Carbohydrate Review Worksheet
If you're searching for an effective tool to solidify your understanding of carbohydrates, look no further than the Carbohydrate Review Worksheet. This comprehensive resource is designed to cater to students and individuals interested in deepening their knowledge of this important biological entity.
Table of Images 👆
- Carbohydrates Review Worksheet
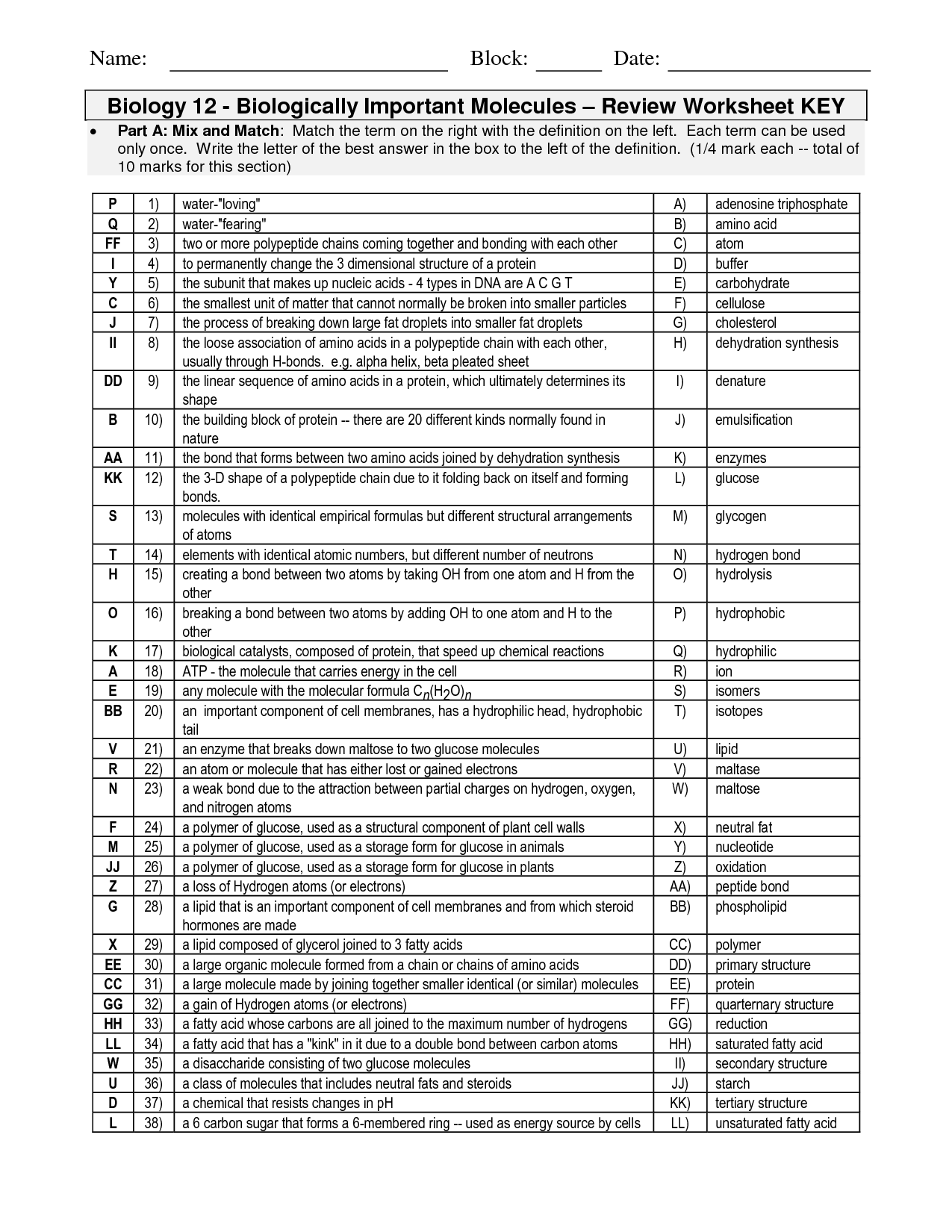
- Macromolecules Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
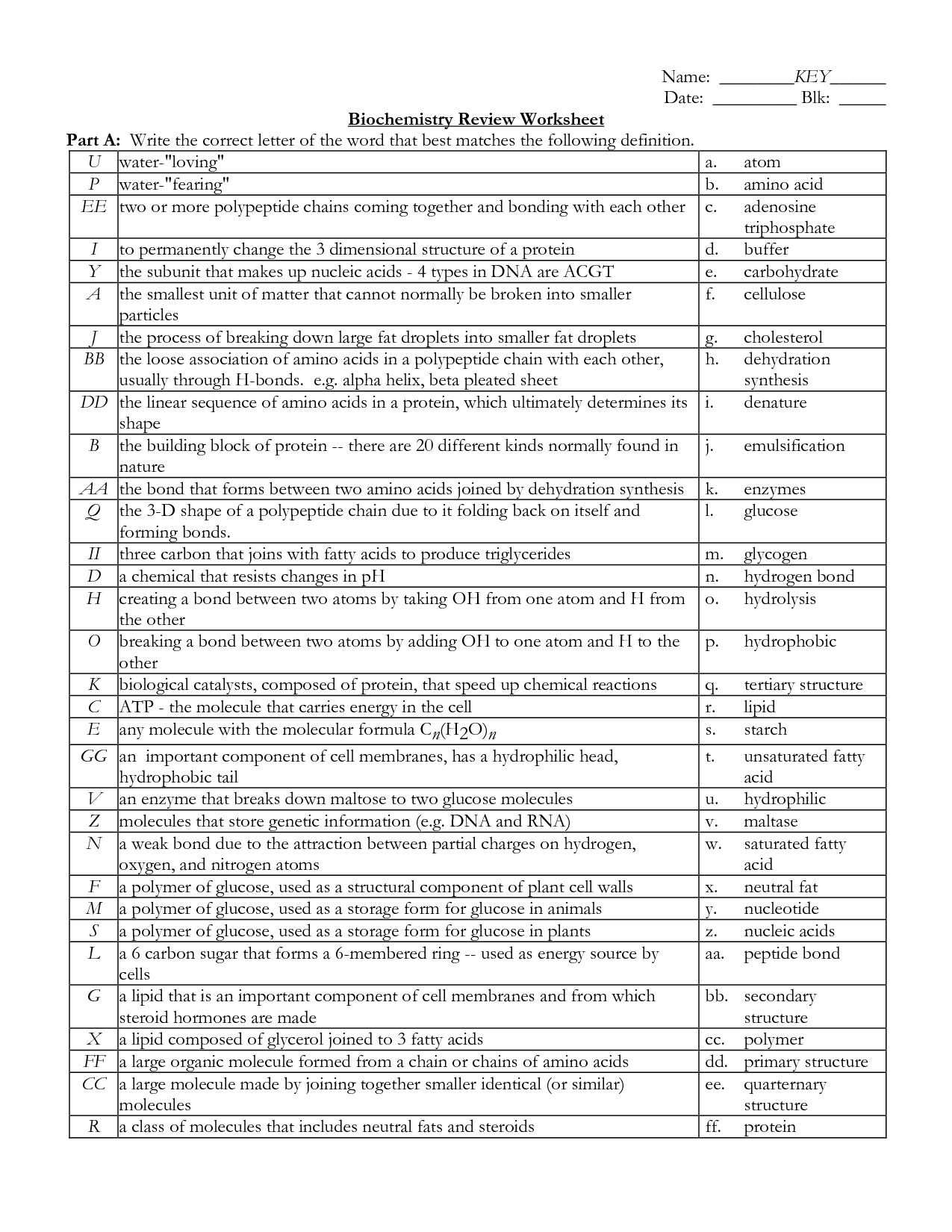
- Biochemistry Review Worksheet
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Amino Acid Codon Worksheet Answers
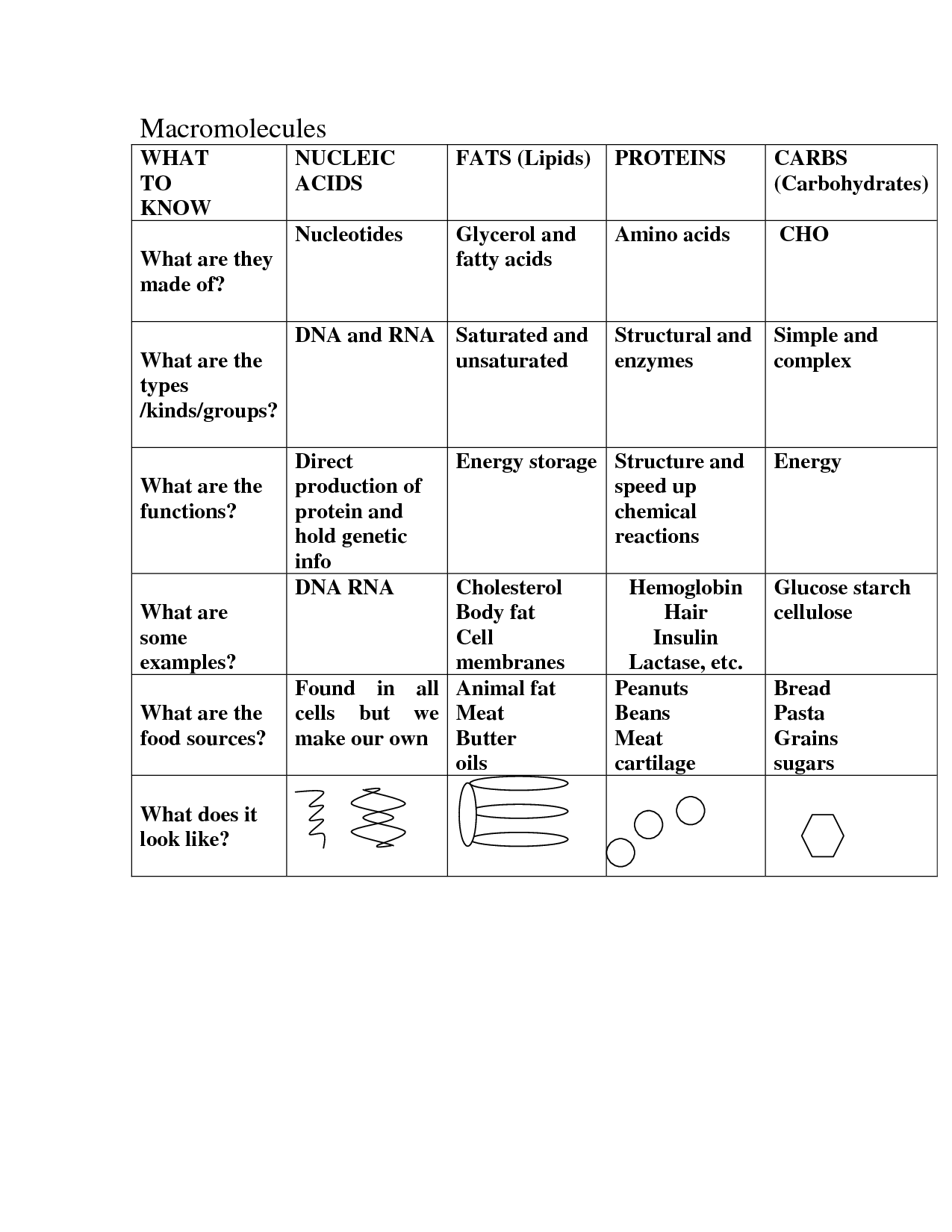
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Digestive System Review Worksheet
- Respiratory System Worksheet Answer Key
- Nomenclature Worksheet 2 Answer Key
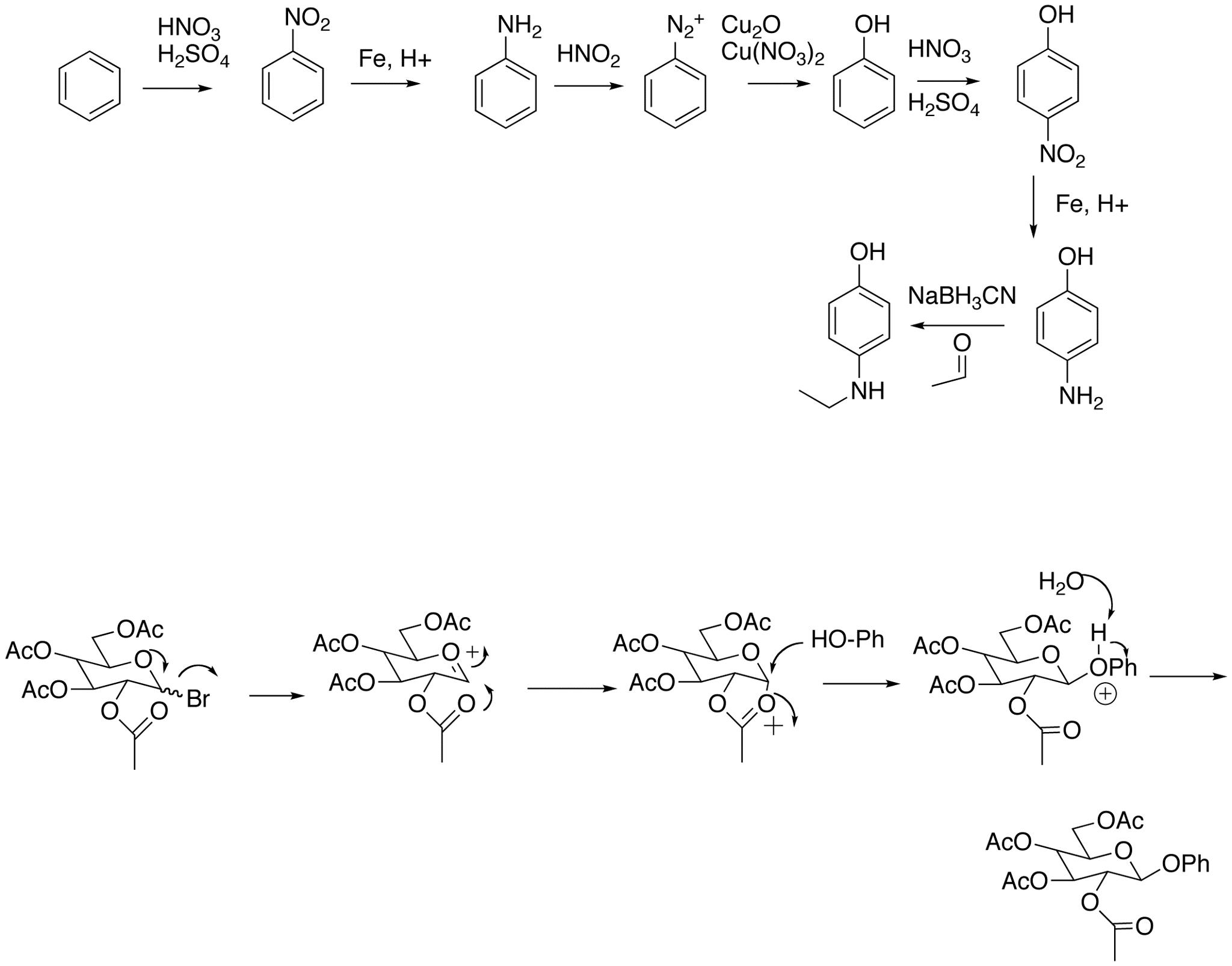
- Ketone and Aldehyde Synthesis Problems
- Worksheet Carbohydrates Protein Fats for Middle School
- Biology Carbohydrates Worksheet
- Biochemistry Notes Worksheet
- Synthesis Reaction Worksheet
- Photosynthesis Diagrams Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are one of the main macronutrients that provide the body with energy. They are found in a wide range of foods, including grains, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Carbohydrates can be broken down into sugars, which are then used by the body as a primary source of energy for various functions, such as physical activity and brain function.
What are the main functions of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for the body, providing fuel for various physiological processes and bodily functions. They also play a crucial role in supporting brain function, aiding in digestion and metabolism, and assisting in the synthesis of proteins and fats. Additionally, carbohydrates contribute to maintaining healthy gut bacteria and support the immune system.
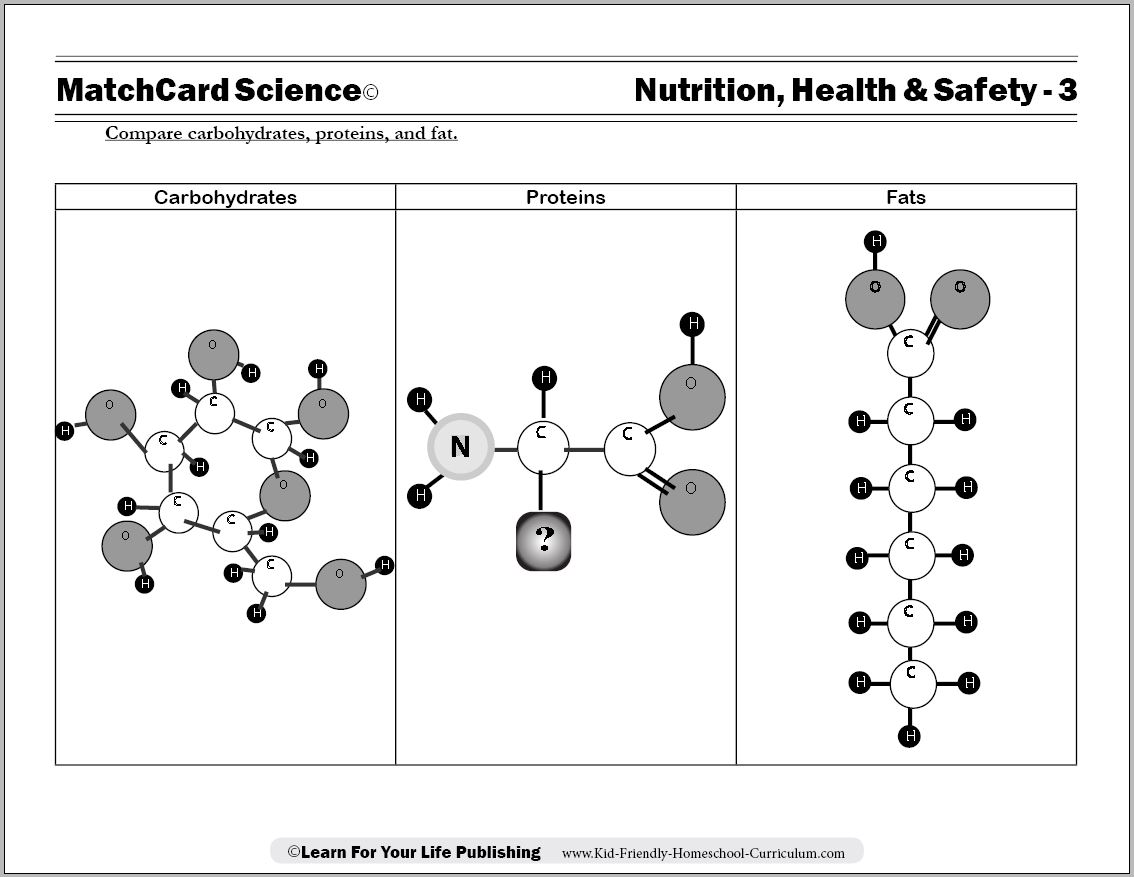
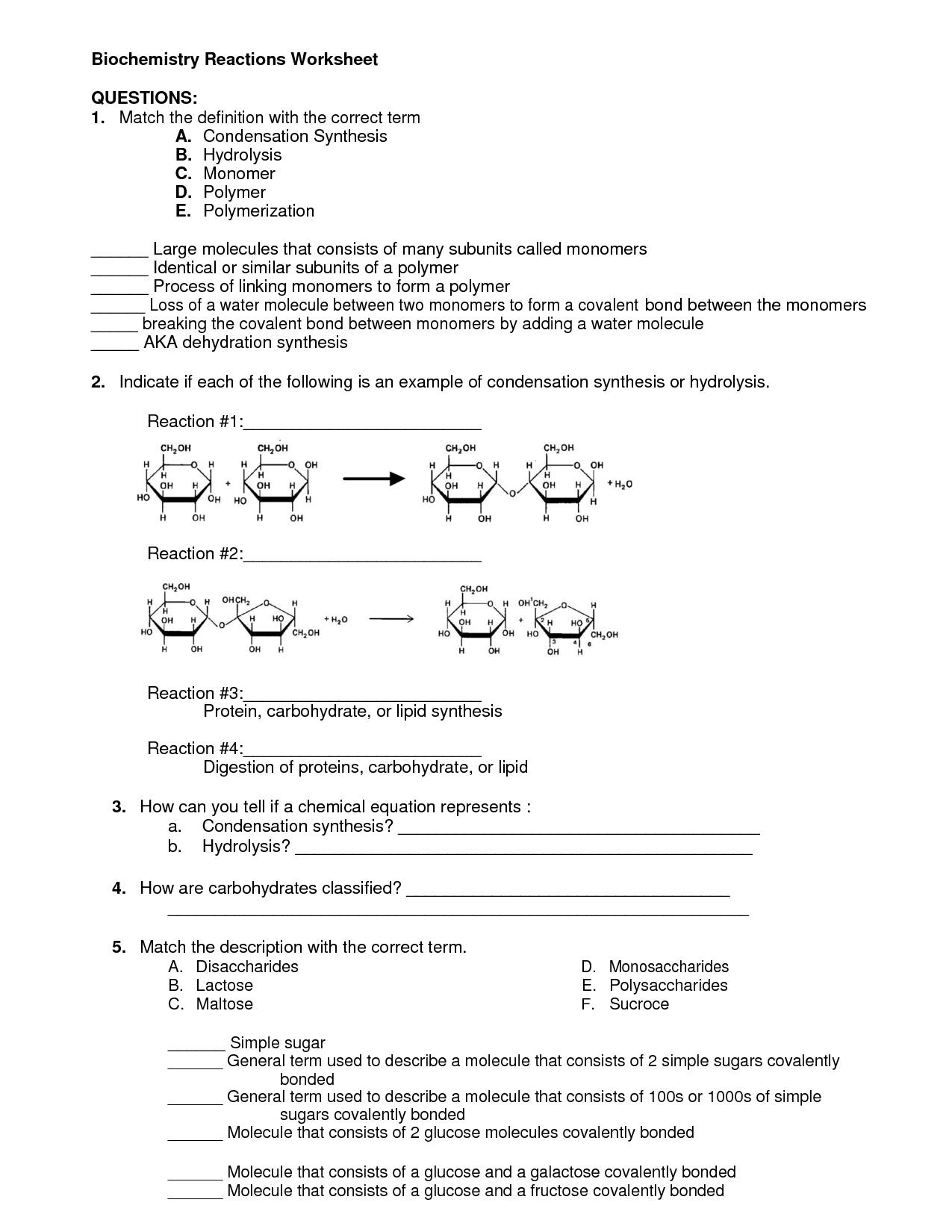
How are carbohydrates classified?
Carbohydrates are classified based on their chemical structures as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharide units, such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Polysaccharides consist of multiple monosaccharide units and include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
What are the basic building blocks of carbohydrates?
The basic building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides, which are single sugar molecules. These monosaccharides can join together through condensation reactions to form disaccharides (two sugar molecules) and polysaccharides (multiple sugar molecules). Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Explain the difference between simple and complex carbohydrates.
Simple carbohydrates, or sugars, are made up of one or two sugar molecules and are quickly broken down and absorbed by the body, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Examples include table sugar, honey, and fruit. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates have three or more sugar molecules linked together, requiring more time to be digested and leading to a slower and more sustained release of energy. Foods like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes are sources of complex carbohydrates.
What is the role of glucose in the body?
Glucose is a primary source of energy for the body's cells and is essential for the functioning of many organs and tissues, particularly the brain. It is obtained from the breakdown of carbohydrates in the diet and is transported via the bloodstream to various cells to fuel their metabolic activities. Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use, serving as a critical energy reserve.
How do carbohydrates provide energy to the body?
Carbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose, which is the primary source of energy for cells. Once consumed, carbohydrates are digested into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to cells where it is used as fuel to power various cellular processes and activities. Additionally, excess glucose can be stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for later use when energy demands are higher, such as during physical activity or periods of fasting.
What is the recommended daily intake of carbohydrates?
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates varies depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health goals. However, general guidelines suggest that carbohydrates should make up 45-65% of total daily caloric intake. It is important to focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from sources like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, and to limit intake of refined sugars and processed foods for overall health and well-being.
Describe the process of carbohydrate digestion.
Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the enzyme amylase breaking down complex carbohydrates into smaller sugars. The partially digested carbohydrates move to the stomach where they are further broken down by gastric juices before entering the small intestine. In the small intestine, enzymes from the pancreas and intestine break down the carbohydrates into simple sugars like glucose, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream and used for energy by the body. Any remaining undigested carbohydrates pass into the large intestine where they can be fermented by gut bacteria.
How are carbohydrates stored in the body?
Carbohydrates are stored in the body in the form of glycogen, which is primarily stored in the liver and muscles. When carbohydrate intake exceeds immediate energy needs, the excess glucose is converted into glycogen for storage. This stored glycogen can then be broken down into glucose when energy demands increase, providing a quick source of energy for the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments