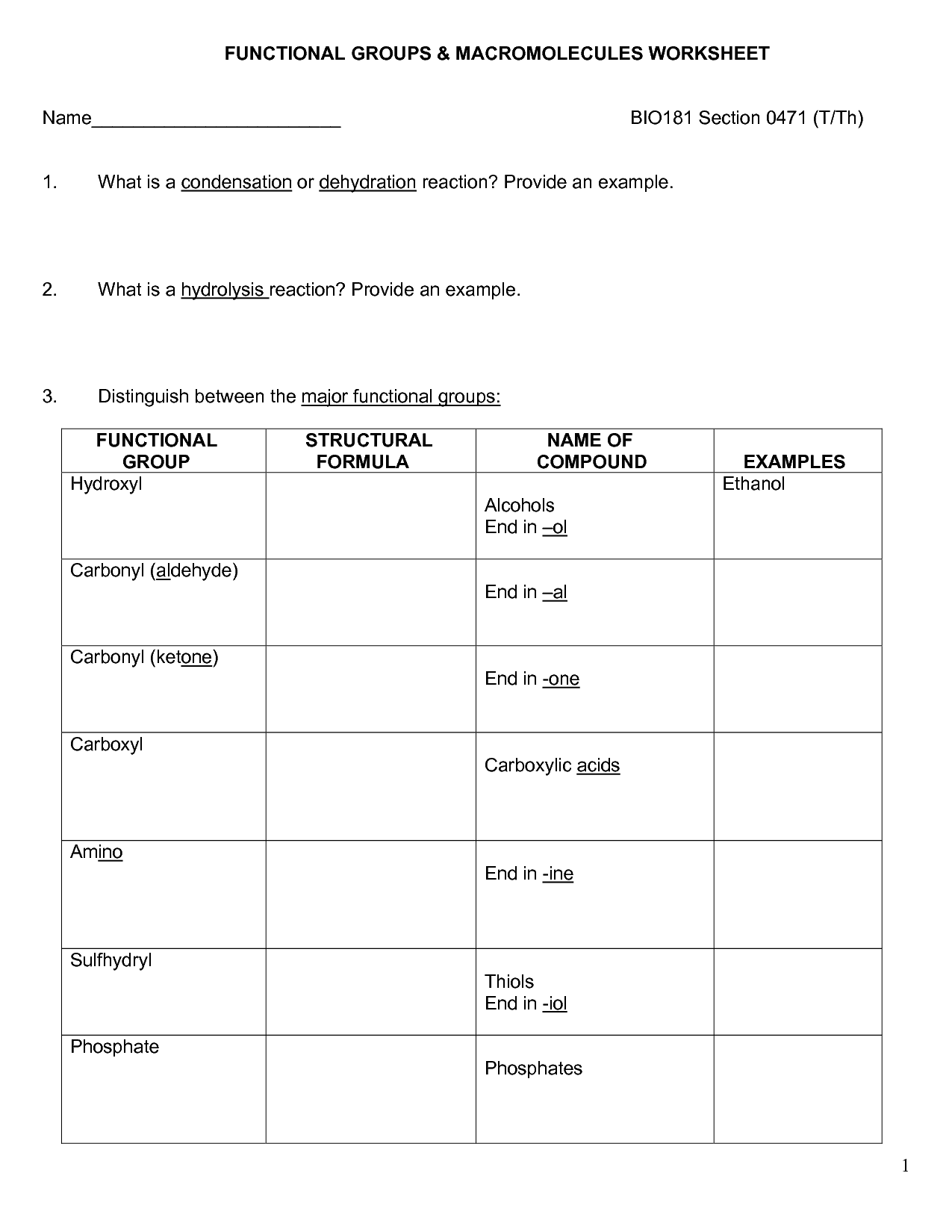
What functional groups are present in a carbohydrate molecule?
Carbohydrate molecules contain hydroxyl (OH) functional groups, as well as a carbonyl (C=O) group. The hydroxyl groups are attached to the carbon atoms of the carbohydrate backbone, while the carbonyl group is typically found at either end of the molecule, forming an aldehyde group in aldoses or a ketone group in ketoses.
What is the general formula for a monosaccharide?
The general formula for a monosaccharide is (CH2O)n, where n ranges from 3 to 7. This formula indicates that monosaccharides are composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms in the ratio of 1:2:1, with a minimum of three carbon atoms in the molecule.
What is the difference between an aldose and a ketose sugar?
The main difference between an aldose and a ketose sugar lies in their functional group. Aldose sugars have an aldehyde functional group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketose sugars have a ketone functional group in the middle of the carbon chain. This distinction affects their chemical and structural properties, including their reactivity and potential interactions with other molecules.
How do monosaccharides form disaccharides and polysaccharides?
Monosaccharides form disaccharides and polysaccharides through a process known as dehydration synthesis, where a water molecule is removed to link two monosaccharide molecules together. In disaccharides, two monosaccharides are joined, such as glucose and fructose forming sucrose, while in polysaccharides, many monosaccharides are linked together to form larger molecules, like cellulose or starch.
What is the difference between a reducing sugar and a non-reducing sugar?
A reducing sugar is a carbohydrate that can act as a reducing agent and is capable of reducing other substances, such as the Benedict's reagent. It has a free aldehyde or ketone group that can react with the reagent. On the other hand, a non-reducing sugar is a carbohydrate that lacks a free aldehyde or ketone group and cannot act as a reducing agent. Non-reducing sugars typically include disaccharides like sucrose, which consists of glucose and fructose joined by a glycosidic bond that prevents them from reducing other substances.
What is the purpose of glycosidic linkages in carbohydrate molecules?
Glycosidic linkages in carbohydrate molecules serve to connect monosaccharide units together to form larger carbohydrate structures, such as disaccharides or polysaccharides. This linkage allows for the storage and release of energy, structural support in cell walls, and serves as a way to convey information in cell-to-cell communication processes.
How does the structure of cellulose differ from that of starch?
The structure of cellulose differs from that of starch in that cellulose is a linear polymer composed of β-glucose units linked by β1-4 glycosidic bonds, forming long, straight chains, while starch is a branched polymer composed of α-glucose units linked by α1-4 glycosidic bonds with occasional α1-6 branches. Furthermore, cellulose chains are held together by strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds, making it rigid and water-insoluble, whereas starch is more soluble and readily broken down by enzymes due to its branching and helical structure.
How do carbohydrates provide energy for living organisms?
Carbohydrates are broken down during digestion into glucose, which is the primary source of energy for living organisms. Glucose is then transported through the bloodstream to cells where it is used to produce ATP through cellular respiration. ATP is the main energy currency of cells and is utilized for various biological processes like muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and synthesis of molecules necessary for cell function.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments